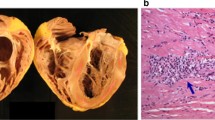
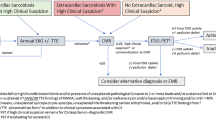
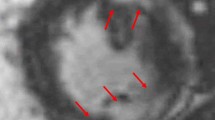
Abstract
Purpose of Review
In this state-of-the-art review, we highlight our current understanding of diagnosis, assessment, and management of cardiac sarcoidosis (CS), focusing on recently published data and expert consensus statement guidelines.
Recent Findings
Academic interest in cardiac sarcoidosis research has increased over the past decade along with increased clinical awareness among clinicians. In 2014, the Heart Rhythm Society published the first expert consensus statement on diagnosing and managing arrhythmias associated with CS. Cardiac magnetic resonance has emerged as a valuable tool both for diagnosing CS and predicting risk of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias based on burden of late gadolinium enhancement. Cardiac fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography now plays a role in diagnosis, risk stratification, and assessing response to immunosuppressive therapy.
Summary
Collaborative, multidisciplinary research efforts are needed to further our understanding of this rare, complex disease. Two large multicenter prospective registries—the international Cardiac Sarcoidosis Consortium and the Canadian Cardiac Sarcoidosis Research Group—are enrolling patients to help provide insights into the natural history of the disease and current treatment strategies. Future research should focus on randomized controlled trials comparing different treatment strategies and identifying and testing novel therapeutic agents.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Valeyre D, Prasse A, Nunes H, Uzunhan Y, Brillet P-Y, Müller-Quernheim J. Sarcoidosis. Lancet. 2014;383:1155–67.
•• Birnie DH, Sauer WH, Bogun F, et al. HRS expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of arrhythmias associated with cardiac sarcoidosis. Heart Rhythm. 2014;11:1304–23 First published expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of arrhythmias in cardiac sarcoidosis. Includes guidelines on screening and diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis.
Silverman KJ, Hutchins GM, Bulkley BH. Cardiac sarcoid: a clinicopathologic study of 84 unselected patients with systemic sarcoidosis. Circulation. 1978;58:1204–11.
Kim JS, Judson MA, Donnino R, Gold M, Cooper LT, Prystowsky EN, et al. Cardiac sarcoidosis. Am Heart J. 2009;157:9–21.
•• Terasaki F, Yoshinaga K. New guidelines for diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis in Japan. Ann Nucl Cardiol. 2017;3:42–5 First set of guidelines that include criteria to diagnose isolated cardiac sarcoidosis.
Kouranos V, Tzelepis GE, Rapti A, et al. Complementary role of CMR to conventional screening in the diagnosis and prognosis of cardiac sarcoidosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017;10:1437–47.
Hulten E, Agarwal V, Cahill M, et al. Presence of late gadolinium enhancement by cardiac magnetic resonance among patients with suspected cardiac sarcoidosis is associated with adverse cardiovascular prognosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016;9:1–9.
Murtagh G, Laffin LJ, Beshai JF, et al. Prognosis of myocardial damage in sarcoidosis patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction: risk stratification using cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.115.003738.
Coleman GC, Shaw PW, Balfour PC, Gonzalez JA, Kramer CM, Patel AR, et al. Prognostic value of myocardial scarring on CMR in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 10(4):411–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2016.05.009.
Puntmann VO, Isted A, Hinojar R, Foote L, Carr-White G, Nagel E. T1 and T2 mapping in recognition of early cardiac involvement in systemic sarcoidosis. Radiology. 2017;285:63–72.
Kim SJ, Pak K, Kim K. Diagnostic performance of F-18 FDG PET for detection of cardiac sarcoidosis; a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nucl Cardiol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-018-01582-y.
Blankstein R, Osborne M, Naya M, et al. Cardiac positron emission tomography enhances prognostic assessments of patients with suspected cardiac sarcoidosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:329–36.
Sperry BW, Tamarappoo BK, Oldan JD, Javed O, Culver DA, Brunken R, et al. Prognostic impact of extent, severity, and heterogeneity of abnormalities on 18F-FDG PET scans for suspected cardiac sarcoidosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;11:336–45.
Vita T, Okada DR, Veillet-Chowdhury M, et al. Complementary value of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography/computed tomography in the assessment of cardiac sarcoidosis. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;11:e007030.
Slart RHJA, Glaudemans AWJM, Lancellotti P, et al. A joint procedural position statement on imaging in cardiac sarcoidosis: from the Cardiovascular and Inflammation & Infection Committees of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine, the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging, and the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017;18:1073–89.
Wicks EC, Menezes LJ, Barnes A, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic value of simultaneous hybrid 18 F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging in cardiac sarcoidosis. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;19:757–67.
Kiko T, Yoshihisa A, Kanno Y, et al. A multiple biomarker approach in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis. Int Heart J. 2018;59:996–1001.
Fujiwara W, Kato Y, Hayashi M, et al. Serum microRNA-126 and -223 as new-generation biomarkers for sarcoidosis in patients with heart failure. J Cardiol. 2018;72:452–7.
Mankad P, Syed H, Syed A et al. C-reactive protein is elevated in sarcoidosis patients with ventricular tachycardia and heart failure. Hear. Rhythm Soc. 2019 Abstr.
