Abstract
Introduction
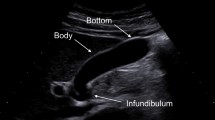
Cholecystectomy for symptomatic cholecystitis is one of the common surgical procedures in the geriatric patients. Increased gallbladder wall thickness is expected due to acute cholecystitis and in some other clinical conditions. Routine histopathological evaluation of cholecystectomy materials are required to confirm the diagnosis and document other pathologies. The aim of this study was to evaluate age-related histopathological gallbladder morphometric measurements.
Methods
A retrospective chart review of 371 cholecystectomy materials was performed. Two groups were designed according to age (<65 and ≥65 years old, respectively). Age and gender analyses for histopathological gallbladder length, diameter and wall thickness were performed. In addition, pathologically confirmed acute inflammation rates were evaluated in this case–control study.
Results
Gallbladder morphometric measurements and pathologically confirmed acute inflammation rates were similar in males and females. Histopathological gallbladder diameter was higher with acute inflammatory changes, but no differences were observed in gallbladder length and wall thickness. Gallbladder wall thickness and pathologically confirmed acute inflammation rates were not comparable between the control and geriatric patients (2.8 ± 1.3 vs 2.6 ± 1.2 mm, and 30/281 (10.7 %) vs 10/74 (13.5 %), respectively, p > 0.05). However, higher gallbladder length and diameter were observed in geriatric group.
Conclusion
Age is an independent factor on histopathological gallbladder length and diameter, but not for gallbladder wall thickness. In addition, pathologically confirmed acute inflammation rate is not higher in geriatric patients. Clinical significance of these findings merits further investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ozkan E, Fersahoğlu MM, Dulundu E et al (2010) Factors affecting mortality and morbidity in emergency abdominal surgery in geriatric patients. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 16(5):439–444
Kauvar DS, Brown BD, Braswell AW et al (2005) Laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the elderly: increased operative complications and conversions to laparotomy. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 15(4):379–382
Agrusa A, Romano G, Frazzetta G et al (2014) Role and outcomes of laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the elderly. Int J Surg. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.08.385
Pérez-Hernández JL, Teuffer-Carrion LT, Díaz-Aldana EV et al (2010) Acute abdominal pain in elderly patients evaluated in the emergency department at a tertiary level. Rev Gastroenterol Mex 75(3):261–266
Yetim I, Dervisoglu A, Karaköse O et al (2010) Is advanced age a significant risk factor for laparoscopic cholecystectomy? Minerva Chir 65(5):507–513
Sánchez-Beorlegui J, Soriano P, Monsalve E et al (2009) Laparoscopic cholecystectomy in octogenarian patients: a comparative study between two geriatric population groups. Cir Esp 85(4):246–251. doi:10.1016/j.ciresp.2008.11.001
Leshchenko IG, Aleksandrov IK, Krechko NA (2007) Elective combined operations—the new problem of geriatric surgery. Khirurgiia (Mosk). 4:28–31
Raman SR, Moradi D, Samaan BM et al (2012) The degree of gallbladder wall thickness and its impact on outcomes after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg Endosc 26(11):3174–3179. doi:10.1007/s00464-012-2310-8 [Epub 2012 Apr 27]
Khan ML, Abbassi MR, Jawed M et al (2014) Male gender and sonographic gall bladder wall thickness: important predictable factors for empyema and gangrene in acute cholecystitis. J Pak Med Assoc 64(2):159–162
Matcuk GR Jr, Grant EG, Ralls PW (2014) Ultrasound measurements of the bile ducts and gallbladder: normal ranges and effects of age, sex, cholecystectomy, and pathologic states. Ultrasound Q 30(1):41–48. doi:10.1097/RUQ.0b013e3182a80c98
Kapoor A, Kapoor A, Mahajan G (2011) Differentiating malignant from benign thickening of the gallbladder wall by the use of acoustic radiation force impulse elastography. J Ultrasound Med 30(11):1499–1507
Kim HJ, Park JH, Park DI et al (2012) Clinical usefulness of endoscopic ultrasonography in the differential diagnosis of gallbladder wall thickening. Dig Dis Sci 57(2):508–515. doi:10.1007/s10620-011-1870-0 [Epub 2011 Aug 31]
Son JY, Kim YJ, Park HS et al (2011) Diffuse gallbladder wall thickening on computed tomography in patients with liver cirrhosis: correlation with clinical and laboratory variables. J Comput Assist Tomogr 35(5):535–538. doi:10.1097/RCT.0b013e31822d2ade
Li WG, Hill NA, Ogden RW et al (2013) Anisotropic behaviour of human gallbladder walls. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 20:363–375. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2013.02.015 [Epub 2013 Mar 1]
West W, James K, Brady-West D (2012) Ultrasound detected asymptomatic cholelithiasis: an age-based protocol for management. West Indian Med J 61(9):903–906
Zhang L, Han Q, Zhang H et al. (2015) Significance and clinical applications of ultrasound score in assessing the clinical severity of acute cholecystitis in the elderly. Aging Clin Exp Res 27(1):21–6. doi:10.1007/s40520-014-0236-9
Fukami Y, Kurumiya Y, Mizuno K et al. (2014) Cholecystectomy in octogenarians: be careful. Updates Surg 66(4):265–8. doi:10.1007/s13304-014-0267-y
Caglià P, Costa S, Tracia A et al (2012) Can laparoscopic cholecystectomy be safety performed in the elderly? Ann Ital Chir 83(1):21–24
Ahmed M, Diggory R (2013) The correlation between ultrasonography and histopathology in the management of gall bladder polyps. Acta Chir Belg 113(3):208–212
Yaylak F, Deger A, Ucar BI et al. (2014) Cholesterolosis in routine histopathological examination after cholecystectomy: what should a surgeon behold in the reports? Int J Surg. 12(11):1187–91. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.08.402
Acknowledgments
No funding was received for this study and publication. All named authors meet the ICMJE criteria for authorship for this manuscript, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given final approval to the version to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yaylak, F., Deger, A., Bayhan, Z. et al. Histopathological gallbladder morphometric measurements in geriatric patients with symptomatic chronic cholecystitis. Ir J Med Sci 185, 871–876 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1385-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1385-3