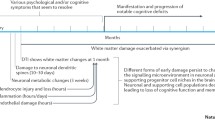
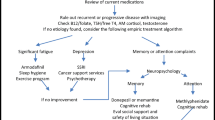
Opinion statement
Radiation-induced cognitive decline in cancer survivors who have received brain radiotherapy is an insidious problem with worsening severity over time. Because of improved survival with modern therapies, an increasing number of long term survivors are affected with limited options for treatment once diagnosed. Recently there has been enthusiasm for evaluating new approaches to prevent the onset of radiation-induced cognitive decline. Clinical trials have assessed the role of pharmaceuticals such as memantine and donepezil in ameliorating the cognitive effects of brain irradiation. Radiosurgery, when clinically appropriate, allows for the avoidance or postponement of whole brain radiotherapy in some patients with brain metastases. Hippocampal-sparing intensity modulated radiotherapy has been proposed as a means of avoiding damage to regions of adult neurogenesis. Finally, cytoprotective agents are being investigated that target the molecular pathways that lead to brain injury and the resultant cognitive decline.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Greene-Schloesser D, Robbins ME, Peiffer AM, Shaw EG, Wheeler KT, Chan MD. Radiation-induced brain injury: a review. Front Oncol. 2012;2:73.
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–96.
Shaw EG, Wang M, Coons SW, Brachman DG, Buckner JC, Stelzer KJ, et al. Randomized trial of radiation therapy plus procarbazine, lomustine, and vincristine chemotherapy for supratentorial adult low-grade glioma: initial results of RTOG 9802. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:3065–70.
Vern-Gross TZ, Lawrence JA, Case LD, McMullen KP, Bourland JD, Metheny-Barlow LJ, et al. Breast cancer subtype affects patterns of failure of brain metastases after treatment with stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurooncol. 2012;110:381–8.
Cochran DC, Chan MD, Aklilu M, Lovato JF, Alphonse NK, Bourland JD, et al. The effect of targeted agents on outcomes in patients with brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma treated with Gamma Knife surgery. J Neurosurg. 2012;116:978–83.
Pearson BE, Markert JM, Fisher WS, Guthrie BL, Fiveash JB, Palmer CA, et al. Hitting a moving target: evolution of a treatment paradigm for atypical meningiomas amid changing diagnostic criteria. Neurosurg Focus. 2008;24:E3.
Auperin A, Arriagada R, Pignon JP, Le Pechoux C, Gregor A, Stephens RJ, et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer in complete remission. Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Overview Collaborative Group. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:476–84.
Ahles TA, Silberfarb PM, Herndon II J, Maurer LH, Kornblith AB, Aisner J, et al. Psychologic and neuropsychologic functioning of patients with limited small-cell lung cancer treated with chemotherapy and radiation therapy with or without warfarin: a study by the Cancer and Leukemia Group B. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:1954–60.
Johnson BE, Patronas N, Hayes W, Grayson J, Becker B, Gnepp D, et al. Neurologic, computed cranial tomographic, and magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities in patients with small-cell lung cancer: further follow-up of 6- to 13-year survivors. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8:48–56.
Meyers CA, Brown PD. Role and relevance of neurocognitive assessment in clinical trials of patients with CNS tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1305–9.
Lee PW, Hung BK, Woo EK, Tai PT, Choi DT. Effects of radiation therapy on neuropsychological functioning in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989;52:488–92.
Robbins ME, Zhao W. Chronic oxidative stress and radiation-induced late normal tissue injury: a review. Int J Radiat Biol. 2004;80:251–9.
Clarke DD, Sokoloff L. Circulation and energy metabolism of the brain. Basic neurochemistry: molecular, cellular, and medical aspects. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven; p. 637–69.
Wink DA, Mitchell JB. Chemical biology of nitric oxide: insights into regulatory, cytotoxic, and cytoprotective mechanisms of nitric oxide. Free Radic Biol Med. 1998;25:434–56.
Peiffer AM, Leyrer CM, Greene-Schloesser DM, Shing E, Kearns WT, Hinson WH, et al. Neuroanatomical target theory as a predictive model for radiation-induced cognitive decline. Neurology. 2013;80:747–53. This important analysis of several prospective CCOP studies suggests that postradiotherapy cognition is dependent upon the dose delivered to volumes of radiation in the brain, and that dose volume histogram analysis may ultimately be able to predict radiation-induced cognitive decline.
Gondi V, Hermann BP, Mehta MP, Tome WA. Hippocampal dosimetry predicts neurocognitive function impairment after fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for benign or low-grade adult brain tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;85:348–54. This analysis suggests that the hippocampi are a target of radiation-induced cognitive decline and suggests that the hippocampal threshold for cognitive changes may be on the order of 7 Gy.
Tofilon PJ, Fike JR. The radioresponse of the central nervous system: a dynamic process. Radiat Res. 2000;153:357–70.
Schultheiss TE, Stephens LC. Invited review: permanent radiation myelopathy. Br J Radiol. 1992;65:737–53.