Liang JJ, Hebl VB, DeSimone CV, et al. Electrogram guidance: a method to increase the precision and diagnosticyieldofendomyocardial biopsy for suspectedcardiac sarcoidosisand myocarditis. JACC Hear Fail. 2014;2:466–73.
Segawa M, Fukuda K, Nakano M, Kondo M, Satake H, Hirano M, et al. Time course and factors correlating with ventricular tachyarrhythmias after introduction of steroid therapy in cardiac sarcoidosis. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2016;9:1–9.
Nagai S, Yokomatsu T, Tanizawa K, Ikezoe K, Handa T, Ito Y, et al. Treatment with methotrexate and low-dose corticosteroids in sarcoidosis patients with cardiac lesions. Intern Med. 2014;53:427–33.
Birnie DH, Nery PB, Ha AC, Beanlands RSB. Cardiac Sarcoidosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:411–21.
Kron J, Chicos A, Bogun F et al (2017) Treatment of cardiac sarcoidosis with steroids and steroid-sparing immunosuppressants: findings from the Cardiac Sarcoidosis Consortium. Hear. Rhythm Soc. 2017 Abstr.
Sadek MM, Yung D, Birnie DH, Beanlands RS, Nery PB. Corticosteroid therapy for cardiac sarcoidosis: a systematic review. Can J Cardiol. 2013;29:1034–41.
Okada DR, Smith J, Derakhshan A, Gowani Z, Misra S, Berger RD, et al. Ventricular arrhythmias in cardiac sarcoidosis. Circulation. 2018;138:1253–64.
Papageorgiou N, Providência R, Bronis K, Dechering DG, Srinivasan N, Eckardt L, et al. Catheter ablation for ventricular tachycardia in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis: a systematic review. Europace. 2018;20:682–91.
Al-Khatib SM, Stevenson WG, Ackerman MJ, et al. 2017 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Heart Rhythm. 2018;15:e73–e189.
Naruse Y, Sekiguchi Y, Nogami A, et al. Systematic treatment approach to ventricular tachycardia in cardiac sarcoidosis. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2014;7:407–13.
Muser D, Santangeli P, Pathak RK, et al. Long-term outcomes of catheter ablation of ventricular tachycardia in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2016;9:1–13.
• Yalagudri S, Zin Thu N, Devidutta S, Saggu D, Thachil A, Chennapragada S, et al. Tailored approach for management of ventricular tachycardia in cardiac sarcoidosis. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2017;28:893–902 Characterization of underlying disease in cardiac sarcoidosis via PET-CT and tailoring management of VT accordingly can help improve clinical outcomes.
Kron J, Sauer W, Schuller J, et al. Efficacy and safety of implantable cardiac defibrillators for treatment of ventricular arrhythmias in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis. EP Eur. 2013;15:347–54.
Schuller JL, Zipse M, Crawford T, et al. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2012;23:925–9.
Betensky BP, Tschabrunn CM, Zado ES, Goldberg LR, Marchlinski FE, Garcia FC, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with cardiac sarcoidosis and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators. Heart Rhythm. 2012;9:884–91.
• Nordenswan HK, Lehtonen J, Ekström K, et al. Outcome of cardiac sarcoidosis presenting with high-grade atrioventricular block. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2018;11:e006145 Findings from this study provide further support for the Heart Rhythm Expert Consensus recommendation to implant intracardiac cardioverter defibrillator for cardiac sarcoidosis patient when permanent pacing is needed.
Kusumoto FM, Schoenfeld MH, Barrett C, et al. 2018 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline on the evaluation and management of patients with bradycardia and cardiac conduction delay. Circulation. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1161/cir.0000000000000628.
Aizer A, Stern EH, Gomes JA, Teirstein AS, Eckart RE, Mehta D. Usefulness of programmed ventricular stimulation in predicting future arrhythmic events in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96:276–82.
Zipse M, Tzou W, Schuller J et al (2019) Electrophysiologic testing for diagnostic evaluation and risk stratification in patients with suspected cardiac sarcoidosis with preserved left and right ventricular systolic function. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol In Press:
Smedema JP, van Geuns RJ, Ector J, Heidbuchel H, Ainslie G, Crijns HJGM. Right ventricular involvement and the extent of left ventricular enhancement with magnetic resonance predict adverse outcome in pulmonary sarcoidosis. ESC Hear Fail. 2018;5:157–71.
Juneau D, Nery P, Russo J, de Kemp RA, Leung E, Beanlands RSB, et al. How common is isolated cardiac sarcoidosis? Extra-cardiac and cardiac findings on clinical examination and whole-body 18F–fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Int J Cardiol. 2018;253:189–93.
Adamson P, Melton I, O’Donnell J, MacDonald S, Crozier I. Cardiac sarcoidosis: the Christchurch experience. Intern Med J. 2014;44:70–6.
Judson MA. Screening sarcoidosis patients for cardiac sarcoidosis: what the data really show. Respir Med. 2019;154:155–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Pranav Mankad, Brian Mitchell, David Birnie, and Jordana Kron declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Myocardial Disease
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mankad, P., Mitchell, B., Birnie, D. et al. Cardiac Sarcoidosis. Curr Cardiol Rep 21, 152 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-019-1238-1
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-019-1238-1