Abstract
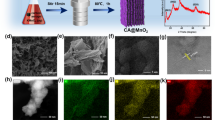
SnO2-reduced graphene oxide (SnO2-rGO) nanocomposites are successfully synthesized via a rapid microwave-assisted method (within 150 s). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observations show the ultrafine SnO2 nanoparticles (~3 nm) are uniformly anchored onto the rGO. The typical SnO2-rGO exhibits a high initial reversible capacity of 260 mAh g−1 at 50 mA g−1, which is higher than that (45 mAh g−1) of the bare SnO2 electrode. The SnO2-rGO electrode also shows high cycling stability (79.6% capacity retention after 100 cycles) and rate capability (150 mAh g−1 at 500 mA g−1). The improved electrochemical performance of the SnO2-rGO is ascribed to extremely tiny SnO2 nanoparticles well distributed on the surface of the rGO and the conductive frameworks provided by rGO, so as to alleviate the aggregation of SnO2 and buffer the volumetric change during charging and discharging.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Kim, K.H. Ha, S.M. Oh, and K.T. Lee, Chem. Eur. J. 20, 11980 (2014).
A. Manthiram, A.V. Murugan, A. Sarkar, and T. Muraliganth, Energy Environ. Sci. 1, 621 (2008).
G.-N. Zhu, Y.-G. Wang, and Y.-Y. Xia, Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 6652 (2012).
M.D. Slater, D. Kim, E. Lee, and C.S. Johnson, Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 947 (2013).
H. Pan, Y.-S. Hu, and L. Chen, Energy Environ. Sci. 6, 2338 (2013).
Y.-X. Wang, Y.-G. Lim, M.-S. Park, S. Chou, J.H. Kim, H. Liu, S.-X. Dou, and Y.-J. Kim, J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 529 (2014).
Y. Xu, Y. Zhu, Y. Liu, and C. Wang, Adv. Energy Mater. 3, 128 (2013).
A. Darwiche, C. Marino, M.T. Sougrati, B. Fraisse, L. Stievano, and L. Monconduit, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 20805 (2012).
H. Bian, J. Zhang, M.-F. Yuen, W. Kang, Y. Zhan, Y. Denis, Z. Xu, and Y.Y. Li, J. Power Sources 307, 634 (2016).
J. Qian, X. Wu, Y. Cao, X. Ai, and H. Yang, Angew. Chem. 125, 4731 (2013).
Q. Sun, Q.-Q. Ren, H. Li, and Z.-W. Fu, Electrochem. Commun. 13, 1462 (2011).
L.-Y. Qi, Y.-W. Zhang, Z. Zuo, Y. Xin, C. Yang, B. Wu, X. Zhang, and H. Zhou, J. Mater. Chem. A. (2016). doi:10.1039/C6TA01836J.
Y. Wang, D. Su, C. Wang, and G. Wang, Electrochem. Commun. 29, 8 (2013).
D. Su, H.-J. Ahn, and G. Wang, Chem. Commun. 49, 3131 (2013).
H. Liu, J. Huang, X. Li, J. Liu, Y. Zhang, and K. Du, Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 4917 (2012).
R.S. Kalubarme, J.-Y. Lee, and C.-J. Park, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 17226 (2015).
M. Gu, A. Kushima, Y. Shao, J.-G. Zhang, J. Liu, N.D. Browning, J. Li, and C. Wang, Nano Lett. 13, 5203 (2013).
X. Zhao, Z. Zhang, F. Yang, Y. Fu, Y. Lai, and J. Li, RSC Adv. 5, 31465 (2015).
Y. Cheng, J. Huang, J. Li, Z. Xu, L. Cao, H. Ouyang, J. Yan, and H. Qi, J. Alloys Compd. 658, 234 (2016).
Y. Zhang, J. Xie, S. Zhang, P. Zhu, G. Cao, and X. Zhao, Electrochim. Acta 151, 8 (2015).
C. Zhong, J. Wang, Z. Chen, and H. Liu, J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 25115 (2011).
Z. Tai, X. Yan, and Q. Xue, J. Electrochem. Soc. 159, A1702 (2012).
X. Jiang, X. Zhu, X. Liu, L. Xiao, X. Ai, H. Yang, and Y. Cao, Electrochim. Acta 196, 431 (2016).
Y. Bai, M. Du, J. Chang, J. Sun, and L. Gao, J. Mater. Chem A 2, 3834 (2014).
M. Dirican, Y. Lu, Y. Ge, O. Yildiz, and X. Zhang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 18387 (2015).
Acknowledgements
We thank financial support by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (No. 2015CB251100) and National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21373155, 21333007, 21303262), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-12-0419) and Hubei National Funds for Distinguished Young Scholars (2014CFA038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, H., Jiang, X., Chen, X. et al. SnO2-Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites via Microwave Route as Anode for Sodium-Ion Battery. JOM 68, 2607–2612 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-2061-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-2061-4