Abstract
Purpose of review
To describe advances in the diagnosis and management of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS), a group of conditions with reversible multifocal narrowing of intracranial arteries.
Recent findings
Over the last decade, multiple cohort studies have characterized RCVS and distinguished it from primary angiitis of the central nervous system and aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Onset with recurrent thunderclap headaches (TCH) occurs in 85–90% of patients; most authors believe that RCVS and primary TCH are similar conditions. Rare cases with concurrent takotsubo cardiomyopathy or extracranial artery narrowing have been published. Stroke and brain edema can develop in up to 40% of inpatients; however, the discharge and 10-year outcome is invariably benign. Pregnancy-associated RCVS may have worse outcome. The pathophysiology remains relatively unknown. There is no specific treatment. Management involves pain relief and removal of identified vasoconstrictive factors. Calcium-channel blockers may help to relieve headaches. Glucocorticoids are associated with significantly worse outcome. The role of intra-arterial vasodilator infusion remains uncertain. The recently developed “RCVS2 score” enables accurate bedside diagnosis with up to 99% specificity and 90% sensitivity, obviating the need for invasive tests such as lumbar puncture, brain biopsy and catheter angiography to exclude mimics or confirm the diagnosis.
Conclusion
RCVS can now be accurately diagnosed using clinical and imaging features available upon presentation. Advances in knowledge about the risk factors, prognosis, and potential harmful effects of certain therapeutic strategies, are expected to optimize the management of this increasingly well recognized syndrome.


Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Singhal AB, Caviness VS, Begleiter AF, Mark EJ, Rordorf G, Koroshetz WJ. Cerebral vasoconstriction and stroke after use of serotonergic drugs. Neurology. 2002;58:130–3.
Singhal AB. Cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2004;11:1–6.
Hajj-Ali RA, Furlan A, Abou-Chebel A, Calabrese LH. Benign angiopathy of the central nervous system: cohort of 16 patients with clinical course and long-term followup. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;47:662–9.
Calabrese LH, Dodick DW, Schwedt TJ, Singhal AB. Narrative review: reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146:34–44.
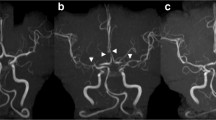
Chen SP, Fuh JL, Wang SJ, Chang FC, Lirng JF, Fang YC, et al. Magnetic resonance angiography in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Ann Neurol. 2010;67:648–56.
Singhal AB, Hajj-Ali RA, Topcuoglu MA, et al. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes: analysis of 139 cases. Arch Neurol. 2011;68:1005–12.
Singhal AB, Topcuoglu MA, Fok JW, Kursun O, Nogueira RG, Frosch MP, et al. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes and primary angiitis of the central nervous system: clinical, imaging, and angiographic comparison. Ann Neurol. 2016;79:882–94.
de Boysson H, Parienti JJ, Mawet J, Arquizan C, Boulouis G, Burcin C, et al. Primary angiitis of the CNS and reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: a comparative study. Neurology. 2018;91:e1468–e78.
Choi HA, Lee MJ, Choi H, Chung CS. Characteristics and demographics of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: a large prospective series of Korean patients. Cephalalgia. 2018;38:765–75.
Caria F, Zedde M, Gamba M, Bersano A, Rasura M, Adami A, et al. The clinical spectrum of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: the Italian Project on Stroke at Young Age (IPSYS). Cephalalgia. 2019;39:1267–76.
Singhal AB, Topcuoglu MA. Glucocorticoid-associated worsening in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Neurology. 2017;88:228–36.
Katz BS, Fugate JE, Ameriso SF, Pujol-Lereis VA, Mandrekar J, Flemming KD, et al. Clinical worsening in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. JAMA Neurol. 2014;71:68–73.
Ducros A, Boukobza M, Porcher R, Sarov M, Valade D, Bousser MG. The clinical and radiological spectrum of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. A prospective series of 67 patients. Brain. 2007;130:3091–101.
Ducros A. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11:906–17.
Serdaru M, Chiras J, Cujas M, Lhermitte F. Isolated benign cerebral vasculitis or migrainous vasospasm? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984;47:73–6.
