Abstract
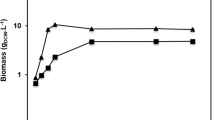
A gene encoding Yarrowia lipolytica lipase LIP2 (YlLIP2) was cloned into a constitutive expression vector pGAPZαA and electrotransformed into the Pichia pastoris X-33 strain. The high-yield clones obtained by high copy and enzyme activity screening were chosen as the host strains for shaking flask and fermentor culture. The results showed that glucose was the optimum carbon source for YlLIP2 production, and the maximum hydrolytic activity of recombinant YlLIP2 reached 1,315 U/ml under the flask culture at 28 °C, pH 7.0, for 48 h. The fed-batch fermentation was carried out in 3- and 10-l bioreactors by continuously feeding glucose into the growing medium for achieving high cell density and YlLIP2 yields. The maximum hydrolytic activity of YlLIP2 and cell density obtained in the 3-l bioreactor were 10,300 U/ml and 116 g dry cell weight (DCW)/l, respectively. The peak hydrolytic activity of YlLIP2 and cell density were further improved in the 10-l fermentor where the values respectively attained were 13,500 U/ml and 120 g DCW/l. The total protein concentration in the supernatant reached 3.3 g/l and the cell viability remained approximately 99% after 80 h of culture. Furthermore, the recombinant YlLIP2 produced in P. pastoris pGAP and pAOX1 systems have similar content of sugar (about 12%) and biochemical characteristics. The above results suggest that the GAP promoter-derived expression system of P. pastoris is effective for the expression of YlLIP2 by high cell density culture and is probably an alternative to the conventional AOX1 promoter expression system in large-scale production of industrial lipases.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Treichel, H., de Oliveira, D., Mazutti, M. A., Di Luccio, M., & Oliveira, J. V. (2010). A Review on Microbial Lipases Production. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 3, 182–196.
Shu, Z. Y., Jiang, H., Lin, R. F., Jiang, Y. M., Lin, L., & Huang, J. Z. (2010). Technical methods to improve yield, activity and stability in the development of microbial lipases. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 62, 1–8.
Yu, M., Lange, S., Richter, S., Tan, T., & Schmid, R. D. (2007). High-level expression of extracellular lipase Lip2 from Yarrowia lipolytica in Pichia pastoris and its purification and characterization. Protein Expression and Purification, 53, 255–263.
Pignede, G., Wang, H., Fudalej, F., Gaillardin, C., Seman, M., & Nicaud, J. M. (2000). Characterization of an extracellular lipase encoded by LIP2 in Yarrowia lipolytica. Journal of Bacteriology, 182, 2802–2810.
Yu, M., Wen, S., & Tan, T. (2010). Enhancing production of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase Lip2 in Pichia pastoris. Engineering in Life Sciences, 10, 1–7.
Fickers, P., Destain, J., & Thonart, P. (2009). Improvement of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase production by fed-batch fermentation. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 49, 212–215.
Fickers, P., Fudalej, F., Nicaud, J. M., Destain, J., & Thonart, P. (2005). Selection of new over-producing derivatives for the improvement of extracellular lipase production by the non-conventional yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Journal of Biotechnology, 115, 379–386.
Turki, S., Ayed, A., Chalghoumi, N., Weekers, F., Thonart, P., & Kallel, H. (2010). An Enhanced Process for the Production of a Highly Purified Extracellular Lipase in the Non-conventional Yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160, 1371–1385.
Liu, W. S., Zhao, H. Y., Jia, B., Xu, L., & Yan, Y. J. (2010). Surface display of active lipase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using Cwp2 as an anchor protein. Biotechnology Letters, 32, 255–260.
Li, P., Anumanthan, A., Gao, X. G., Ilangovan, K., Suzara, V. V., Duzgunes, N., & Renugopalakrishnan, V. (2007). Expression of recombinant proteins in Pichia pastoris. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 142, 105–124.
Brunel, L., Neugnot, V., Landucci, L., Boze, H., Moulin, G., Bigey, F., & Dubreucq, E. (2004). High-level expression of Candida parapsilosis lipase/acyltransferase in Pichia pastoris. Journal of Biotechnology, 111, 41–50.
Cos, O., Ramon, R., Montesinos, J. L., & Valero, F. (2006). Operational strategies, monitoring and control of heterologous protein production in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris under different promoters: a review. Microbial Cell Factories, 5, 17.
