Abstract
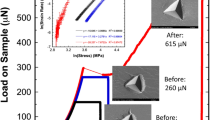
Hydrogen effects on small-volume plasticity and elastic stiffness constants are investigated with nanoindentation of Ni-201 and sonic velocity measurements of bulk Ni single crystals. Elastic modulus of Ni-201, calculated from indentation data, decreases ~ 22% after hydrogen charging. This substantial decrease is independently confirmed by sonic velocity measurements of Ni single crystals; c44 decreases ~ 20% after hydrogen exposure. Furthermore, clear hydrogen–deformation interactions are observed. The maximum shear stress required to nucleate dislocations in hydrogen-charged Ni-201 is markedly lower than in as-annealed material, driven by hydrogen-reduced shear modulus. Additionally, a larger number of depth excursions are detected prior to general yielding in hydrogen-charged material, suggesting cross-slip restriction. Together, these data reveal a direct correlation between hydrogen-affected elastic properties and plastic deformation in Ni alloys.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.P. Lynch, Corros. Sci. 22, 925 (1982).
W. Gerberich, Gaseous Hydrogen Embrittlement of Materials in Energy Technologies. Mechanical Modelling and Future Developments, Vol. 2, ed. R.P. Gangloff and B.P. Somerday (Philadelphia: Woodhead, 2012), pp. 209–246.
H.K. Birnbaum and P. Sofronis, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 176, 191 (1994).
R. Oriani and P. Joshephic, Acta Metall. 22, 1065 (1974).
M. Nagumo, Mater. Sci. Technol. 20, 940 (2004).
Y. Jagodzinski, H. Hanninen, O. Tarasenko, and S. Smuk, Scr. Mater. 43, 245 (2000).
J. Kameda and C. McMahon, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 11, 91 (1980).
W.W. Gerberich and Y.T. Chen, Metall. Trans. A 6, 271 (1975).
R.H. Jones, S.M. Bruemmer, M.T. Thomas, and D.R. Baer, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 14, 1729 (1983).
S.M. Bruemmer, R.H. Jones, M.T. Thomas, and D.R. Baer, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 14, 223 (1983).
S.K. Lawrence, B.P. Somerday, N.R. Moody, and D.F. Bahr, JOM J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 66, 1383 (2014).
S.K. Lawrence, B.P. Somerday, and R.A. Karnesky, JOM J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 69, 45 (2017).
D. Sieborger, H. Knake, and U. Glatzel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 298, 26 (2001).
M. Wen, A. Barnoush, and K. Yokogawa, Comput. Phys. Commun. 182, 1621 (2011).
A. Barnoush and H. Vehoff, Scr. Mater. 55, 195 (2006).
R.E. Green, Treatise on Materials Science: Ultrasonic Investigation of Mechanical Properties (New York: Academic Press, 1973).
J. De Klerk, Proc. Phys. Soc. 73, 337 (1959).
J.R. Neighbours, F.W. Bratten, and C.S. Smith, J. Appl. Phys. 23, 389 (1952).
A. Zielnski, Acta. Met. Mater. 38, 2573 (1990).
S.K. Lawrence, Y. Yagodzinskyy, H. Hänninen, F. Tuomisto, E. Korhonen, Z.D. Harris, and B.P. Somerday, Acta Mater. 128, 218 (2017).
H.M. Ledbetter and R.P. Reed, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2, 531 (1973).
J. Melngailis, Phys. Status Solidi 16, 247 (1966).
P.J. Ferreira, I.M. Robertson, and H.K. Birnbaum, Acta Mater. 47, 2991 (1999).
P.J. Ferreira, I.M. Robertson, and H.K. Birnbaum, Acta Mater. 46, 1749 (1998).
D. Lorenz, A. Zeckzer, U. Hilpert, P. Grau, H. Johansen, and H. Leipner, Phys. Rev. B 67, 1 (2003).
T.A. Michalske and J.E. Houston, Acta Mater. 46, 391 (1998).
A.A. Zbib and D.F. Bahr, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 38, 2249 (2007).
D.F. Bahr and G. Vasquez, J. Mater. Res. 20, 1947 (2005).
M. Wen, L. Zhang, B. An, S. Fukuyama, and K. Yokogawa, Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 80, 1 (2009).
A. Barnoush, M. Asgari, and R. Johnsen, Scr. Mater. 66, 414 (2012).
A. Barnoush, N. Kheradmand, and T. Hajilou, Scr. Mater. 108, 76 (2015).
H. Osono, T. Kino, Y. Kurokawa, and Y. Fukai, J. Alloys Compd. 231, 41 (1995).
K. Takai, H. Shoda, H. Suzuki, and M. Nagumo, Acta Mater. 56, 5158 (2008).
I. Salehinia and S.N. Medyanik, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 42A, 3868 (2011).
K. Nibur, D. Bahr, and B. Somerday, Acta Mater. 54, 2677 (2006).
R. Kirchheim, Scr. Mater. 62, 67 (2010).
R.H.W. Honeycombe, Plastic Deformation of Metals, 2nd ed. (London: Edward Arnold, 1984).
Acknowledgements
This work was performed while SKL was affiliated with Sandia National Laboratories and was supported by the DOE NNSA Stewardship Science Graduate Fellowship [Grant DE-NA0002135] and the Laboratory Directed Research and Development program at Sandia National Laboratories [Grant SNL-LDRD-173116], a multimission laboratory managed and operated by National Technology and Engineering Solutions of Sandia, LLC., a wholly owned subsidiary of Honeywell International, Inc., for the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration under Contract DE-NA-0003525. SAND2018-2771J.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lawrence, S.K., Somerday, B.P., Ingraham, M.D. et al. Probing the Effect of Hydrogen on Elastic Properties and Plastic Deformation in Nickel Using Nanoindentation and Ultrasonic Methods. JOM 70, 1068–1073 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-018-2850-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-018-2850-z