Abstract
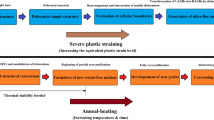
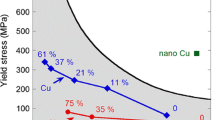
The microstructures of ultrafine-grained nanostructured materials developed by severe plastic deformation are widely varied in their grain size and grain-size distribution; grain boundaries and their structures; lattice defects, especially dislocations; point defects; and impurities. All of these features can be influenced by the way severe plastic deformation is applied, and thereby have decisive effects on the physical and mechanical properties of the material. Probably, the most important factors determining microstructure are the imposed stress tensor, the degree and rate of strain, the temperature of deformation, the chemical composition of the deformed material, and the type of crystal lattice, showing that in order to develop specific properties, it is crucial to understand and optimize the microstructure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.Z. Valiev, R.K. Islamgaliev, and I.V. Alexandrov, Progr. Mater. Sci., 45 (2) (2000), p. 103.
Z. Horita et al., Mater. Sci. Forum, 204–206 (1996), p. 437.
Z. Horita et al., J. Mater. Res., 13 (1998), p. 446.
K. Zhang et al., J. Appl. Phys., 84 (1998), p. 1924.
T. Ungár and A. Borbély, Appl. Phys. Letters, 69 (1996), p. 3173.
T. Ungár et al., J. Appl. Cryst., 32 (1999), p. 992.
T. Ungár and M. Zehetbauer, Scripta Mater., 35 (1996), p. 1467.
M. Zehetbauer et al., Acta Mater., 47 (1999), p. 1053.
J. Gil Sevillano, P. van Houtte, and E. Aernoudt, Progr. Mater. Sci., 25 (1980), p. 2.
M. Zehetbauer and V. Seumer, Acta Metall. Mater., 41 (1993), p. 577.
H.P. Stüwe, Z. Metallk., 56 (1965), p. 633.
I. Kovács, Acta Met., 15 (1967), p. 1731.
J.M. Alberdi (Ph.D. thesis, University of Navarra, 1984).
D.A. Hughes, J.C. Gibeling, and W. Nix, Proc. 7th ICSMA, ed. H.J. McQueen et al. (Oxford, U.K.: Pergamon, 1985) p. 105.
M. Müller et al., Scripta Metall. Mater., 35 (1996), p. 1461.
A.D. Rollett (Ph.D. thesis, Drexel University, 1988).
P. Haasen, J. Phys. France, 50 (1989), p. 2445.
D. Kuhlmann-Wilsdorf, Mat. Sci. Eng., A113 (1989), p. 1.
A.S. Argon and P. Haasen, Acta Metall. Mater., 41 (1993), p. 3289.
M. Zehetbauer, Acta Metall. Mater., 41 (1993), p. 589.
Y. Estrin et al., Acta Mater., 46 (1998), p. 5509.
H. Mughrabi et al., Phil. Mag., 53 (1986), p. 793.
T. Ungár et al., Phil. Mag., 64 (1991), p. 495.
H. Mughrabi, Acta Metall., 31 (1983), p. 1367.
D.A. Hughes and N. Hansen, Metall. Trans., 24A (1993), p. 2021.
M. Zehetbauer and P. Les, Kovove Materialy (Metallic Materials), 36 (1998), p. 153.
M.A. Krivoglaz, Theory of X-ray and Thermal Neutron Scattering by Real Crystals (New York: Plenum Press, 1969); X-ray and Neutron Diffraction in Nonideal Crystals (Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer-Verlag, 1996).
P. Suortti, The Rietveld Method, vol. 5, ed. R.A. Young (London: Oxford University Press, 1993), pp. 167–185.
R. Kuzel, Jr. and P. Klimanek, J. Appl. Cryst., 22 (1989), p. 299.
G.K. Williamson and W.H. Hall, Acta Metall., 1 (1953), p. 22.
B.E. Warren, Progr. Metal Phys., 8 (1959), p. 147.
T. Ungár and G. Tichy, Phys. Stat. Sol. (a), 171 (1999), p. 425.
M. Wilkens, Phys. Stat. Sol. (a), 104 (1987), p. K1.
T. Ungár and G. Ribárik, to be published.
T. Ungár et al., Nanostructured Mater., 11 (1999), p. 103.
P. Debye, Verh. Deutsch. Phys. Ges., 15 (1913), pp. 678, 738, 857.
I. Waller, Zeitschr. Physik, 17 (1923), p. 398.
B.E. Warren, X-ray Diffraction (Reading MA: Addison-Wesley, 1969), pp. 151–203.
I.V. Alexandrov et al., Proc. Int. Conf. Textures of materials, ICOTOM-11, ed. Z. Liang, L. Zuo, and Y. Chu Beijing: Int. Acad. Pub., 1996), p. 929.
S.S. Xu, X-ray Diffraction in Metals (Ithaca, Shanghai: Science Technical Publication Press, 1962).
R.W. James, The Optical Principles of the Diffraction of X-ray (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 1965).
I. Kopacz et al., to be published.
K. Zhang et al., J. Appl. Phys., 80 (1996), p. 5617.
K. Zhang et al., J. Phys. D, 30 (1997), p. 3008.
K. Zhang, I.V. Alexandrov, and K. Lu, NanoStructured Materials, 9 (1997), p. 347.
I.V. Alexandrov et al., Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 234–236 (1997), p. 331.
I.V. Alexandrov and R.Z. Valiev, Philos. Mag. B, 73 (1996), p. 861.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
For more information, contact T. Ungár, Department of General Physics, Eötvös University Budapest, H-1518, P.O.B. 32, Budapest, Hungary.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ungár, T., Alexandrov, I. & Zehetbauer, M. Ultrafine-grained microstructures evolving during severe plastic deformation. JOM 52, 34–36 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-000-0129-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-000-0129-6