Abstract
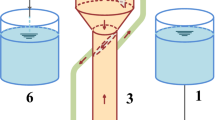
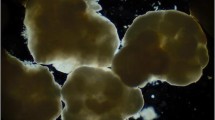
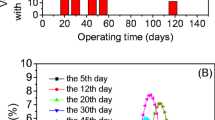
An expanded granular sludge bed (EGSB) reactor was adopted to study the influence factors and rule of enhancing granular sludge concentration and performance. The experiment was performed at 33 °C, pH 6.0–8.0 with continuous flow by adding proper quantity of nutritional trace elements. The results show that SLR was the key of steady operation of EGSB reactor. The increment of the granular sludge was influenced by volume loading rate (VLR), liquid up-flow velocity and sludge loading rate (SLR). Concentration of granular sludge increased rapidly when liquid up-flow velocity was over 0.94 m · h−1 with SLR being at 1.0–2.0 d−1. With the propriety parameters: liquid up-flow velocity 2.52 m · h−1, SLR 1.0–2.2 d−1 and VLR 8.2–13.1 kg · m−3 · d−1, 23 days’ continuous operation resulted in an increment by over 80% of granular sludge concentration in the EGSB reactor, plus good granular sludge property.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lettinga G, Nelsen V, Hobma A F M, et al. Use of the Up-flow Sludge Blanket (UASB) Reactor Concept for Biological Wastewater Treatment, Especially for Anaerobic Treatment [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 1980, 22:699–734.
Jeison D, Chamy R. Comparison of the Behavior of Expanded Granular Sludge Bed (EGSB) and Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Reactors in Dilute and Concentrated [J]. Water Science Technology, 1999, 40(8):91–97.
Hu Jichui. Theory and Technology of Anaerobic Bio-treatment Wastewater [M]. Beijing: Architectural Industry Publish of China, 2003 (Ch).
He Yanling. Anaerobic Bio-Treatment of Wastewater [M]. Beijing: Light Industry Publish of China, 1998 (Ch).
Nunez L A, Martinez B. Anaerobic Treatment of Slaughterhouse Wastewater in an Expanded Granular Sludge Bed (EGSB) Reactor [J]. Water Science Technology, 1999, 40(8): 99–106.
Zoutberg G R, Frankin R. Anaerobic Treatment of Chemical and Brewery Wastewater with a New Type of Anaerobic Reactor: the Bio-Bed EGSB Reactor [J]. Water Science Technology, 1996, 34(5–6):375–381.
Zoutberg G R, Eker Z. Anaerobic Treatment of Potato Processing Wastewater [J]. Water Science Technology, 1999, 40(1):297–304.
Zuo Jiane, Wang Yanchun, Chen Hao. Experimental Study on Treating High Concentration Wastewater of EGSB Reactor [J]. Marsh Gas of China, 2001, 19(2):8–11 (Ch).
National Environmental Protecting Bureau. Detecting and Analyzing Method of Water and Wastewater [M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Environmental Science Publish of China, 1997:233–237 (Ch).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by Key Project of the Tenth Five-Year Plan of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (02-2-2)
Biography: LI Huili (1970–), female, Ph.D. candidate, research direction: controlling water pollution.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Lü, B., Wang, D. et al. Optimizing conditions of enhancing granule sludge concentration and performance. Wuhan Univ. J. of Nat. Sci. 12, 548–552 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-006-0079-0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-006-0079-0
Key words
- expanded granular sludge bed (EGSB) reactor
- granular sludge
- volume loading rate (VLR)
- Liquid up-flow velocity
- sludge loading rate (SLR)