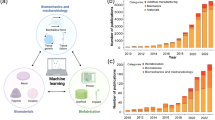
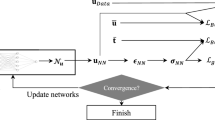
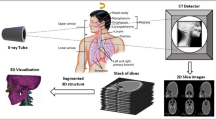
Abstract
This article reviewed current advancements in mechanobiology (MB) and its applications to investigate human tissue (soft and hard) using machine learning (ML) techniques. The study explores the use of ML for diagnosing tissue disorders and injuries and highlights the challenges and limitations of applying ML to MB. In addition, a detailed assessment of the many distinct experimental methodologies, computational studies and computer models may be utilized for MB analysis. The initial section introduces MB, their generation-wise developments, and the broad classification of human tissues and their disorders. This study also focussed on the computational studies of the different numerical models of human tissues. The final part examined various studies to classify and early detection of human tissue disorders with the help of ML techniques. Overall, the paper offers insights into the potential of ML for understanding human tissue’s complex behaviour and advancing the biomechanics field.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim S, Uroz M, Bays JL, Chen CS (2021) Harnessing mechanobiology for tissue Engineering. Dev Cell 56:180–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2020.12.017
Briggs GH, A PRSL (1934) Measurements of the relative velocities of the α-particles from radon, radium A, and radium C’. Proc r soc London ser A, Contain Pap a. Math Phys Character 143:604–617. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1934.0022
Rigby BJ, Hirai N, Spikes JD, Eyring H (1959) The Mechanical Properties of Rat tail Tendon. J Gen Physiol 43:265–283. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.43.2.265
Mason P (1965) The viscoelasticity and structure of keratin and collagen. Kolloid-Zeitschrift Z für Polym 202:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01497101
Bell E, Ivarsson B, Merrill C (1979) Production of a tissue-like structure by contraction of collagen lattices by human fibroblasts of different proliferative potential in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 76:1274–1278. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.76.3.1274
Grenoble DE, Katz JL, Dunn KL et al (1972) The elastic properties of hard tissues and apatites. J Biomed Mater Res 6:221–233. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.820060311
Wesly RLR, Vaishnav RN, Fuchs et al (1975) et a. JCA, Static linear and nonlinear elastic properties of normal and arterialized venous tissue in dog and man. Circ Res 37:509–520. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.37.4.509
Huiskes R, Chao EYS (1983) A survey of finite element analysis in orthopedic biomechanics: the first decade. J Biomech 16:385–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9290(83)90072-6
Simon BR (1992) Multiphase poroelastic finite element models for soft tissue structures. Appl Mech Rev 45:191–218. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3121397
Legant WR, Pathak A, Yang MT et al (2009) Microfabricated tissue gauges to measure and manipulate forces from 3D microtissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:10097–10102. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0900174106
Sarvazyan A, Egorov V (2012) Mechanical imaging - a technology for 3-D visualization and characterization of soft tissue abnormalities: a review. Curr Med Imaging Rev 8:64–73. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340512799220571
Egorov V, Kearney T, Pollak SB et al (2009) Differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions by mechanical imaging. Breast Cancer Res Treat 118:67–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0369-2
Weiss RE, Egorov V, Ayrapetyan S et al (2008) Prostate mechanical imaging: a new method for prostate Assessment. Urology 71:425–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2007.11.021
Fernandes MG, da Silva LP, Marques AP (2019) Skin mechanobiology and biomechanics: from homeostasis to Wound Healing. Advances in Biomechanics and tissue regeneration. Elsevier, pp 343–360
Fereidoonnezhad B, Naghdabadi R, Sohrabpour S, Holzapfel GA (2017) A mechanobiological model for damage-induced growth in arterial tissue with application to in-stent restenosis. J Mech Phys Solids 101:311–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2017.01.016
Kruse SA, Rose GH, Glaser KJ et al (2008) Magnetic resonance elastography of the brain. NeuroImage 39:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.08.030
Velasco MA, Narváez-Tovar CA, Garzón-Alvarado DA (2015) Design, materials, and mechanobiology of biodegradable scaffolds for bone tissue Engineering. Biomed Res Int 2015:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/729076
Chanet S, Martin AC (2014) Mechanical Force Sensing in Tissues. In: Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science. pp 317–352
Goecks J, Jalili V, Heiser LM, Gray JW (2020) How machine learning will transform Biomedicine. Cell 181:92–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.022
