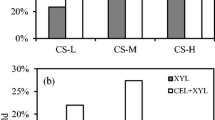
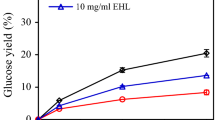
Abstract
Addition of additives has been confirmed to increase cellulase performance in the hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials. In the hydrolysis of xylan-containing lignocellulosic biomass, xylanase can synergistically enhance the performance of cellulase. However, the role of additives in xylan hydrolysis by xylanase is not yet clear. In this work, with the presence of additives (bovine serum albumin, poly(ethylene glycol), and Tween), the hydrolysis of isolated xylan and the xylan in corn stover increased to different extents. Additives increased free xylanase in supernatants in the hydrolysis with xylanase, indicating the reduction of the adsorption of xylanase on corn stover and insoluble xylan. Enhanced hydrolysis of Avicel and corn stover by additives suggested that besides the prevention of unproductive binding of xylanase to lignin by additives, reducing the adsorption of xylanase on substrates was also contributed to enzymatic hydrolysis. The increment of xylanase activity by additives suggests that the additives were activators of xylanase. The results of this work indicate that the supplementation of additives could improve xylanase performance, synergistically enhanced the cellulose hydrolysis, and beneficial for the recycling of xylanase.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- CBH:
-
Cellobiohydrolase
- CEL:
-
Cellulase preparation
- CS:
-
Corn stover
- DM:
-
Dry matter
- EG:
-
Endoglucanase
- PEG:
-
Poly(ethylene glycol)
- XYL:
-
Xylanase
References
Szczodrak, J., & Fiedurek, J. (1996). Biomass and Bioenergy, 10, 367–375.
Sánchez, Ó. J., & Cardona, C. A. (2008). Bioresource Technology, 99, 5270–5295.
Jørgensen, H., Kristensen, J. B., & Felby, C. (2007). Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 1, 119–134.
Zheng, Y., Pan, Z., Zhang, R., Wang, D., & Jenkins, B. (2008). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 146, 231–248.
Zhang, J., Moilanen, U., Tang, M., & Viikari, L. (2013). Biotechnology Biofuels, 6, 18.
Kristensen, J. B., Börjesson, J., Bruun, M. H., Tjerneld, F., & Jørgensen, H. (2007). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 40, 888–895.
Yang, B., & Wyman, C. E. (2008). Biofuels Bioproducts and Biorefining, 2, 26–40.
Alvira, P., Tomás-Pejó, E., Ballesteros, M., & Negro, M. J. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 4851–4861.
García-Aparicio, M. P., Ballesteros, M., Manzanares, P., Ballesteros, I., González, A., & Negro, M. J. (2007). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 136–140, 353–366.
Qing, Q., Yang, B., & Wyman, C. E. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101, 5941–5951.
Kaar, W. E., & Holtzapple, M. T. (1998). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 59(4), 419–427.
Eriksson, T., Börjesson, J., & Tjerneld, F. (2002). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 31, 353–364.
Börjesson, J., Peterson, R., & Tjerneld, F. (2007). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 40, 754–762.
Sipos, B., Dienes, D., Schleichera, Á., Perazzini, R., Crestini, C., Siika-aho, M., et al. (2010). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 47, 84–90.
Seo, D., Fujit, H., & Sakoda, A. (2011). Bioresource Technology, 102, 9605–9612.
Yang, B., & Wyman, C. E. (2006). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 94(4), 611–617.
Kumar, R., & Wyman, C. E. (2009). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 102(6), 1544–1557.
Börjesson, J., Engqvist, M., Sipos, B., & Tjerneld, F. (2007). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 41, 186–195.
Sluiter, A., Hames, B., Ruiz, R., Scarlata, C., Sluiter, J., Templeton, D., et al. (2008). Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory.
Ryan, S. E., Nolan, K., Thompson, R., Gubitz, G. M., Savage, A., & Tuohy, G. M. (2003). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 33, 775–785.
Zhang, Y., Xu, X., Zhang, Y., & Li, J. (2011). Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 16, 930–936.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Bailey, M. J., Biely, P., & Poutanen, K. (1992). Journal of Biotechnology, 23, 257–270.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Zhang, J., Tuomainen, P., Siika-Aho, M., & Viikari, L. (2011). Bioresource Technology, 102(19), 9090–9095.
Zilliox, C., & Debeire, P. (1998). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 22, 58–63.
Selig, M. J., Knoshaug, E. P., Adney, W. S., Himmel, M. E., & Decker, S. R. (2008). Bioresource Technology, 99, 4997–5005.
Kim, T. Y., Kim, J. S., Sunwoo, C., & Lee, Y. Y. (2003). Bioresource Technology, 90, 39–47.
Berlin, A., Gilkes, N., Kilburn, D., Bura, R., Markov, A., Skomarovsky, A., et al. (2005). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 37, 175–184.
Tu, M., Pan, X., & Saddler, J. N. (2009). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 57, 7771–7778.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31270622).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, X., Sun, Z., Xin, D. et al. Enhanced Xylanase Performance in the Hydrolysis of Lignocellulosic Materials by Surfactants and Non-catalytic Protein. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172, 2106–2118 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0673-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0673-5