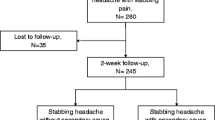
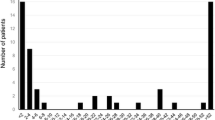
Abstract
Purpose of Review
To provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature on primary stabbing headache.
Recent Findings
Changes to the ICHD-3 criteria have resulted in increased sensitivity to capture primary stabbing headache (PSH). According to the ICHD-3, the sharp stabbing pain is no longer restricted to the first division of the trigeminal nerve. Age, gender, and co-morbidities such as migraine seem to influence the prevalence of PSH. Subclassification into monophasic, intermittent, and chronic forms have been proposed in a recent prospective study and may be helpful from a prognostication perspective; however, further studies are required.
Summary
Secondary etiologies for stabbing headaches are part of the differential diagnosis of primary stabbing headache; therefore, it is reasonable to perform neuroimaging. For severe frequent attacks, indomethacin continues to be considered first line. Other treatment options include COX2 inhibitors and melatonin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Lansche RK. Ophthalmodynia Periodica. Headache. 1964;4:247–9.
Rasmussen BK, Olesen J. Symptomatic and nonsymptomatic headaches in a general population. Neurology. 1992;42(6):1225–31.
Pereira-Monteiro J. Cefaleias. Estudo Epidemiologico e Clinico de uma Populacao Urbana [thesis]. Porto, Portugal; 1995.
Sjaastad O, Pettersen H, Bakketeig LS. The Vaga study; epidemiology of headache I: the prevalence of ultrashort paroxysms. Cephalalgia. 2001;21(3):207–15.
Pareja JA, Sjaastad O. Primary stabbing headache. Handb Clin Neurol. 2010;97:453–7.
Liang X, Ying G, Huang Q, Wang J, Li N, Tan G, et al. Characteristics of primary stabbing headache in a tertiary neurological clinic in China. Pain Med. 2014;15(5):871–5.
Tugba T, Serap U, Esra O, Ozlem C, Ufuk E, Levent EI. Features of stabbing, cough, exertional and sexual headaches in a Turkish population of headache patients. J Clin Neurosci 2008;15(7):774–7, 777.
Dodick DPJ. Primary stabbing, cough, exertional, and thunderclap headaches. In: Olesen JGP, Ramadan NM, et al., editors. The headaches. 3. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2006. p. 831–2.
Pareja JA, Ruiz J, de Isla C, al-Sabbah H, Espejo J. Idiopathic stabbing headache (jabs and jolts syndrome). Cephalalgia. 1996;16(2):93–6.
Sjaastad O, Pettersen H, Bakketeig LS. The Vaga study of headache epidemiology II. Jabs: clinical manifestations. Acta Neurol Scand. 2002;105(1):25–31.
Fuh JL, Kuo KH, Wang SJ. Primary stabbing headache in a headache clinic. Cephalalgia. 2007;27(9):1005–9.
Fusco C, Pisani F, Faienza C. Idiopathic stabbing headache: clinical characteristics of children and adolescents. Brain Dev. 2003;25(4):237–40.
Hagler S, Ballaban-Gil K, Robbins MS. Primary stabbing headache in adults and pediatrics: a review. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2014;18(10):450.
• Society HCCotIH. Headache classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) the international classification of headache disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia. 2018;38(1):1–211 Latest clinical definition of PSH.
Classification and diagnostic criteria for headache disorders, cranial neuralgias and facial pain. Headache classification Committee of the International Headache Society. Cephalalgia 1988;8 Suppl 7:1–96.
Society HCSotIH. The international classification of headache disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia. 2004;24(Suppl 1):9–160.
Soriani S, Battistella PA, Arnaldi C, De Carlo L, Cernetti R, Corra S, et al. Juvenile idiopathic stabbing headache. Headache. 1996;36(9):565–7.
Sjaastad O, Pettersen H, Bakketeig LS. Long-lasting cephalic jabs (?) the Vaga study of headache epidemiology. Cephalalgia. 2005;25(8):581–92.
•• Lee M, Chu MK, Lee J, Yoo J, Song HK. Field testing primary stabbing headache criteria according to the 3rd beta edition of international classification of headache disorders: a clinic-based study. J Headache Pain. 2016;17:21 Field testing of ICHD-3, which showed increased sensitivity to capture patients with PSH in comparison to ICHD-2.
Robbins MS, Evans RW. Primary and secondary stabbing headache. Headache. 2015;55(4):565–70.
Piovesan EJ, Kowacs PA, Lange MC, Pacheco C, Piovesan LRM, Werneck LC. Prevalence and semiologic aspects of the idiopathic stabbing headache in a migraine population. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2001;59(2A):201–5.