FRCN IPO (2018) Fundamentals of Applied Pathophysiology. John Wiley & Sons Ltd
Ian Peate MN (2017) Fundamentals of anatomy and physiology. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd
Merriam-Webster.com Medical Dictionary (2020) Soft Tissue
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary (2012) Hard Tissue
Jelínková H (2013) Introduction: the history of lasers in medicine. Lasers for medical applications. Elsevier, pp 1–13
Boskey AL (1988) Calcified Tissues: Chemistry and Biochemistry. pp 171–186
Turan M, Uzun Yaylacı E, Yaylacı M (2023) Free vibration and buckling of functionally graded porous beams using analytical, finite element, and artificial neural network methods. Arch Appl Mech 93:1351–1372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-022-02332-w
Yaylacı M, Abanoz M, Yaylacı EU et al (2022) Evaluation of the contact problem of functionally graded layer resting on rigid foundation pressed via rigid punch by analytical and numerical (FEM and MLP) methods. Arch Appl Mech 92:1953–1971. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-022-02159-5
Murat Yaylaci; Merve Abanoz; Ecren Uzun Yaylaci; Hasan Olmez; Dursun Murat Sekban; Ahmet Birinci (2022) The contact problem of the functionally graded layer resting on rigid foundation pressed via rigid punch. Steel Compos Struct 43:661–672
Murat Yaylaci; Bahar Şengül Şabano; Mehmet Emin Özdemir; Ahmet Birinci (2022) Solving the contact problem of functionally graded layers resting on a HP and pressed with a uniformly distributed load by analytical and numerical methods. Struct Eng Mech 82:401–416. https://doi.org/10.12989/sem.2022.82.3.401
Yaylaci EU, Oner E, Yaylaci M, Ozdemir ME, Abushattal A, Birinci A (2022) Application of artificial neural networks in the analysis of the continuous contact problem. Struct Eng Mech 84:35–48. https://doi.org/10.12989/sem.2022.84.1.035
McConnon A (2021) Understanding tissue stiffness and how cells restrict the way extracellular matrices can deform. https://doi.org/10.1063/10.0004780. Scilight 2021:
Abbas Y, Carnicer-Lombarte A, Gardner L et al (2019) Tissue stiffness at the human maternal-fetal interface. Hum Reprod 34:1999–2008. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dez139
Graham HK, McConnell JC, Limbert G, Sherratt MJ (2019) How stiff is skin? Exp Dermatol 28:4–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.13826
Allijn I, Ribeiro M, Poot A et al (2020) Membranes for Modelling Cardiac tissue stiffness in Vitro based on poly(trimethylene carbonate) and poly(ethylene glycol) polymers. Membr (Basel) 10:274. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100274
Yin Z, Romano AJ, Manduca A et al (2018) Stiffness and Beyond. Top Magn Reson Imaging 27:305–318. https://doi.org/10.1097/RMR.0000000000000178
Handorf AM, Zhou Y, Halanski MA, Li W-J (2015) Tissue stiffness dictates Development, Homeostasis, and Disease Progression. Organogenesis 11:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476278.2015.1019687
Hinz B (2012) Mechanical aspects of lung fibrosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc 9:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1513/pats.201202-017AW
Mueller S (2010) Liver stiffness: a novel parameter for the diagnosis of liver disease. Hepatic Med Evid Res 49. https://doi.org/10.2147/hmer.s7394
Li Y, Wu M, Zhang Z et al (2019) Application of External Force regulates the Migration and differentiation of adipose-derived Stem/Progenitor cells by altering tissue stiffness. Tissue Eng - Part A 25:1614–1622. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tea.2019.0046
Budday S, Kuhl E (2020) Modeling the life cycle of the human brain. Curr Opin Biomed Eng 15:16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cobme.2019.12.009
Karpiński R, Łukasz, Jaworski (2017) and PC The structural and mechanical properties of the bone. In: Journal of Technology and Exploitation in mechanical Engineering. Elsevier, pp 43–51
Sommer G, Schriefl AJ, Andrä M et al (2015) Biomechanical properties and microstructure of human ventricular myocardium. Acta Biomater 24:172–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2015.06.031
Hsu CK, Lin HH, Harn HIC et al (2018) Mechanical forces in skin disorders. J Dermatol Sci 90:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2018.03.004
Dabrowska AK, Rotaru GM, Derler S et al (2016) Materials used to simulate physical properties of human skin. Ski Res Technol 22:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/srt.12235
Rama Mohan Rao M, Satyanarayana MRS, Bhaskara Raju VVS, Venubabu Y (2018) Dynamic analysis of elastomers. Mater Today Proc 5:2650–2659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.01.045
Estermann SJ, Pahr DH, Reisinger A (2020) Hyperelastic and viscoelastic characterization of hepatic tissue under uniaxial tension in time and frequency domain. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 112:104038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2020.104038
Chen S, Sun L, Zhou X et al (2020) Mechanically and biologically skin-like elastomers for bio-integrated electronics. Nat Commun 11:1107. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14446-2
