Abstract
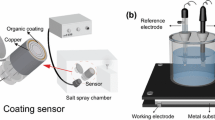
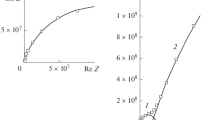
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is used to derive an expression for predicting the service life of organic coating in a C4-type environment (industrial and costal areas with moderate salinity) as defined in ISO 12944 standard for paints and varnishes—corrosion protection of steel structures by protective paint systems. Three coating systems with a record of 2, 5, and 10 years of durability were selected for the study. The selection was also based on proven composition and dry film thickness (DFT) of the coatings as per ISO 12944. Electrochemical impedance measurements of the paint-coated panels were carried out by exposing the coated mild steel panels without scribe in different corrosive environments such as immersion in NaCl solution, neutral salt spray, etc. Neutral salt spray exposure was found to be the most severe corrosive environment among all the three coating systems. In most of the cases, EIS gave early indication of coating failure when compared to visual defects such as blistering and over-film corrosion.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacon, RC, Smith, JJ, Rugg, FM, “Electrolytic Resistance in Evaluating the Protective Merit of Coatings on Metal.” Ind. Eng. Chem., 40 161–167 (1948)
Loveday, D, Peterson P, Rodgers B, “Evaluation of Organic Coatings with Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Part 3: Protocols for Testing Coatings with EIS.” JCT CoatingsTech., 22–27 (2005)
Mansfeld, F, Shih, H, Greene, H, Tsai, CH, “Electrochemical Impedance: Analysis and Interpretation.” In: Scully, J, Silverman, DC, Kendig, M (eds.) ASTM STP 1181, p. 37. ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1993
Taylor, SR, “Assessing the Moisture Barrier Properties of Polymeric Coatings Using Electrical and Electrochemical Methods.” IIEEE Trans. Electr. Insul., 24 787–806 (1989)
Al-Janabi, YT, Al-Ramis, AM, Al-Mutairi, HMS, “Life Prediction of High Temperature Coatings by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy.” Proceedings of NACE Corrosion, Paper 759, 2000
Geenen, FM, “Characterization of Organic Coatings with Impedance Measurements.” Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, 1991
Silverman, DC, “Electrochemical Techniques—Simple Tests for Complex Predictions in the Chemical Process Industries.” Corros. Rev., 10 31–77 (1992)
Bierwagen, G, Tallmann, D, Li, J, He, L, Jeffcoate, C, “EIS Studies of Coated Metals in Accelerated Exposure.” Prog. Org. Coat., 46 149–158 (2003)
Leidheiser, H, Jr, “Electrical and Electrochemical Measurements as Predictors of Corrosion at Metal-Organic Coating Interface.” Prog. Org. Coat., 7 79–104 (1979)
Leidheiser, H, Jr, “Electrochemical Methods for Appraising Corrosion Protective Coatings.” J. Coat. Technol., 802 21–31 (1991)
Gray LGS, Appleman BR, “EIS: Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy—A Tool to Predict Remaining Coating Life.” J. Protective Coat. Lining, 66–74 (2003)
Kendig, M, Scully, J, “Basic Aspects of Electrochemical Impedance Application for the Life Prediction of Organic Coatings on Metals.” Corrosion, 46 22–29 (1990)
Scully, J, Hensley, ST, “Lifetime Prediction for Organic Coatings on Steel and a Magnesium Alloy Using Electrochemical Impedance Methods.” Corrosion, 50 705–716 (1994)
Bierwagen, G, Li, J, He L, Tallman, D, “Fundamentals of the Measurement of Corrosion Protection and the Prediction of Its Lifetime in Organic Coatings.” Proceedings of Second International Symposium on Service Life Prediction Methodology and Metrologies, Chapter 16, pp. 316–350, Monterey, CA, 1999
Vreijling, MPW, van Westing, EPM, Ferrari, GM, van der Weijde DH, de Wit, JHW, “Application of Electrochemical Impedance Measurements in the Determination of the Service Life of Organic Coatings.” Proceedings of Electrochem. Soc. (Advances in Corrosion Protection by Organic Coatings II), Vol. 95–13, pp. 193–210, 1995
van der Weijde, DH, van Westing, EPM, Ferrari, GM, de Wit, JHW, “Lifetime Prediction of Organic Coatings with Impedance Spectroscopy.” Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng., 74 12–13 (1996)
Scully, JR, “Electrochemical Impedance of Organic-Coated Steel: Correlation of Impedance Parameters with Long-Term Coating Deterioration.” J. Electrochem. Soc., 136 979–990 (1989)
Floyd, FL, Avudaiappan, S, Gibson, J, Mehta, B, Smith, P, Provder, T, Escarsega, J, “Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy to Predict the Corrosion Resistance of Unexposed Coated Metal Panels.” Prog. Org. Coat., 66 8–34 (2009)
Sonke, J., Bos, WM, “Research News: EIS Can Help Quantify Corrosion Resistance of Coatings (Full Report).” J. Protect. Coat. Lining, 1–25 (2008)
Hinderliter, BR, Croll, SG, Tallman, DE, Su, Q, Bierwagen, GP, “Interpretation of EIS Data from Accelerated Exposure of Coated Metals Based on Modelling of Coating Physical Properties.” Electrochim. Acta, 51 4505–4515 (2006)
ISO 12944-1:1998 (E), Paints and Varnishes—Corrosion Protection of Steel Structures by Protective Paint Systems, 1st edn., p. 4, 1998
ASTM B 117-03, “Standard Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus.” ASTM Standards, October 2003
ASTM G 85-02, “Standard Practice for Modified Salt Spray (Fog) Testing.” ASTM Standards, February 2003
ASTM D 5894-05, “Standard Practice for Cyclic Salt Fog/UV Exposure of Painted Metal (Alternating Exposures in a Fog/Dry Cabinet and a UV/Condensation Cabinet).” ASTM Standards, July 2005
ISO 16773-2:2007 (E), Paints and Varnishes—Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) on High Impedance Coated Specimens. Part 2: Collection of Data, 1st edn., 2007
Shreepathi, S, Bajaj, P, Mallik, BP, “Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Investigations of Epoxy Zinc Rich Coatings: Role of Zn Content on Corrosion Protection Mechanism.” Electrochim. Acta, 55 5129–5134 (2010)
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge Management of Asian Paints Ltd. for permitting this study to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shreepathi, S., Guin, A.K., Naik, S.M. et al. Service life prediction of organic coatings: electrochemical impedance spectroscopy vs actual service life. J Coat Technol Res 8, 191–200 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-010-9299-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-010-9299-5