Macauley-Patrick, S., Fazenda, M. L., McNeil, B., & Harvey, L. M. (2005). Heterologous protein production using the Pichia pastoris expression system. Yeast, 22, 249–270.
Cereghino, J. L., & Cregg, J. M. (2000). Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 24, 45–66.
Zhang, A. L., Luo, J. X., Zhang, T. Y., Pan, Y. W., Tan, Y. H., Fu, C. Y., & Tu, F. Z. (2009). Recent advances on the GAP promoter derived expression system of Pichia pastoris. Molecular Biology Reports, 36, 1611–1619.
Waterham, H. R., Digan, M. E., Koutz, P. J., Lair, S. V., & Cregg, J. M. (1997). Isolation of the Pichia pastoris glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and regulation and use of its promoter. Gene, 186, 37–44.
Menendez, C., Hernandez, L., Banguela, A., & Pais, J. (2004). Functional production and secretion of the Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus fructose-releasing exo-levanase (LsdB) in Pichia pastoris. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 34, 446–452.
Khasa, Y. P., Khushoo, A., Srivastava, L., & Mukherjee, K. J. (2007). Kinetic studies of constitutive human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (hGM-CSF) expression in continuous culture of Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology Letters, 29, 1903–1908.
Vassileva, A., Chugh, D. A., Swaminathan, S., & Khanna, N. (2001). Expression of hepatitis B surface antigen in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris using the GAP promoter. Journal of Biotechnology, 88, 21–35.
Sinha, J., Plantz, B. A., Zhang, W., Gouthro, M., Schlegel, V., Liu, C. P., & Meagher, M. M. (2003). Improved production of recombinant ovine interferon-tau by mut(+) strain of Pichia pastoris using an optimized methanol feed profile. Biotechnology Progress, 19, 794–802.
Stratton, J., Chiruvolu, V., & Meagher, M. (1998). High cell-density fermentation. Methods in Molecular Biology, 103, 107–120.
Kojima, Y., & Shimizu, S. (2003). Purification and characterization of the lipase from Pseudomonas fluorescens HU380. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 96, 219–226.
Braford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Hohenblum, H., Borth, N., & Mattanovich, D. (2003). Assessing viability and cell-associated product of recombinant protein producing Pichia pastoris with flow cytometry. Journal of Biotechnology, 102, 281–290.
Pal, Y., Khushoo, A., & Mukherjee, K. (2006). Process optimization of constitutive human granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (hGM-CSF) expression in Pichia pastoris fed-batch culture. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 69, 650–657.
Delroisse, J. M., Dannau, M., Gilsoul, J. J., El, M. T., Destain, J., Portetelle, D., Thonart, P., Haubruge, E., & Vandenbol, M. (2005). Expression of a synthetic gene encoding a Tribolium castaneum carboxylesterase in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expression and Purification, 42, 286–294.
Zhang, A. L., Zhang, T. Y., Luo, J. X., Chen, S. C., Guan, W. J., Fu, C. Y., Peng, S. Q., & Li, H. L. (2007). Constitutive expression of human angiostatin in Pichia pastoris by high-density cell culture. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 34, 117–122.
Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, D., Li, J., Hua, Z., Du, G., & Chen, J. (2010). Enhancement of cell viability and alkaline polygalacturonate lyase production by sorbitol co-feeding with methanol in Pichia pastoris fermentation. Bioresource Technology, 101, 1318–1323.
Zhu, T., Guo, M., Sun, C., Qian, J., Zhuang, Y., Chu, J., & Zhang, S. (2009). A systematical investigation on the genetic stability of multi-copy Pichia pastoris strains. Biotechnology Letters, 31, 679–684.
Jolivet, P., Bordes, F., Fudalej, F., Cancino, M., Vignaud, C., Dossat, V., Burghoffer, C., Marty, A., Chardot, T., & Nicaud, J. M. (2007). Analysis of Yarrowia lipolytica extracellular lipase Lip2p glycosylation. FEMS Yeast Research, 7, 1317–1327.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of P.R. China (NSFC) (nos. 31070089 and 31170078), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (nos. 2010AA101501 and 2011AA02A204), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2009CDA046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Sun, Y., Ke, F. et al. Constitutive Expression of Yarrowia lipolytica Lipase LIP2 in Pichia pastoris Using GAP as Promoter. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166, 1355–1367 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9524-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9524-4