Chanda A (2018) Biomechanical modeling of human skin tissue surrogates. Biomimetics 3:18. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics3030018
Prevost TP, Balakrishnan A, Suresh S, Socrate S (2011) Biomechanics of brain tissue. Acta Biomater 7:83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2010.06.035
Patel SS, Kumar EK, Panda SK, Sharma N (2023) State of Art Review on computational modelling and analysis and making of Brain Phantom. Arch Comput Methods Eng 30:2527–2541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-022-09875-9
Fallenstein GT, Hulce VD, Melvin JW (1969) Dynamic mechanical properties of human brain tissue. J Biomech 2:217–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9290(69)90079-7
Budday S, Sommer G, Birkl C et al (2017) Mechanical characterization of human brain tissue. Acta Biomater 48:319–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2016.10.036
Jin X, Zhu F, Mao H et al (2013) A comprehensive experimental study on material properties of human brain tissue. J Biomech 46:2795–2801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2013.09.001
Budday S, Ovaert TC, Holzapfel GA et al (2020) Fifty shades of brain: a review on the mechanical testing and modeling of Brain tissue. Springer Netherlands
Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, Discher DE (2006) Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 126:677–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.044
Streitberger KJ, Sack I, Krefting D et al (2012) Brain viscoelasticity alteration in chronic-progressive multiple sclerosis. PLoS ONE 7. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029888
Wuerfel J, Paul F, Beierbach B et al (2010) MR-elastography reveals degradation of tissue integrity in multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage 49:2520–2525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.06.018
Gerischer LM, Fehlner A, Köbe T et al (2018) Combining viscoelasticity, diffusivity and volume of the hippocampus for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease based on magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage Clin 18:485–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2017.12.023
Murphy MC, Jones DT, Jack CR et al (2016) Regional brain stiffness changes across the Alzheimer’s disease spectrum. NeuroImage Clin 10:283–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2015.12.007
Schregel K, Née Tysiak EW, Garteiser P et al (2012) Demyelination reduces brain parenchymal stiffness quantified in vivo by magnetic resonance elastography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:6650–6655. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200151109
Johnson CL, Telzer EH (2018) Magnetic resonance elastography for examining developmental changes in the mechanical properties of the brain. Dev Cogn Neurosci 33:176–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2017.08.010
Rashid B, Destrade M, Gilchrist MD (2014) Mechanical characterization of brain tissue in tension at dynamic strain rates. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 33:43–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2012.07.015
Rashid B, Destrade M, Gilchrist MD (2012) Mechanical characterization of brain tissue in compression at dynamic strain rates. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 10:23–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2012.01.022
Stephens EH, de Jonge N, McNeill MP et al (2010) Age-related changes in Material Behavior of Porcine Mitral and aortic valves and correlation to Matrix Composition. Tissue Eng Part A 16:867–878. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tea.2009.0288
Van Geemen D, Soares ALF, Oomen PJA et al (2016) Age-dependent changes in geometry, tissue composition and mechanical properties of fetal to adult cryopreserved human heart valves. PLoS ONE 11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0149020
Al Makhzoomi AK, Kirk TB, Dye DE, Allison GT (2021) Contribution of glycosaminoglycans to the structural and mechanical properties of tendons – A multiscale study. J Biomech 128:110796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2021.110796
Arani AT, Ghorbanpour Arani A, Kolahchi R (2015) Non-newtonian pulsating blood flow-induced dynamic instability of visco-carotid artery within soft surrounding visco-tissue using differential cubature method. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C J Mech Eng Sci 229:3002–3012. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406214566038
Jiang Y, Song Q, Luo X (2022) 3D cohesive finite element minimum invasive surgery Simulation based on Kelvin-Voigt Model. Chin J Mech Eng (English Ed 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10033-022-00743-y
Loeser RF, Goldring SR, Scanzello CR, Goldring MB (2012) Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum 64:1697–1707. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.34453
