Abstract
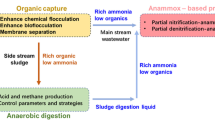
Large-scale amine-based CO2 capture will generate waste containing large amounts of ammonia, in addition to contaminants such as the actual amine as well as degradation products thereof. Monoethanolamine (MEA) has been a dominant amine applied so far in this context. This study reveals how biological N removal can be achieved even in systems heavily contaminated by MEA in post- as well as pre-denitrification treatment systems, elucidating the rate-limiting factors of nitrification as well as aerobic and denitrifying biodegradation of MEA. The hydrolysis of MEA to ammonia readily occurred both in post- and pre-denitrification treatment systems with a hydraulic retention time of 7 h. MEA removal was ≥99 ± 1 % and total nitrogen removal 77 ± 10 % in both treatment systems. This study clearly demonstrates the advantage of pre-denitrification over post-denitrification for achieving biological nitrogen removal from MEA-contaminated effluents. Besides the removal of MEA, the removal efficiency of total nitrogen as well as organic matter was high without additional carbon source supplied.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reynolds, A. J., Verheyen, T. V., Adeloju, S. B., Meuleman, E., & Feron, P. (2012). Environmental Science and Technology, 46, 3643–3654.
Strazisar, B. R., Anderson, R. R., & White, C. M. (2003). Energy & Fuels, 17, 1034–1039.
Goff, G. S., & Rochelle, G. T. (2004). Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 43, 6400–6408.
Botheju, D., Li, Y., Hovland, J., Haugen, H. A., & Bakke, R. (2011). Energy Procedia, 4, 496–503.
Lai, B., & Shieh, W. K. (1996). Water Research, 30, 2530–2534.
Ohtaguchi, K., Koide, K., & Yokoyama, T. (1995). Energy Convers. Manage, 36, 401–404.
Ohtaguchi, K., & Yokoyama, T. (1997). Energy Convers. Manage, 38, S539–S544.
Hauser, I., Einbu, A., Ostgaard, K., Svendsen, H. F., & Cervantes, F. J. (2012). Biotechnol. Lett., 1–6.
Liberackl, A. B., Neeper-Bradley, T. L., Breslin, W. J., & Zielke, G. J. (1996). Toxicological Sciences, 31, 117–123.
Ndegwa, A. W., Wong, R. C. K., Chu, A., Bentley, L. R., & Lunn, S. R. D. (2004). Journal of Environmental Engineering and Science, 3, 137–145.
Bakalova, S., Mincheva, V., Doycheva, A., Groudeva, V., & Dimkov, R. (2008). Biotechnology and Biotechnological Equipment, 22, 716–720.
Kim, D. J., Lim, Y., Cho, D., & Rhee, I. (2010). Korean J. Chemical Engineer, 27, 1521–1526.
Mrklas, O., Chu, A., Lunn, S., & Bentley, L. R. (2004). Water, Air, Soil Pollution, 159, 249–263.
Eide-Haugmo, I., Brakstad, O. G., Hoff, K. A., Sørheim, K. R., da Silva, E. F., & Svendsen, H. F. (2009). Energy Procedia, 1, 1297–1304.
Zhu, G., Peng, Y., Li, B., Guo, J., Yang, Q., & Wang, S. (2008). In reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. In D. Whitacre (Ed.), Biological Removal of Nitrogen from Wastewater (Vol. 192, pp. 159–195). New York: Springer.
Read, M. L., Etrych, T., Ulbrich, K., & Seymour, L. W. (1999). FEBS Letters, 461, 96–100.
Tiedje, J. M., Sexstone, A. J., Myrold, D. D., & Robinson, J. A. (1983). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 48, 569–583.
Bernet, N., Delgenes, N., & Moletta, R. (1996). Environmental Technology, 17, 293–300.
Cervantes, F. J., De la Rosa, D. A., & Gómez, J. (2001). Bioresource Technology, 79, 165–170.
Kaplan, B. H., & Stadtman, E. R. (1968). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 243, 1787–1793.
Abend, A., Bandarian, V., Nitsche, R., Stupperich, E., Rétey, J., & Reed, G. H. (1999). Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 370, 138–141.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hauser, I., Colaço, A.B., Skjæran, J.A. et al. Biological N Removal from Wastes Generated from Amine-Based CO2 Capture: Case Monoethanolamine. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169, 1449–1458 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-0075-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-0075-0