Jackson M, Lennox G, Jaspan T, Jefferson D. Migraine angiitis precipitated by sex headache and leading to watershed infarction. Cephalalgia. 1993;13:427–30.
Call GK, Fleming MC, Sealfon S, Levine H, Kistler JP, Fisher CM. Reversible cerebral segmental vasoconstriction. Stroke. 1988;19:1159–70.
Day JW, Raskin NH. Thunderclap headache: symptom of unruptured cerebral aneurysm. Lancet. 1986;2:1247–8.
Dodick DW, Brown RD Jr, Britton JW, Huston J 3rd. Nonaneurysmal thunderclap headache with diffuse, multifocal, segmental, and reversible vasospasm. Cephalalgia. 1999;19:118–23.
Kaye BR, Fainstat M. Cerebral vasculitis associated with cocaine abuse. JAMA. 1987;258:2104–6.
Martin K, Rogers T, Kavanaugh A. Central nervous system angiopathy associated with cocaine abuse. J Rheumatol. 1995;22:780–2.
Bogousslavsky J, Despland PA, Regli F, Dubuis PY. Postpartum cerebral angiopathy: reversible vasoconstriction assessed by transcranial Doppler ultrasounds. Eur Neurol. 1989;29:102–5.
Barinagarrementeria F, Cantu C, Balderrama J. Postpartum cerebral angiopathy with cerebral infarction due to ergonovine use. Stroke. 1992;23:1364–6.
Calabrese LH, Gragg LA, Furlan AJ. Benign angiopathy: a distinct subset of angiographically defined primary angiitis of the central nervous system. J Rheumatol. 1993;20:2046–50.
Razavi M, Bendixen B, Maley JE, Shoaib M, Zargarian M, Razavi B, et al. CNS pseudovasculitis in a patient with pheochromocytoma. Neurology. 1999;52:1088–90.
Coffino SW, Fryer RH. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome in pediatrics: a case series and review. J Child Neurol. 2017;32:614–23.
Liu HY, Fuh JL, Lirng JF, Chen SP, Wang SJ. Three paediatric patients with reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Cephalalgia. 2010;30:354–9.
Topcuoglu MA, McKee KE, Singhal AB. Gender and hormonal influences in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Eur Stroke J. 2016;1:199–204.
Iancu-Gontard D, Oppenheim C, Touze E, et al. Evaluation of hyperintense vessels on FLAIR MRI for the diagnosis of multiple intracerebral arterial stenoses. Stroke. 2003;34:1886–91.
Chen SP, Fuh JL, Lirng JF, Wang SJ. Hyperintense vessels on flair imaging in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Cephalalgia. 2012;32:271–8.
Topcuoglu MA, Singhal AB. Hemorrhagic reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: features and mechanisms. Stroke. 2016;47:1742–7.
Ducros A, Fiedler U, Porcher R, Boukobza M, Stapf C, Bousser MG. Hemorrhagic manifestations of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: frequency, features, and risk factors. Stroke. 2010;41:2505–11.
Chen SP, Fuh JL, Chang FC, Lirng JF, Shia BC, Wang SJ. Transcranial color doppler study for reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Ann Neurol. 2008;63:751–7.
Mijalski C, Dakay K, Miller-Patterson C, Saad A, Silver B, Khan M. Magnesium for treatment of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: case series. Neurohospitalist. 2016;6:111–3.
Muehlschlegel S, Rordorf G, Bodock M, Sims JR. Dantrolene mediates vasorelaxation in cerebral vasoconstriction: a case series. Neurocrit Care. 2009;10:116–21.
Topcuoglu MA, Chan ST, Silva GS, Smith EE, Kwong KK, Singhal AB. Cerebral vasomotor reactivity in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Cephalalgia. 2017;37:541–7.
Chen CY, Chen SP, Fuh JL, Lirng JF, Chang FC, Wang YF, et al. Vascular wall imaging in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome - a 3-T contrast-enhanced MRI study. J Headache Pain. 2018;19:74.
Mandell DM, Matouk CC, Farb RI, Krings T, Agid R, terBrugge K, et al. Vessel wall MRI to differentiate between reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome and central nervous system vasculitis: preliminary results. Stroke. 2012;43:860–2.