Florencio-Silva R, Sasso GRDS, Sasso-Cerri E et al (2015) Biology of Bone tissue: structure, function, and factors that influence bone cells. Biomed Res Int 2015:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/421746
Goldring MB, Goldring SR (2010) Articular cartilage and subchondral bone in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1192:230–237. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05240.x
Leng H, Reyes MJ, Dong XN, Wang X (2013) Effect of age on mechanical properties of the collagen phase in different orientations of human cortical bone. Bone 55:288–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2013.04.006
Burstein A, Reilly D, Martens M (1976) Aging of bone tissue. J Bone Jt Surg 58:82–86. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-197658010-00015
Escoffier C, de Rigal J, Rochefort A et al (1989) Age-related mechanical properties of human skin: an in vivo study. J Invest Dermatol 93:353–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-202x(89)90058-4
Łagan SD, Liber-Kneć A (2017) Experimental testing and constitutive modeling of the mechanical properties of the swine skin tissue. Acta Bioeng Biomech 19:93–102. https://doi.org/10.5277/ABB-00755-2016-02
Müller AC, Guido S (2016) Introduction to Machine Learning with Python
Dietterich TC, Bishop D, Heckerman M, Jordan, Kearns M (2010) Introduction to machine learning. The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England
Safaei N, Safaei B, Seyedekrami S et al (2022) E-CatBoost: an efficient machine learning framework for predicting ICU mortality using the eICU. Collaborative Research Database
(2020) What Is Machine Learning (ML)? In: UC Berkeley
Subasi A (2020) Machine learning techniques. Practical machine learning for Data Analysis using Python. Elsevier, pp 91–202
Yu T, Han Q-K, Qin Z-Y, Wen B-C (2006) Identification of Crack Location and Depth in Rotating Machinery Based on Artificial Neural Network. In: IOMAC 2009–3rd International Operational Modal Analysis Conference. pp 982–990
Sarkar D, Bali R, Sharma T (2018) Practical machine learning with Python. Apress, Berkeley, CA
Balu A, Nallagonda S, Xu F et al (2019) A Deep Learning Framework for Design and Analysis of Surgical Bioprosthetic Heart Valves. Sci Rep 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54707-9
Sohail A, Ashiq U (2023) Quantum inspired improved AI computing for the sensors of cardiac mechano-biology. Sens Int 4:100212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sintl.2022.100212
Cai Y, Wu S, Zhao W et al (2018) Concussion classification via deep learning using whole-brain white matter fiber strains. PLoS ONE 13:e0197992. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0197992
Shim VB, Holdsworth S, Champagne AA et al (2020) Rapid Prediction of Brain Injury Pattern in mTBI by combining FE Analysis with a machine-learning based Approach. IEEE Access 8:179457–179465. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3026350
Mukund K, Subramaniam S (2020) Skeletal muscle: a review of molecular structure and function, in health and disease. WIREs Syst Biol Med 12:1–46. https://doi.org/10.1002/wsbm.1462
Wise SG, Weiss AS (2009) Tropoelastin. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:494–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2008.03.017
Shoulders MD, Raines RT (2009) Collagen structure and Stability. Annu Rev Biochem 78:929–958. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.032207.120833
Ahmed Z, Mohamed K, Zeeshan S, Dong X (2020) Artificial intelligence with multi-functional machine learning platform development for better healthcare and precision medicine. Database 2020:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/baaa010
Bohr A, Memarzadeh K (2020) The rise of artificial intelligence in healthcare applications. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. Elsevier, pp 25–60
Kuehlmann B, Bonham CA, Zucal I et al (2020) Mechanotransduction in Wound Healing and Fibrosis. J Clin Med 9:1423. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051423
Saxby DJ, Killen BA, Pizzolato C et al (2020) Machine learning methods to support personalized neuromusculoskeletal modelling. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 19:1169–1185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-020-01367-8
Buchanan TS, Lloyd DG, Manal K, Besier TF (2004) Neuromusculoskeletal modeling: estimation of muscle forces and joint moments and movements from measurements of neural command. J Appl Biomech 20:367–395. https://doi.org/10.1123/jab.20.4.367
Linka K, Reiter N, Würges J et al (2021) Unraveling the local relation between tissue composition and human brain mechanics through machine learning. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.704738
Yang X, Zhao D, Yu F et al (2022) An optimized machine learning framework for predicting intradialytic hypotension using indexes of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorders. Comput Biol Med 145:105510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105510
AlDera SA, Othman MT, Ben (2022) A model for classification and diagnosis of skin disease using machine learning and image Processing techniques. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 13:252–259. https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2022.0130531
