Abstract
Purpose of Review
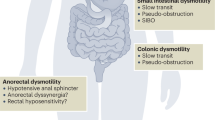
Systemic sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disorder commonly involving the gastrointestinal tract, including the colon and anorectum. In this review, we summarize major clinical manifestations and highlight recent developments in physiology, diagnostics, and treatment.
Recent Findings
The exact pathophysiology of systemic sclerosis is unclear and likely multifactorial. The role of the microbiome on gastrointestinal manifestations has led to a better understanding of potential pathogenic gut flora. Carbohydrate malabsorption is common. Evaluation using fecal calprotectin and high-resolution anorectal manometry may broaden our understanding of the etiologies of diarrhea and fecal incontinence and help with early recognition of pathology. Prucalopride, a high-affinity 5HT4 agonist, and pyridostigmine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, may help improve colonic transit in patients with constipation. Intravenous immunoglobulins have been used to target muscarinic receptor antibodies that are believed to contribute to gastrointestinal dysmotility.
Summary
Colonic and anorectal manifestations of systemic sclerosis include constipation, diarrhea, and fecal incontinence, and can diminish quality of life for these patients. Recent studies regarding pathophysiology as well as diagnostic and treatment options are promising. Further targeted studies to facilitate early intervention and better management of refractory symptoms are still needed.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Sallam H, McNearney TA, Chen JD. Systematic review: pathophysiology and management of gastrointestinal dysmotility in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Mar 15;23(6):691–712.
Nagaraja V, Hays RD, Khanna PP, Spiegel BMR, Chang L, Melmed GY, et al. Construct validity of the patient-reported outcomes measurement information system gastrointestinal symptom scales in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res. 2014 Nov;66(11):1725–30.
Khanna D, Nagaraja V, Gladue H, Chey W, Pimentel M, Frech T. Measuring response in the gastrointestinal tract in systemic sclerosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013 Nov;25(6):700–6.
Sakkas LI, Simopoulou T, Daoussis D, et al. Intestinal involvement in systemic sclerosis: a clinical review. Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Apr;63(4):833–4.
Denton CP, Khanna D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet. 2017 Oct 7;390(10103):1685–99.
Stern EP, Denton CP. The pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Rheum Dis Clin N Am. 2015 Aug;41(3):367–82.
• McFarlane IM, Bhamra MS, Kreps A, et al. Gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Sunnyvale). 2018;8(1):235. Current review about the pathogenesis and GI clinical manifestations of systemic sclerosis.
Furue M, Mitoma C, Mitoma H, Tsuji G, Chiba T, Nakahara T, et al. Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis – current concept and emerging treatments. Immunol Res. 2017;65(4):790–7.
Kumar S, Singh J, Kedika R, Mendoza F, Jimenez SA, Blomain ES, et al. Role of muscarinic-3 receptor antibody in systemic sclerosis: correlation with disease duration and effects of IVIG. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016;310(11):G1052–60.
Steen VD, Medsger TA Jr. Severe organ involvement in systemic sclerosis with diffuse scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43(11):2437–44.
Svegliati S, Spadoni T, Moroncini G, Gabrielli A. NADPH oxidase, oxidative stress and fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018;125:90–7.
Vona R, Giovannetti A, Gambardella L, Malorni W, Pietraforte D, Straface E. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of systemic scleroderma: an overview. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(7):3308–14.
Doridot L, Jeljeli M, Chene C, et al. Implication of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of systematic sclerosis via inflammation, autoimmunity and fibrosis. Redox Biol. 2019;25:101122.
• Bellochi C, Volkmann ER. Update on the gastrointestinal microbiome in systemic sclerosis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018;20(8):49. Current review characterizing the role of the microbiome in systemic sclerosis.
Patrone V, Puglisi E, Cardinali M, Schnitzler TS, Svegliati S, Festa A, et al. Gut microbiota profile in systemic sclerosis patients with and without clinical evidence of gastrointestinal involvement. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):14874.
Battle WM, Snape WJ Jr, Wright S, et al. Abnormal colonic motility in progressive systemic sclerosis. Ann Intern Med. 1981;94(6):749–52.
• Vigone B, Caronni M, Severino A, Bellocchi C, Baldassarri AR, Fraquelli M, et al. Preliminary safety and efficacy profile of prucalopride in the treatment of systemic sclerosis (SSc)-related intestinal involvement: results from the open label cross-over PROGASS study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):145. Pivotal study examining prucalopride as a treatment option in systemic sclerosis patients.
• Ahuja NK, Mische L, Clarke JO, et al. Pyridostigmine for the treatment of gastrointestinal symptoms in systemic sclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2018;48(1):111–6. Pivotal study examining pyridostigmine as a treatment option in systemic sclerosis patients.
Bharucha AE, Low PA, Camilleri M, Burton D, Gehrking TL, Zinsmeister AR. Pilot study of pyridostigmine in constipated patients with autonomic neuropathy. Clin Auton Res. 2008;18(4):194–202.
Marie I, Leroi AM, Menard JF, Levesque H, Quillard M, Ducrotte P. Fecal calprotectin in systemic sclerosis and review of the literature. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14(6):547–54.
Zhong C, Qu C, Wang B, Liang S, Zeng B. Probiotics for preventing and treating small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: a meta-analysis and systematic review of current evidence. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2017;51(4):300–11.
Frech TM, Khanna D, Maranian P, et al. Probiotics for the treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated gastrointestinal bloating/distension. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29(2 Suppl 65):S22–5.
• Smith E, Pauling JD. The efficacy of dietary intervention on gastrointestinal involvement in systemic sclerosis: a systematic literature review. Semin Arthitis Rheum. 2018. Comprehensive review of the evidence regarding dietary modification for gastrointestinal symptoms in systemic sclerosis.