DeAngelis LM, Delattre JY, Posner JB. Radiation-induced dementia in patients cured of brain metastases. Neurology. 1989;39:789–96.
DeAngelis LM, Seiferheld W, Schold SC, Fisher B, Schultz CJ. Combination chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary central nervous system lymphoma: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Study 93-10. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:4643–8.
Shaw EG, Rosdhal R, D'Agostino Jr RB, Lovato J, Naughton MJ, Robbins ME, et al. Phase II study of donepezil in irradiated brain tumor patients: effect on cognitive function, mood, and quality of life. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1415–20.
Rapp SR, Case D, Peiffer AM, Naughton MJ, Stieber VW, GK B. Phase III Randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial of donepezil in irradiated brain tumor survivors. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2006 [Abstract]. This randomized phase II study presented at ASCO 2013 suggests that the population of patients with worse post-radiotherapy cognition is the population most likely to benefit from donepezil after development of radiation-induced cognitive changes.
Danysz W, Parsons CG, Karcz-Kubicha M, Schwaier A, Popik P, Wedzony K, et al. GlycineB antagonists as potential therapeutic agents. Previous hopes and present reality. Amino Acids. 1998;14:235–9.
Brown PD, Pugh S, Laack NN, Wefel JS, Khuntia D, Meyers C, et al. Memantine for the prevention of cognitive dysfunction in patients receiving whole-brain radiotherapy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neuro-Oncology. 2013;15:1429–37. This seminal randomized phase III study conducted by the RTOG found that patients treated with memantine experienced less radiation-induced memory changes compared with placebo.
DeLong R, Friedman H, Friedman N, Gustafson K, Oakes J. Methylphenidate in neuropsychological sequelae of radiotherapy and chemotherapy of childhood brain tumors and leukemia. J Child Neurol. 1992;7:462–3.
Weitzner MA, Meyers CA, Valentine AD. Methylphenidate in the treatment of neurobehavioral slowing associated with cancer and cancer treatment. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1995;7:347–50.
Meyers CA, Weitzner MA, Valentine AD, Levin VA. Methylphenidate therapy improves cognition, mood, and function of brain tumor patients. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:2522–7.
Butler Jr JM, Case LD, Atkins J, Frizzell B, Sanders G, Griffin P, et al. A phase III, double-blind, placebo-controlled prospective randomized clinical trial of d-threo-methylphenidate HCl in brain tumor patients receiving radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;69:1496–501.
Cott J. NCDEU update. Natural product formulations available in Europe for psychotropic indications. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1995;31:745–51.
Attia A, Rapp SR, Case LD, D'Agostino R, Lesser G, Naughton M, et al. Phase II study of Ginkgo biloba in irradiated brain tumor patients: effect on cognitive function, quality of life, and mood. J Neurooncol. 2012;109:357–63.
Lee EQ, Muzikansky A, Kesari S, Wong ET, Fadul CE, Norden AD, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled pilot trial of armodafinil for fatigue in patients with gliomas undergoing radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:2004. [Abstract].
Shaw EG, Case D, Bryant D, Grisell D, Lesser GJ, Monitto DC, et al. Phase II double-blind placebo-controlled study of armodafinil for brain radiation induced fatigue. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:9505. [Abstract].
Klein M, Heimans JJ, Aaronson NK, van der Ploeg HM, Grit J, Muller M, et al. Effect of radiotherapy and other treatment-related factors on mid-term to long-term cognitive sequelae in low-grade gliomas: a comparative study. Lancet. 2002;360:1361–8.
Tsao MN, Lloyd N, Wong RK, Chow E, Rakovitch E, Laperriere N, et al. Whole brain radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed multiple brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;4, CD003869.
Le Pechoux C, Dunant A, Senan S, Wolfson A, Quoix E, Faivre-Finn C, et al. Standard-dose vs higher-dose prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) in patients with limited-stage small-cell lung cancer in complete remission after chemotherapy and thoracic radiotherapy (PCI 99-01, EORTC 22003-08004, RTOG 0212, and IFCT 99-01): a randomised clinical trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:467–74. This prospective randomized study of 2 fractionation regimens of whole brain radiotherapy demonstrated that total dose of radiation to the brain was predictive of late cognitive toxicity.
Wolfson AH, Bae K, Komaki R, Meyers C, Movsas B, Le Pechoux C, et al. Primary analysis of a phase II randomized trial Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 0212: impact of different total doses and schedules of prophylactic cranial irradiation on chronic neurotoxicity and quality of life for patients with limited-disease small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81:77–84.
Torres IJ, Mundt AJ, Sweeney PJ, Llanes-Macy S, Dunaway L, Castillo M, et al. A longitudinal neuropsychological study of partial brain radiation in adults with brain tumors. Neurology. 2003;60:1113–8.
Merchant TE, Mulhern RK, Krasin MJ, Kun LE, Williams T, Li C, et al. Preliminary results from a phase II trial of conformal radiation therapy and evaluation of radiation-related CNS effects for pediatric patients with localized ependymoma. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3156–62.