Mathur P, Srivastava S, Xu X, Mehta JL (2020) Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Cardiovascular Disease. Clin Med Insights Cardiol 14. https://doi.org/10.1177/1179546820927404
Dhiya Al-Jumeily, Iram S, Hussain AJ, Francois-Benois V (2014) PF Early Detection Method of Alzheimer’s Disease Using EEG Signals
Verma AK, Pal S, Kumar S (2021) Prediction of Different Classes of Skin Disease Using Machine Learning Techniques. In: Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. pp 91–100
Uysal G, Ozturk M (2020) Hippocampal atrophy based Alzheimer ’ s disease diagnosis via machine learning methods. J Neurosci Methods 337:108669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108669
Saranya A, Kottilingam K A Survey on Bone Fracture Identification Techniques using Quantitative and Learning Based Algorithms. In: 2021 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and, Systems S (2021) (ICAIS). IEEE, pp 241–248
Shen SC, Peña Fernández M, Tozzi G, Buehler MJ (2021) Deep learning approach to assess damage mechanics of bone tissue. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 123:104761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2021.104761
Krois J, Ekert T, Meinhold L et al (2019) Deep learning for the Radiographic detection of Periodontal Bone loss. Sci Rep 9:8495. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44839-3
Lee H, Tajmir S, Lee J et al (2017) Fully automated Deep Learning System for Bone Age Assessment. J Digit Imaging 30:427–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-017-9955-8
Hossen MN, Panneerselvam V, Koundal D et al (2022) Federated Machine Learning for detection of skin Diseases and Enhancement of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) security. IEEE J Biomed Heal Informatics XX:1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2022.3149288
Elngar AA, Kumar R, Hayat A, Churi P (2021) Intelligent System for Skin Disease Prediction using Machine Learning. J Phys Conf Ser 1998:012037. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1998/1/012037
Li R, Rui G, Chen W et al (2018) Early detection of Alzheimer’s Disease using non-invasive Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Front Aging Neurosci 10:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00366
Castellazzi G, Cuzzoni MG, Cotta Ramusino M et al (2020) A Machine Learning Approach for the Differential diagnosis of Alzheimer and Vascular Dementia Fed by MRI selected features. Front Neuroinform 14:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2020.00025
Dalmış MU, Vreemann S, Kooi T et al (2018) Fully automated detection of breast cancer in screening MRI using convolutional neural networks. J Med Imaging 5:1. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.jmi.5.1.014502
Akbari H, Bakas S, Pisapia JM et al (2018) In vivo evaluation of EGFRvIII mutation in primary glioblastoma patients via complex multiparametric MRI signature. Neuro Oncol 20:1068–1079. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noy033
Abràmoff MD, Lou Y, Erginay A et al (2016) Improved automated detection of diabetic retinopathy on a publicly available dataset through integration of deep learning. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 57:5200–5206. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.16-19964
Chaves R, Ramírez J, Górriz JM, Illán IA (2012) Functional brain image classification using association rules defined over discriminant regions. Pattern Recognit Lett 33:1666–1672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2012.04.011
Klöppel S, Stonnington CM, Chu C et al (2008) Automatic classification of MR scans in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 131:681–689. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awm319
Suk H, Il, Lee SW, Shen D (2014) Hierarchical feature representation and multimodal fusion with deep learning for AD/MCI diagnosis. NeuroImage 101:569–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.06.077
Liu L, Zhao S, Chen H, Wang A (2020) A new machine learning method for identifying Alzheimer’s disease. Simul Model Pract Theory 99:102023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2019.102023
Kim D, Kim K (2018) Detection of early stage Alzheimer’s disease using EEG relative power with deep neural network. Proc Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc EMBS 2018–July:352–355. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2018.8512231
Lodha P, Talele A, Degaonkar K Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Machine Learning. In: 2018 Fourth International Conference on Computing Communication, Control, Automation (2018) (ICCUBEA). IEEE, pp 1–4
Zhang Y, Dong Z, Phillips P et al (2015) Detection of subjects and brain regions related to Alzheimer’s disease using 3D MRI scans based on eigenbrain and machine learning. Front Comput Neurosci 9:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncom.2015.00066