Obusez EC, Hui F, Hajj-Ali RA, et al. High-resolution MRI vessel wall imaging: spatial and temporal patterns of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome and central nervous system vasculitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014;35:1527–32.
Mawet J, Boukobza M, Franc J, Sarov M, Arnold M, Bousser MG, et al. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome and cervical artery dissection in 20 patients. Neurology. 2013;81:821–4.
Topcuoglu MA, Kursun O, Singhal AB. Coexisting vascular lesions in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Cephalalgia. 2017;37:29–35.
Mukerji SS, Buchbinder BR, Singhal AB. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome with reversible renal artery stenosis. Neurology. 2015;85:201–2.
John S, Hajj-Ali RA, Min D, Calabrese LH, Cerejo R, Uchino K. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: is it more than just cerebral vasoconstriction? Cephalalgia. 2015;35:631–4.
Boitet R, Gaillard N, Bendiab E, Corti L, Roos C, Reynes J, Costalat V, Arquizan C, Ducros A. Concomitant reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome and transient global amnesia. J Neurol. 2020;267(2):390–394.
Kamm K, Schöberl F, Grabova D, Straube A, Zwergal A. RCVS and TGA: a common pathophysiology? J Neurol. 2019;266(11):2872–2874.
Isahaya K, Shinohara K, Akamatu M, Shimizu T, Sakurai K, Shiraishi M, Akiyama H, Hasegawa Y. Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome Presenting with Transient Global Amnesia. Intern Med. 2017;56(12):1569–1573.
Laeeq R, Berman JS, Khalid U, Lakkis NM, Tabbaa R. Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome Associated with Coronary Artery Vasospasm. Tex Heart Inst J. 2019;46(2):139–142.
Enderton E, Cardwell M. Postpartum takotsubo cardiomyopathy with reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: a case report. Case Reports in Perinatal Medicine. 2013;2(1–2):21–24.
Nighoghossian N, Trouillas P, Loire R, Perrin L, Trillet V, Gamondes P. Catecholamine syndrome, carcinoid lung tumor and stroke. Eur Neurol. 1994;34:288–9.
Yarnell PR, Caplan LR. Basilar artery narrowing and hyperparathyroidism: illustrative case. Stroke. 1986;17:1022–4.
Rocha EA, Topcuoglu MA, Silva GS, Singhal AB. RCVS2 score and diagnostic approach for reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Neurology. 2019;92:e639–e47.
Muehlschlegel S, Kursun O, Topcuoglu MA, Fok J, Singhal AB. Differentiating reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome with subarachnoid hemorrhage from other causes of subarachnoid hemorrhage. JAMA Neurol. 2013;70:1254–60.
Hajj-Ali RA, Singhal AB, Benseler S, Molloy E, Calabrese LH. Primary angiitis of the CNS. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10:561–72.
Camargo ECS, Singhal AB. Cerebral arteriopathies, venous thrombosis, and migraine. Semin Neurol. 2017;37:339–50.
Singhal AB. Diagnostic challenges in RCVS, PACNS, and other cerebral arteriopathies. Cephalalgia. 2011;31:1067–70.
Wong LK. Global burden of intracranial atherosclerosis. Int J Stroke. 2006;1:158–9.
Erdbruegger U, Grossheim M, Hertel B, Wyss K, Kirsch T, Woywodt A, et al. Diagnostic role of endothelial microparticles in vasculitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47:1820–5.
Hajj-Ali RA, Major J, Langford C, Hoffman GS, Clark T, Zhang L, et al. The interface of inflammation and subclinical atherosclerosis in granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s): a preliminary study. Transl Res. 2015;166:366–74.
Kass-Hout T, Kass-Hout O, Sun CH, et al. A novel approach to diagnose reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: a case series. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015;24:e31–7.
Soo Y, Singhal AB, Leung T, Yu S, Mak H, Hao Q, et al. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome with posterior leucoencephalopathy after oral contraceptive pills. Cephalalgia. 2010;30:42–5.
Singhal AB, Kimberly WT, Schaefer PW, Hedley-Whyte ET. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 8-2009. A 36-year-old woman with headache, hypertension, and seizure 2 weeks post partum. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1126–37.