Marie I, Leroi AM, Gourcerol G, Levesque H, Menard JF, Ducrotte P. Lactose malabsorption in systemic sclerosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;44(10):1123–33.
Marie I, Leroi AM, Gourcerol G, Levesque H, Ménard JF, Ducrotte P. Fructose malabsorption in systemic sclerosis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(39):e1601.
• Gomes JP, Santos L, Shoenfeld Y. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) in the vanguard therapy of systemic sclerosis. Clin Immunol. 2018. Current review regarding IVIG use in systemic sclerosis.
Sanges S, Riviere S, Mekinian A, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulins in systemic sclerosis: data from a French nationwide cohort of 46 patients and review of the literature. Autoimm Rev. 2017;16(4):377–84.
Raja J, Nihtyanova SI, Murray CD, Denton CP, Ong VH. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55(1):115–9.
Bharadwaj S, Tandon P, Gohel T, Corrigan ML, Coughlin KL, Shatnawei A, et al. Gastrointestinal manifestations, malnutrition, and role of enteral and parenteral nutrition in patients with scleroderma. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2015;49(7):559–64.
Preis E, Franz K, Siegert E, Makowka A, March C, Riemekasten G, et al. The impact of malnutrition on quality of life in patients with systemic sclerosis. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2018;72(4):504–10.
Baron M, Hudson M, Steele R, et al. Malnutrition is common in systemic sclerosis: results from the Canadian scleroderma research group database. J Rheumatol. 2009;36(12):2737–43.
Duchini A, Sessoms SL. Gastrointestinal hemorrhage in patients with systemic sclerosis and CREST syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93(9):1453–6.
Jharap B, Koudstaal LG, Neefjes-Borst EA, et al. Colonic telangiectasias in progressive systemic sclerosis. Endoscopy. 2012;44(Suppl 2 UCTN):E42–3.
Wang YJ, Wang YM, Zheng YM, et al. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis: six case reports and a review of the literature. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018;18(1):100.
Castro-Pocas R, Araujo T, Pedroto I. Endoscopic ultrasound of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Endoscopy. 2015;47(Suppl 1 UCTN):E274.
Kaneko M, Sasaki S, Teruya S, et al. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis in patients with systemic sclerosis: a case report and review of 39 Japanese cases. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2016;2016:2474515.
Lepri G, Guiducci S, Bellando-Randome S, et al. Evidence for oesophageal and anorectal involvement in very early systemic sclerosis (VEDOSS): report from a single VEDOSS/EUSTAR centre. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(1):124–8.
Richard N, Hudson M, Gyger G, et al. Clinical correlates of faecal incontinence in systemic sclerosis: identifying therapeutic avenues. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017;56(4):581–8.
Garros A, Marjoux S, Khouatra C, Coppere B, Grange C, Hot A, et al. Prevalence of fecal incontinence in a cohort of systemic sclerosis patients within a regional referral network. United European Gastroenterol J. 2017;5(7):1046–50.
Omair MA, Lee P. Effect of gastrointestinal manifestations on quality of life in 87 consecutive patients with systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 2012;39(5):992–6.
Franck-Larsson K, Graf W, Ronnblom A. Lower gastrointestinal symptoms and quality of life in patients with systemic sclerosis: a population-based study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;21(2):176–82.
Thoua NM, Schizas A, Forbes A, Denton CP, Emmanuel AV. Internal anal sphincter atrophy in patients with systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011;50(9):1596–602.
Heyt GJ, Oh MK, Alemzadeh N, Rivera S, Jimenez SA, Rattan S, et al. Impaired rectoanal inhibitory response in scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): an association with fecal incontinence. Dig Dis Sci. 2004;49(6):1040–5.
Thoua NM, Abdel-Halin M, Forbes A, et al. Fecal incontinence in systemic sclerosis is secondary to neuropathy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107(4):597–603.
Luciano L, Granel B, Bernit E, et al. Esophageal and anorectal involvement in systemic sclerosis: a systematic assessment with high resolution manometry. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016;34 Suppl 100(5):63–9.
Kumar S, Singh J, Rattan S, DiMarino AJ, Cohen S, Jimenez SA. Review article: pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of gastrointestinal involvement in systemic sclerosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;45(7):883–98.
Pinsk I, Brown J, Phang PT. Assessment of sonographic quality of anal sphincter muscles in patients with faecal incontinence. Color Dis. 2009;11(9):933–40.
• Collins J, Mazor Y, Jones M, et al. Efficacy of anorectal biofeedback in scleroderma patients with fecal incontinence: a case-control study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2016;51(12):1433–8. Pivotal study supporting the use of biofeedback for fecal incontinence in systemic sclerosis patients.
Kenefick NJ, Vaizey CJ, Nicholls RJ, Cohen R, Kamm MA. Sacral nerve stimulation for faecal incontinence due to systemic sclerosis. Gut. 2002;51(6):881–3.
Butt SK, Alam A, Cohen R, Krogh K, Buntzen S, Emmanuel A. Lack of effect of sacral nerve stimulation for incontinence in patients with systemic sclerosis. Color Dis. 2015;17(10):903–7.
Petersen S, Tobisch A, Puhl G, et al. Stubborn rectal prolapse in systemic sclerosis. Reumatologia. 2017;55(2):100–3.
Leighton JA, Valdovinos MA, Pemberton JH, Rath DM, Camilleri M. Anorectal dysfunction and rectal prolapse in progressive systemic sclerosis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1993;36(2):182–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Large Intestine
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sattar, B., Chokshi, R.V. Colonic and Anorectal Manifestations of Systemic Sclerosis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 21, 33 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-019-0699-0
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-019-0699-0