Trambaiolli LR, Lorena AC, Fraga FJ et al (2011) Improving Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis with machine learning techniques. Clin EEG Neurosci 42:160–165. https://doi.org/10.1177/155005941104200304
Ismail M, Hofmann K, El Ghany MAA (2019) Early Diagnoses of Alzheimer using EEG data and deep neural networks classification. https://doi.org/10.1109/GCIoT47977.2019.9058417. 2019 IEEE Glob Conf Internet Things, GCIoT 2019
Almubark I, Chang LC, Nguyen T et al (2019) Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Patient Neuropsychological and Cognitive Data and Machine Learning Techniques. Proc – 2019 IEEE Int Conf Big Data, Big Data 2019 5971–5973. https://doi.org/10.1109/BigData47090.2019.9006583
Buettner R, Schunter M (2019) Efficient machine learning based detection of heart disease. 2019 IEEE Int Conf E-Health Networking, Appl Serv Heal 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/HealthCom46333.2019.9009429
Nashif S, Raihan MR, Islam MR, Imam MH (2018) Heart Disease detection by using machine learning algorithms and a Real-Time Cardiovascular Health Monitoring System. World J Eng Technol 06:854–873. https://doi.org/10.4236/wjet.2018.64057
Liu S, Feng M, Qiao T et al (2022) Deep learning for the Automatic diagnosis and analysis of bone metastasis on bone scintigrams. Cancer Manag Res Volume 14:51–65. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S340114
Murugan A, Nair SAH, Preethi AAP, Kumar KPS (2021) Diagnosis of skin cancer using machine learning techniques. Microprocess Microsyst 81:103727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpro.2020.103727
Kshirsagar PR, Manoharan H, Shitharth S et al (2022) Deep learning approaches for prognosis of automated skin disease. Life 12:426. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030426
Xiong X, Guo X, Wang Y (2021) Modeling of human skin by the Use of Deep Learning. Complexity 2021:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5531585
Koklu M, Ozkan IA (2017) Skin lesion classification using machine learning algorithms. Int J Intell Syst Appl Eng 4:285–289. https://doi.org/10.18201/ijisae.2017534420
Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA et al (2017) Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 542:115–118. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21056
Gupta L, Jayavanth S, Ramaiah A (2009) Identification of different types of lymphoblasts in acute lymphoblastic leukemia using relevance vector machines. In: 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE, pp 6675–6678
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H et al (2015) ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis 211–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y
Jyoti Islam and Yanqing Zhang (2017) A Novel Deep Learning based multi-class classification method for Alzheimer’. s Disease Detection Using Brain MRI Data
Talo M, Yildirim O, Baloglu UB et al (2019) Convolutional neural networks for multi-class brain disease detection using MRI images. Comput Med Imaging Graph 78:101673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2019.101673
Otoom AF, Abdallah EE, Kilani Y et al (2015) Effective diagnosis and monitoring of heart disease. Int J Softw Eng its Appl 9:143–156. https://doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2015.9.1.12
Chaurasia V, Pal S (2013) Data Mining Approach to Detect Heart Dieses. 2:56–66
Dwivedi AK (2016) Performance evaluation of different machine learning techniques for prediction of heart disease. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2604-1
Pravin R, Kshirsagar H, Manoharan S (2020) Shitharth 3 AMA 4, Nabeel Albishry 5 and Praveen Kumar Balachandran 6 Deep Learning Approaches for Prognosis of Automated Skin Disease. SN Comput Sci 1:345. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030426
Trevor Fernando Z, Trivedi P, Patni A, Trivedi P (2013) Docaid: Predictive Healthcare Analytics Using Na\“{i}ve Bayes Classification. In: Proceedings of the Student Research Symposium (SRS’13). Research Publishing Services, Singapore, pp 49–53
Chang CL, Chen CH (2009) Applying decision tree and neural network to increase quality of dermatologic diagnosis. Expert Syst Appl 36:4035–4041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.03.007
Verma AK, Pal S, Kumar S (2019) Classification of skin disease using ensemble data mining techniques. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 20:1887–1894. https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.6.1887
Yadav DC, Pal S (2022) Thyroid prediction using ensemble data mining techniques. Int J Inf Technol 14:1273–1283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-019-00395-7
Funding
Authors have received no funding for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Meher, A.K., Kumar, E.K., Gangwar, A. et al. Review on Mechanobiological Analysis and Computational Study of Human Tissue (Soft and Hard) Using Machine Learning Techniques: A Mechanical Perspective. Arch Computat Methods Eng 31, 957–972 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-023-10003-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-023-10003-4