Sjaastad O, Bakketeig LS. The rare, unilateral headaches. Vaga study of headache epidemiology. J Headache Pain. 2007;8(1):19–27.
Martins IP, Parreira E, Costa I. Extratrigeminal ice-pick status. Headache. 1995;35(2):107–10.
Kim CH, Song HK, Lee JH, Kim WK, Chu MK, Lee BC. Paroxysmal stabbing headache in the retroauricular regions. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2005;23(6):765–9.
Shin JH, Song HK, Lee JH, Kim WK, Chu MK. Paroxysmal stabbing headache in the multiple dermatomes of the head and neck: a variant of primary stabbing headache or occipital neuralgia? Cephalalgia. 2007;27(10):1101–8.
Kim DY, Lee MJ, Choi HA, Choi H, Chung CS. Clinical patterns of primary stabbing headache: a single clinic-based prospective study. J Headache Pain. 2017a;18(1):44.
•• Kim DY, Lee MJ, Choi HA, Choi H, Chung C-S. Clinical patterns of primary stabbing headache: a single clinic-based prospective study. J Headache Pain. 2017b;18(1):44 Most recent prospective observational trial on clinical features of PSH.
Selekler HM, Komşuoğlu S. The relationship of stabbing headaches with migraine attacks. Agri. 2005;17(1):45–8.
Ozge A, Faedda N, Abu-Arafeh I, Gelfand AA, Goadsby PJ, Cuvellier JC, et al. Experts’ opinion about the primary headache diagnostic criteria of the ICHD-3rd edition beta in children and adolescents. J Headache Pain. 2017;18(1):109.
Myers KA, Smyth KA. Preadolescent indomethacin-responsive headaches without autonomic symptoms. Headache. 2013;53(6):977–80.
Mukharesh LO, Jan MM. Primary stabbing “ice-pick” headache. Pediatr Neurol. 2011;45(4):268–70.
Victorio MC. Uncommon pediatric primary headache disorders. Pediatr Ann. 2018;47(2):e69–73.
Kakisaka Y, Ohara T, Hino-Fukuyo N, Uematsu M, Kure S. Abdominal and lower back pain in pediatric idiopathic stabbing headache. Pediatrics. 2014;133(1):e245–7.
Selekler HM, Budak F. Idiopathic stabbing headache and experimental ice cream headache (short-lived headaches). Eur Neurol. 2004;51(1):6–9.
Sjaastad O, Bakketeig LS, Petersen HC. Migraine with aura: visual disturbances and interrelationship with the pain phase. Vaga study of headache epidemiology. J Headache Pain. 2006;7(3):127–35.
Pedraza MI, Guerrero-Peral AL, Herrero-Velazquez S, Mulero P, Baron J, Ruiz M, et al. Primary stabbing headache: clinical characteristics and response to treatment in a series of 67 patients. Rev Neurol. 2012;55(8):469–74.
Raskin NH, Schwartz RK. Icepick-like pain. Neurology. 1980;30(2):203–5.
Wang SJ, Fuh JL. The “other” headaches: primary cough, exertion, sex, and primary stabbing headaches. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2010;14(1):41–6.
Montella S, Ranieri A, Marchese M, De Simone R. Primary stabbing headache: a new dural sinus stenosis-associated primary headache? Neurol Sci. 2013;34(Suppl 1):S157–9.
Ergun U, Ozer G, Sekercan S, Artan E, Kudiaki C, Ucler S, et al. Headaches in the different phases of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a tendency for stabbing headaches during relapses. Neurologist. 2009;15(4):212–6.
Rampello L, Malaguarnera M, Rampello L, Nicoletti G, Battaglia G. Stabbing headache in patients with autoimmune disorders. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2012;114(6):751–3.
Robbins MS. Transient stabbing headache from an acute thalamic hemorrhage. J Headache Pain. 2011;12(3):373–5.
Tentschert S, Wimmer R, Greisenegger S, Lang W, Lalouschek W. Headache at stroke onset in 2196 patients with ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2005;36(2):e1–3.
Marin LF, Felicio AC, Santos WA, Silva PC, Gorinchteyn JC, Marinho IS. Stabbing headache as the initial manifestation of herpetic meningoencephalitis. J Headache Pain. 2010;11(5):445–6.
Rozen TD. Brief sharp stabs of head pain and giant cell arteritis. Headache. 2010;50(9):1516–9.
Klein M, Woehrl B, Zeller G, Straube A. Stabbing headache as a sign of relapses in multiple sclerosis. Headache. 2013;53(7):1159–61.
