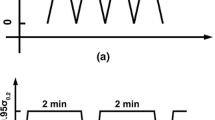
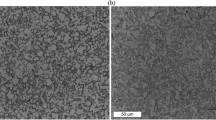
Abstract
In this work, the dwell fatigue sensitivity of the alloy IMI 834 has been investigated as a function of microstructures obtained through three different thermomechanical processing routes. The different thermomechanical process routes led to three different product forms of IMI 834, namely, forged billet, hot rolled bar and forged cylinder. All the product forms had bimodal microstructure, however, with different microstructural features and microtextural characteristics. It was found that the Dwell Fatigue Debit (DFD), which is defined as the ratio of number of cycles to failure in fatigue to number of cycles to failure in dwell fatigue, was highest in the forged cylinder followed by forged billet and then the hot rolled bar. The DFD parameter was directly related to the volume fraction of primary α grains. Furthermore, EBSD characterization revealed that the spatial distribution of texture components was different, which could further account for the difference in DFD. The texture components are responsible for the lowest fatigue and dwell fatigue lives of the forged billet. On the other hand, the presence of these components as hard-soft grain interfaces in the forged cylinder is responsible for its highest dwell fatigue debit. This study emphasizes the importance of microtexture in the dwell fatigue behaviour of titanium alloys.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Banerjee and J.C. Williams, Acta Mater. 61, 844 (2013).
G.Lutjering and J.C.Williams, Titanium, Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York, 201.
M.R. Bache and W.J. Evans, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 409, 319–321 (2001).
E.M. Eltis and G.L. Wilde, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 6, 549 (1974).
W.J. Evans, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 243, 89 (1998).
Z. Song and D.W. Hoeppner, Int. J. Fatigue 4, 211 (1988).
Z. Zhang, M.A. Cuddihy, and F.P.E. Dunne, Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 471, 20150214 (2015).
Z. Zheng, A. Stapleton, K. Fox, and F.P.E. Dunne, Int. J. Plast. 111, 234 (2018).
K.U. Yazar, S. Mishra, A. Karmakar, A. Bhattacharjee, and S. Suwas, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 51, 5036 (2020).
T. Neeraj, D.H. Hou, G.S. Daehn, and M.J. Mills, Acta Mater. 48, 1225 (2000).
M.E. Kassner and K. Smith, Integr. Med. Res. 3, 280 (2014).
V. Sinha, M.J. Mills, and J.C. Williams, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 35, 3141 (2004).
J. Peng, C. Zhou, Q. Dai, and X. He, Mater. Des. 71, 1 (2015).
K.U. Yazar, M. Shamitha, and S. Suwas, Philos. Mag. 101, 1443 (2021).
S. Bahl, S. Mishra, K.U. Yazar, I.R. Kola, K. Chatterjee, and S. Suwas, Addit. Manuf. 28, 65 (2019).
K.U. Yazar, S. Mishra, L. Kumar, S. Bahl, T.K. Kumar, and S. Suwas, Int. J. Plast. 152, 103140 (2022).
F. Bridier, P. Villechaise, and J. Mendez, Acta Mater. 56, 3951 (2008).
Z. Zhang, Acta Mater. 156, 254 (2018).
V. Hasija, S. Ghosh, M.J. Mills, and D.S. Joseph, Acta Mater. 51, 4533 (2003).
F.P.E. Dunne, A. Walker, and D. Rugg, Proc. R. Soc. A 463, 1467 (2007).
T.B. Britton, F.P.E. Dunne, and A.J. Wilkinson, Proc. R. Soc. A. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 471, 1 (2015).
Z. Zheng, D.S. Balint, and F.P.E. Dunne, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 96, 411 (2016).
Z. Zhang, T.S. Jun, T.B. Britton, and F.P.E. Dunne, Acta Mater. 118, 317 (2016).
G. Venkataramani, K. Kirane, and S. Ghosh, Int. J. Plast. 24, 428 (2008).
S. Ghosh and P. Chakraborty, Int. J. Fatigue 48, 231 (2013).
N. Gey, M. Humbert, P. Vo, M. Jahazi, and P. Bocher, Acta Mater. 56, 4298 (2008).
E. Uta, N. Gey, P. Bocher, M. Humbert, and J. Gilgert, J. Microsc. 233, 451 (2009).
S. Roy and S. Suwas, Scr. Mater. 154, 1 (2018).
S. Roy and S. Suwas, Acta Mater. 134, 283 (2017).
M. Bache, M. Cope, H.M. Davies, W.J. Evans, and G. Harrison, Int. J. Fatigue 19, 83 (1997).
G. J. Baxter, Fatigue Damage Accumulation in Titanium Alloy IMI 834, University of Sheffield, (1994).
C. Vivek, K. Prasad, V. Singh, and A. Bhattacharjee, Int. J. Fatigue 91, 100 (2016).
K. Prasad, R. Sarkar, V. Kumar, K.B.S. Rao, and M. Sundararaman, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 662, 373 (2016).
G. Lutjering, Mater. Sci. Eng. A A243, 32 (1998).
I. Balasundar, T. Raghu, and B.P. Kashyap, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 609, 241 (2014).
E. Lee, Microstructure Evolution and Microstrucure/Mechanical Properties Relationships in α + β Titanium Alloys (The Ohio State University, 2004).
M. Levy, Handbook of elastic properties of solids, liquids and gases. Academic Press 1, 255 (2000).
A.L. Pilchak, A. Bhattacharjee, A.H. Rosenberger, and J.C. Williams, Int. J. Fatigue 31, 989 (2009).
V. Sinha, J.E. Spowart, M.J. Mills, and J.C. Williams, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 1507 (2006).
A. L. Pilchak, A. Hutson, W. J. Porter, D. Buchanan, and R. John, in Proceedings of the 13th World Conference on Titanium,1, 993 (2016).
V. Sinha, M.J. Mills, and J.C. Williams, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 2015 (2005).
A.G. Fitzner, Effects of Alloying Elements on Twinning in Alpha Titanium Alloys (University of Manchester, Thesis, 2014).
V. Sinha, R.B. Schwarz, M.J. Mills, and J.C. Williams, Acta Mater. 188, 315 (2020).
C. Lavogiez, S. Hémery, and P. Villechaise, Scr. Mater. 183, 117 (2020).
A. P. Woodfield, M. D. Forman, R. R. Corderman, J. A. Sutliff, Eff. Microstruct. Dwell Fatigue Behav. Ti-6242, Titanium’95, 1116 (1995).
A.P. Woodfield, M.D. Gorman, J.A. Sutliff, and R.R. Corderman, TMS 98, 111 (1998).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Prof. Dipankar Banerjee, Department of Materials Engineering IISc, Bangalore, India, for his encouragement to carry out this work. The authors acknowledge Prof. Satish V Kailas for the fatigue and dwell fatigue testing facility at the Mechanical Engineering Department, IISc, Bangalore, India. K.U. Yazar thanks Mr. Shubhendu A. Dutta and Ms. M. Shamitha for their help in experiments. He thanks Mr. Jivan Kumar, GTRE Bangalore, for some important technical inputs. The financial support from Aeronautics Research and Development Board, India under GTMAP program is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
TOn behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yazar, K.U., Bhattacharjee, A. & Suwas, S. Effect of Thermomechanical Processing on the Dwell Fatigue Behaviour of Near Alpha Titanium Alloy IMI 834. JOM 75, 218–231 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05547-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05547-y