Chen SP, Chung YT, Liu TY, Wang YF, Fuh JL, Wang SJ. Oxidative stress and increased formation of vasoconstricting F2-isoprostanes in patients with reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;61:243–8.
Chen SP, Fuh JL, Wang SJ, Tsai SJ, Hong CJ, Yang AC. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene Val66Met polymorphism modulates reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. PLoS One. 2011;6:e18024.
Chen SP, Wang YF, Huang PH, Chi CW, Fuh JL, Wang SJ. Reduced circulating endothelial progenitor cells in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. J Headache Pain. 2014;15:82.
Chen SP, Yang AC, Fuh JL, Wang SJ. Autonomic dysfunction in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. J Headache Pain. 2013;14:94.
Hsu WH, Wang SJ, Chao YM, et al. Urine metabolomics signatures in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Cephalalgia 2020:333102419897621.
Cho S, Ling YH, Lee MJ, Chen SP, Fuh JL, Lirng JF, et al. Temporal profile of blood-brain barrier breakdown in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Stroke. 2020;51:1451–7.
Lee MJ, Cha J, Choi HA, Woo SY, Kim S, Wang SJ, et al. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: implications for pathophysiology and diagnosis. Ann Neurol. 2017;81:454–66.
Singhal AB. Postpartum angiopathy with reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy. Arch Neurol. 2004;61:411–6.
Bartynski WS, Boardman JF. Catheter angiography, MR angiography, and MR perfusion in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29:447–55.
Farid H, Tatum JK, Wong C, Halbach VV, Hetts SW. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: treatment with combined intra-arterial verapamil infusion and intracranial angioplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32:E184–7.
Ringer AJ, Qureshi AI, Kim SH, Fessler RD, Guterman LR, Hopkins LN. Angioplasty for cerebral vasospasm from eclampsia. Surg Neurol. 2001;56:373–8 discussion 8-9.
Song JK, Fisher S, Seifert TD, Cacayorin ED, Alexandrov AV, Malkoff MD, et al. Postpartum cerebral angiopathy: atypical features and treatment with intracranial balloon angioplasty. Neuroradiology. 2004;46:1022–6.
Bouchard M, Verreault S, Gariepy JL, Dupre N. Intra-arterial milrinone for reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Headache. 2009;49:142–5.
Fugate JE, Wijdicks EF, Parisi JE, Kallmes DF, Cloft HJ, Flemming KD, et al. Fulminant postpartum cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Arch Neurol. 2012;69:111–7.
Kunchok A, Castley HC, Aldous L, Hawke SH, Torzillo E, Parker GD, et al. Fatal reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 2018;385:146–50.
Valencia-Mendoza M, Ramirez-Rodriguez N, Vargas-Avila N, et al. Fatal reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: a systematic review of case series and case reports. J Clin Neurosci. 2019;70:183–8.
Buckle RM, Duboulay G, Smith B. Death due to cerebral vasospasm. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1964;27:440–4.
John S, Singhal AB, Calabrese L, Uchino K, Hammad T, Tepper S, et al. Long-term outcomes after reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Cephalalgia. 2016;36:387–94.
Boitet R, de Gaalon S, Duflos C, Marin G, Mawet J, Burcin C, et al. Long-term outcomes after reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Stroke. 2020;51:670–3.
Chen SP, Fuh JL, Lirng JF, Wang YF, Wang SJ. Recurrence of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: a long-term follow-up study. Neurology. 2015;84:1552–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Dr. Rocha reports the following conflicts: Medlink, Inc.
Dr. Singhal reports the following conflicts: UptoDate Medicine Inc.; Medlink, Inc.; Medicolegal Expert Witness; Biogen; Omniox; Deck Therapeutics; NIH-NINDS U24 NS107243, U01 NS095869, U01 NS110728.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Cerebrovascular Disease and Stroke
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rocha, E.A., Singhal, A.B. Current Treatment Options in Cardiovascular Medicine: Update on Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome. Curr Treat Options Cardio Med 22, 18 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11936-020-00819-9
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11936-020-00819-9