Mascellino AM, Lay CL, Newman LC. Stabbing headache as the presenting manifestation of intracranial meningioma: a report of two patients. Headache. 2001;41(6):599–601.
Levy MJ, Matharu MS, Goadsby PJ. Prolactinomas, dopamine agonists and headache: two case reports. Eur J Neurol. 2003;10(2):169–73.
Weng HY, Cohen AS, Schankin C, Goadsby PJ. Phenotypic and treatment outcome data on SUNCT and SUNA, including a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Cephalalgia. 2018;38(9):1554–63.
Chua AL, Nahas S. Ice pick headache. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2016;20(5):30.
Dodick DW. Indomethacin-responsive headache syndromes. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2004;8(1):19–26.
VanderPluym J. Indomethacin-responsive headaches. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2015;15(2):516.
Goodman LS, Brunton LL, Chabner B, Knollmann BC. Goodman & Gilman’s pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 12th ed. Laurence L. Brunton ; associate editors BAC, Björn C. Knollmann, editor. New York2011.
Ferrante E, Rossi P, Tassorelli C, Lisotto C, Nappi G. Focus on therapy of primary stabbing headache. J Headache Pain. 2010;11(2):157–60.
O'Connor MB, Murphy E, Phelan MJ, Regan MJ. Primary stabbing headache can be responsive to etoricoxib, a selective COX-2 inhibitor. Eur J Neurol. 2008;15(1):e1.
Piovesan EJ, Zukerman E, Kowacs PA, Werneck LC. COX-2 inhibitor for the treatment of idiopathic stabbing headache secondary to cerebrovascular diseases. Cephalalgia. 2002;22(3):197–200.
Rozen TD. Melatonin as treatment for idiopathic stabbing headache. Neurology. 2003;61(6):865–6.
Leite Pacheco R, de Oliveira Cruz Latorraca C, Adriano Leal Freitas da Costa A, Luiza Cabrera Martimbianco A, Vianna Pachito D, Riera R. Melatonin for preventing primary headache: a systematic review. Int J Clin Pract. 2018;72(7):e13203.
Gelfand AA, Goadsby PJ. The role of melatonin in the treatment of primary headache disorders. Headache. 2016;56(8):1257–66.
Gelfand AA. Melatonin in the treatment of primary headache disorders. Headache. 2017;57(6):848–9.
Bermudez Salazar M, Rojas Ceron CA, Arana Munoz RS. Prophylaxis with melatonin for primary stabbing headache in pediatrics: a case report. Colomb Med. 2018;49(3):244–8.
Piovesan EJ, Teive HG, Kowacs PA, Silva LL, Werneck LC. Botulinum neurotoxin type-A for primary stabbing headache: an open study. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2010;68(2):212–5.
Franca MC Jr, Costa AL, Maciel JA Jr. Gabapentin-responsive idiopathic stabbing headache. Cephalalgia. 2004;24(11):993–6.
Ranieri A, Topa A, Cavaliere M, De Simone R. Recurrent epistaxis following stabbing headache responsive to acetazolamide. Neurol Sci. 2014;35(Suppl 1):181–3.
Jacome DE. Exploding head syndrome and idiopathic stabbing headache relieved by nifedipine. Cephalalgia. 2001;21(5):617–8.
Godoy DA, Rabinstein AA, Biestro A, Ainslie PN, Di Napoli M. Effects of indomethacin test on intracranial pressure and cerebral hemodynamics in patients with refractory intracranial hypertension: a feasibility study. Neurosurgery. 2012;71(2):245–57 discussion 57-8.
Celebisoy N, Gokcay F, Sirin H, Akyurekli O. Treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension: topiramate vs acetazolamide, an open-label study. Acta Neurol Scand. 2007;116(5):322–7.
Gelfand A, Qubty W, Patniyot I, Pletcher M, Goadsby P, Cummings S. Melatonin for adolescent migraine prevention: a pilot internet-based randomized controlled trial (P2. 163). AAN Enterprises; 2017.
Bermúdez Salazar M, Rojas Cerón CA, Arana Muñoz RS. Prophylaxis with melatonin for primary stabbing headache in pediatrics: a case report. Colomb Méd. 2018;49(3):244–8.
Andersen LPH, Gögenur I, Rosenberg J, Reiter RJ. The safety of melatonin in humans. Clin Drug Investig. 2016;36(3):169–75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Esma Dilli reports honoraria from Allergen and royalties from Lippincott. Danielle Murray reports no potential conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Headache
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murray, D., Dilli, E. Primary Stabbing Headache. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 19, 47 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-019-0955-6
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-019-0955-6