MacDonald SM, Safai S, Trofimov A, Wolfgang J, Fullerton B, Yeap BY, et al. Proton radiotherapy for childhood ependymoma: initial clinical outcomes and dose comparisons. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;71:979–86.
McAllister B, Archambeau JO, Nguyen MC, Slater JD, Loredo L, Schulte R, et al. Proton therapy for pediatric cranial tumors: preliminary report on treatment and disease-related morbidities. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;39:455–60.
Steinvorth S, Wenz F, Wildermuth S, Essig M, Fuss M, Lohr F, et al. Cognitive function in patients with cerebral arteriovenous malformations after radiosurgery: prospective long-term follow-up. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;54:1430–7.
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG, et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:1037–44.
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T, Akabane A, Higuchi Y, Kawagishi J, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:387–95. This prospective single arm multi-institutional study demonstrated that radiosurgery can be safely and effectively performed on patients with between four and ten metastases, and that neurocognition remains stable with radiosurgery.
Ayala-Peacock DN, Peiffer AM, Lucas JT, Isom S, Kuremsky JG, Urbanic JJ, et al. A nomogram for predicting distant brain failure in patients treated with gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery without whole brain radiotherapy. Neuro Oncol. 2014.
Raber J, Rola R, LeFevour A, Morhardt D, Curley J, Mizumatsu S, et al. Radiation-induced cognitive impairments are associated with changes in indicators of hippocampal neurogenesis. Radiat Res. 2004;162:39–47.
Rola R, Raber J, Rizk A, Otsuka S, VandenBerg SR, Morhardt DR, et al. Radiation-induced impairment of hippocampal neurogenesis is associated with cognitive deficits in young mice. Exp Neurol. 2004;188:316–30.
Cheung M, Chan AS, Law SC, Chan JH, Tse VK. Cognitive function of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma with and without temporal lobe radionecrosis. Arch Neurol. 2000;57:1347–52.
Gondi V, Mehta MP, Pugh S, Tome WA, Kanner A, Caine C, et al. Memory preservation with conformal avoidance of the hippocampus during whole-brain radiation therapy for patients with brain metastases: primary endpoint results of RTOG 0933. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;87:1186.
Matthews DR, Charbonnel BH, Hanefeld M, Brunetti P, Schernthaner G. Long-term therapy with addition of pioglitazone to metformin compared with the addition of gliclazide to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, comparative study. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2005;21:167–74.
Zhao W, Payne V, Tommasi E, Diz DI, Hsu FC, Robbins ME. Administration of the peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist pioglitazone during fractionated brain irradiation prevents radiation-induced cognitive impairment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67:6–9.
Greene-Schloesser D, Payne V, Peiffer AM, Hsu FC, Riddle DR, Zhao W, et al. The peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha agonist, fenofibrate, prevents fractionated whole-brain irradiation-induced cognitive impairment. Radiat Res. 2014;181:33–44.
Panigrahy D, Kaipainen A, Huang S, Butterfield CE, Barnes CM, Fannon M, et al. PPARalpha agonist fenofibrate suppresses tumor growth through direct and indirect angiogenesis inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:985–90.
Choudhary R, Li H, Winn RA, Sorenson AL, Weiser-Evans MC, Nemenoff RA. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma inhibits transformed growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells through selective suppression of Snail. Neoplasia. 2010;12:224–34.
Blume A, Herdegen T, Unger T. Angiotensin peptides and inducible transcription factors. J Mol Med (Berl). 1999;77:339–57.
von Bohlen und Halbach O, Albrecht D. The CNS renin-angiotensin system. Cell Tissue Res. 2006;326:599–616.
Jenrow KA, Brown SL, Liu J, Kolozsvary A, Lapanowski K, Kim JH. Ramipril mitigates radiation-induced impairment of neurogenesis in the rat dentate gyrus. Radiat Oncol. 2011;5:6.
Wong-Goodrich SJ, Pfau ML, Flores CT, Fraser JA, Williams CL, Jones LW. Voluntary running prevents progressive memory decline and increases adult hippocampal neurogenesis and growth factor expression after whole-brain irradiation. Cancer Res. 2010;70:9329–38.
Ji JF, Ji SJ, Sun R, Li K, Zhang Y, Zhang LY, et al. Forced running exercise attenuates hippocampal neurogenesis impairment and the neurocognitive deficits induced by whole-brain irradiation via the BDNF-mediated pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;443:646–51.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Glenn Lesser received speaker’s fees from Merck, research support for clinical trials from EMD Serono, Immunocellular Therapeutics, and from Celldex, and is the DSMB Chairman for Stemline, and Abbvie. Albert Attia, Brandi R. Page, and Michael Chan declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attia, A., Page, B.R., Lesser, G.J. et al. Treatment of Radiation-Induced Cognitive Decline. Curr. Treat. Options in Oncol. 15, 539–550 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-014-0307-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-014-0307-3