Abstract
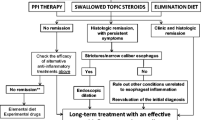
A number of recent studies have demonstrated that a variety of treatments effectively improve symptoms and histology in the majority of patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Therapeutic options include pharmacologic treatments, such as oral and topical corticosteroids and leukotriene-receptor antagonists. In children, the high response rates to dietary modification and elimination suggest that certain foods may serve as environmental triggers for the eosinophilic infiltration. Because many adults present with strictures, endoscopic esophageal dilation is another management modality. Despite these treatment options, several controversies exist in the recommended treatment strategy. Whether the goal of therapy is resolution of symptoms, tissue eosinophilia, or both remains uncertain owing to the paucity of data on the natural history of the condition. Furthermore, important differences in the clinical presentations of eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults point toward the possible need for different treatment approaches in the two patient populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Liacouras CA, Wenner WJ, Brown K, Ruchelli E: Primary eosinophilic esophagitis in children: successful treatment with oral corticosteroids. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1998, 26:380–385.
Liacouras CA, Spergel JM, Ruchelli E, et al.: Eosinophilic esophagitis: a 10-year experience in 381 children. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005, 3:1198–1206.
Spergel JM, Beausoleil JL, Mascarenhas M, et al.: The use of skin prick tests and patch tests to identify causative foods in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002, 109:363–368.
Gonsalves N, Policarpio-Nicolas M, Zhang Q, et al.: Histopathologic variability and endoscopic correlates in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc 2006, 64:313–319.
Attwood S, Smyrk T, Demeester T, et al.: Esophageal eosinophilia with dysphagia. Dig Dis Sci 1993, 38:109–116.
Desai TK, Stecevic V, Chang CH: Association of eosinophilic inflammation with esophageal food impaction in adults. Gastrointest Endosc 2005, 61:795–801.
Liacouras CA: Eosinophilic esophagitis: treatment in 2005. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2006, 22:147–152.
Patel SM, Falchuk KR: Three brothers with dysphagia caused by eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc 2005, 61:165–167.
Remedios M, Campbell C, Jones D, et al.: Eosinophilic Esophagitis in adults: clinical, endoscopic, histologic findings, and response to fluticasone propionate. Gastrointest Endosc 2006, 63:3–12.
Sundaram S, Sunku B, Nelson SP, et al.: Adherent white plaques: an endoscopic finding in eosinophilic esophagitis. Journal of Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2004, 38:208–212.
Straumann A, Spichtin H-P, Grize L, et al.: Natural history of primary eosinophilic esophagitis: a follow-up of 30 adult patients for up to 11.5 years. Gastroenterology 2003, 125:1660–1669.
Straumann A, Rossi L, Simon HU, et al.: Fragility of the esophageal mucosa: a pathognomonic endoscopic sign of primary eosinophilic esophagitis? Gastrointest Endosc 1994, 124:1419–1429.
Fogg MI, Ruchelli E, Spergel J: Pollen and eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003, 112:796–797.
Konikoff MR, Noel RJ, Blanchard C, et al.: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of fluticasone propionate for pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2006, 131:1381–1391.
Stevoff C, Rao S, Parsons W, et al.: EUS and histopathologic correlates in eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc 2001, 54:373–377.
Fox V, Nurko S, Teitelbaum J, et al.: High-resolution EUS in children with eosinophilic “allergic” esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc 2003, 57:30–36.
Ngo P, Furuta GT, Antonioli DA, et al.: Eosinophils in the esophagus—peptic or allergic eosinophilic esophagitis? Case series of three patients with esophageal eosinophilia. Am J Gastroenterol 2006, 101:1666–1670.
Morrow JB, Vargo JJ, Goldblum Jr, et al.: The ringed esophagus: histologic features of GERD. Am J Gastroenterol 2001, 96:984–989.
Baxi S, Gupta S, Swigonski N, et al.: Clinical presentation of patients with eosinophilic inflammation of the esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2006, 64:473–478
Faubion WA Jr, Perrault J, Bergart LJ, et al.: Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with inhaled corticosteroids. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1998, 27:90–93.
Teitelbaum JE, Fox VL, Twarog FJ, et al.: Eosinophilic esophagitis in children: immunopathological analysis and response to fluticasone propionate. Gastroenterology 2002, 122:1216–1225.
Noel RJ, Putnam PE, Collins MH, et al.: Clinical and immunopathologic effects of swallowed fluticasone for eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004, 2:568–575.
Arora AS, Perrault J, Smyrk TC: Topical corticosteroid treatment of dysphagia due to eosinophilic esophagitis in adults. Mayo Clin Proc 2003, 78:830–835.
Aceves SS, Dohil R, Newbury RO, Bastian JF: Topical viscous budesonide suspension for treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005, 116:705–706.
Shuto J, Nagata M, Terashi Y, et al.: Esophageal candidiasis as a complication of inhaled steroid therapy. Arerugi 2003, 52:1053–1064.
Fukishima C, Matsuse H, Tomari S, et al.: Oral candidiasis associated with inhaled corticosteroid use: comparison of fluticasone and beclamethasone. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2003, 90:646–651.
Attwood SE, Lewis CJ, Bronder CS, et al.: Eosinophilic oesophagitis: a novel treatment using Montelukast. Gut 2003, 52:181–185.
Kaplan M, Mutlu EA, Jakate S, et al.: Endoscopy in eosinophilic esophagitis: “feline” esophagus and perforation risk. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2003, 1:433–437.
Cuss FM: Beyond the histamine receptor: effect of antihistamines on mast cells. Clin Exper Allergy 1999, 29(Suppl 3):54–59.
Volonakis M, Katsarou-Katsari A, Stratigos J: Etiologic factors in childhood chronic urticaria. Ann Allergy 1992, 69:61–65.
Sedgwick JB, Busse W: Inhibitory effect of cetirizine on cytokine-enhanced in vitro eosinophil survival. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 1997, 78:581–585.
Kelly KJ, Lazenby AJ, Rowe PC, et al.: Eosinophilic esophagitis attributed to gastroesophageal reflux: improvement with amino acid-based formula. Gastroenterology 1995, 109:1503–1512.
Markowitz JE, Spergel JM, Ruchelli E, et al.: Elemental diet is an effective treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adolescents. Am J Gastroenterol 2003, 98:777–782.
Kagalwalla A, Sentongo TA, Ritz S, et al.: Effect of six-food elimination diet on clinical and histologic outcomes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006, 4:1097–1102.
Spergel JM, Andrews T, Brown-Whitehorn TF, et al.: Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with specific food elimination diet directed by a combination of skin prick and patch tests. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2005, 95:336–343.
Assa’ad A: Detection of causative foods by skin prick and atopy patch tests in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis: things are not what they seem. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2005, 95:309–311.
Potter JW, Saeian K, Staff D, et al.: Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: an emerging problem with unique esophageal features. Gastroint Endosc 2004, 59:355–361.
Gonsalves N, Kirmali K, Hirano I: Safety and response of esophageal dilation in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis (EE): A single center experience of 81 patients [abstract]. Gastroenterology 2007, in press.
Garrett J, Jameson S, Thomson B, et al.: Anti-interleukin-5 (mepolizumab) therapy for hypereosinophilic syndromes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004, 113:115–119.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, A., Hirano, I. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis: Drugs, diet, or dilation?. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 9, 181–188 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-007-0016-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-007-0016-1