Abstract
Introduction
There have been reports of thalidomide-affected people suffering a deterioration in their disability over time [1, 2]. This study assessed changes in disabilities among thalidomide-affected people in the Irish population.
Methods
A questionnaire, assessing musculo-skeletal health, quality-of-life, general health and illness intrusiveness was sent to 26 people affected by thalidomide in the Republic of Ireland.
Results
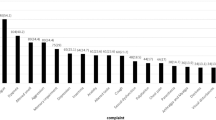
Seventeen (65%) responded. Six (35%) respondents were not working as a result of their disability. Eleven (65%) reported a worsening of their disability over time, with nine of them reporting the deterioration as moderate to severe. The impact of this decline was measured by respondents in terms of ability to perform daily tasks, emotional health and finances (due to extra costs related to clothing, transport, housing alterations and heating).
Conclusion
There is a need to continually review the physical, psychological and social needs of thalidomide survivors in order to ensure optimum care is made available.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edworthy S, Edworthy S, Wolbring G (1999) Thalidomide Survivors; a questionnaire survey on musculo-skeletal abnormalities, general health and quality of life. Available at: http://www.thalidomide.ca/en/information/thalidomide_survivors.html
Nippert I, Edler B, Schmidt-Herterich C (2002) 40 years later: the health related quality of life of women affected by thalidomide. Community Genet 5:209–216
March LM, Bagga H (2004) Epidemiology of osteoarthritis in Australia. Med J Aust 180(Suppl 5):S6–S10
Devins GM, Binik YM, Hutchinson TA et al (1983) The emotional impact of end-stage renal disease: importance of patients’ perceptions of intrusiveness and control. Int J Psychiatry Med 13:327–343
Devins GM (1994) Illness intrusiveness and the psychosocial impact of lifestyle disruptions in chronic life-threatening disease. Adv Ren Replace Ther 1:251–263
Van Brakel WH, Reed NK, Red DS (1999) Grading impairment in leprosy. Int J Lepr 68:106
Devins GM, Edworthy SM, Seland TP et al (1993) Differences in illness intrusiveness across rheumatoid arthritis, end-stage renal disease, and multiple sclerosis. J Nerv Ment Dis 181:377–381
Devins GM, Armstrong SJ, Mandin H et al (1990) Recurrent pain, illness intrusiveness, and quality of life in end-stage renal disease. Pain 42:279–285
Devins GM, Mandin H, Hons RB et al (1990) Illness intrusiveness and quality of life in end-stage renal disease: Comparison and stability across treatment modalities. Health Psychol 9:117–142
Devins GM, Edworthy SM, Guthrie NG et al (1992) Illness intrusiveness in rheumatoid arthritis: differential impact on depressive symptoms over the adult lifespan. J Rheumatol 19:709–715
Stanford/Garfield Kaiser Chronic Disease Dissemination Study. Results reported in: Lorig KR, Sobel, DS, Ritter PL et al. (2001) Effect of a self-management program for patients with chronic disease. Eff Clin Pract 4:256–262
Devins GM, Flanagan M, Morehouse R et al (1995) Differential illness intrusiveness associated with sleep promoting medications. Eur Psychiatry 10(Suppl. 3):153s–159s
Devins GM, Styra R, O’Connor P, Gray et al (1996) Psychosocial impact of illness intrusiveness moderated by age in multiple sclerosis. Psychol Health Med 1:179–191
Antony MM, Roth D, Swinson RP et al (1998) Illness intrusiveness in individuals with panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, or social phobia. J Nerv Ment Dis 186(5):311–315
Robb JC, Cooke RG, Devins GM et al (1997) Quality of life and lifestyle disruption in bipolar disorder. J Psychiatr Res 31:509–517
Newman RJ (1999) Shoulder joint replacement for osteoarthrosis in association with thalidomide-induced phocomelia. Clin Rehabil 13:250
Steven MM (1992) Prevalence of chronic arthritis in four geographical areas of the Scottish Highlands. Ann Rheum Dis 51:186–194
Jamoom EW, Horner-Johnson W, Suzuki R et al, RRTC Expert Group on Health Status Measurement (2008) Age at disability onset and self-reported health status. BMC Public Health 8:10
Conflict of interest
The lead author was affected by thalidomide. There exists a possibility that the Government may give further financial assistance to people affected by thalidomide and potentially, the results of this study could affect such a settlement. To minimise this conflict all three authors independently assessed the results of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Carroll, A., O’Reilly, F. & Whitford, D.L. What has happened to people affected by thalidomide 50 years on?. Ir J Med Sci 180, 475–478 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-011-0683-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-011-0683-7