Abstract
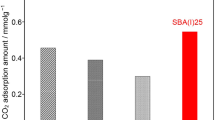
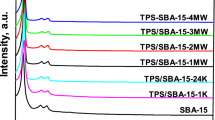
Microwave-assisted post-synthetic detemplating method was applied to remove successfully the occluded organic template from the mesoporous silica frameworks of as-synthesized SBA-15 within a short period of time compared to a conventional method, such as furnace calcination. The nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherm studies showed that the resultant detemplated SBA-15 had a very high specific surface area of 1,271 m2/g, large pore size of 9.21 nm and high pore volume of 2.10 cm3/g; while the powder X-ray diffraction patterns and high-resolution TEM images of these support materials revealed the presence of highly ordered mesopores without any structural shrinkage. Both the microwave power and time during post-synthetic microwave irradiation were found to influence the morphological structure of the SBA-15 support. To evaluate the adsorption performance of the microwave-irradiated SBA-15 support, CO2 adsorption uptake was measured after functionalizing it with different loadings of polyethyleneimine (PEI) under 9.7% CO2/N2 mixture at 75oC. The maximum CO2 uptake was 3.63 mmol CO2/g (0.16 g/g), with an optimum PEI loading of 70 wt%. Because of the significant improvement in structural characteristics, the microwave-irradiated SBA-15 supports facilitated more PEI incorporation that contributed to about 15% higher CO2 uptake than that of conventional furnace calcined one. In addition, the sorbent demonstrated very good cyclic stability when tested over 25 cycles and for a total duration of 20 h in humid conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a0 :
-
unit cell parameter
- wd :
-
wall thickness
- dp :
-
BJH pore diameter
- d100 :
-
d-spacing of (100) diffraction peak
- qf :
-
instantaneous adsorption values at time t
- qe :
-
instantaneous adsorption values at equilibrium
- kn, m: and n:
-
model parameters
- AAD:
-
average absolute deviation
- θ :
-
diffractionangle
References
U. Cubasch, D. Wuebbles, D. Chen, M. C. Facchini, D. Frame, N. Mahowald and J.-G. Winther, Introduction. In: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, T. F. Stocker, D. Qin, G.-K. Plattner, M. Tignor, S. K. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, V. Bex and P. M. Midgley (eds.), Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA (2013).
A. B. Rao and E. S. Rubin, Environ. Sci. Technol., 36, 4467 (2002).
D. Singh, E. Croiset, P. L. Douglas and M. A. Douglas, Energy Convers. Manag., 44, 3073 (2003).
M. YT. Le, S. Y. Lee and S. J. Park, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 39, 12340 (2014).
Y. Choe, K.-J. Oh, S.-S. Kim and S.-W Park, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 27, 962 (2010).
K.-S. Hwang, L. Han, D.-W Park, K.-J. Oh, S.-S. Kim and S.-W Park, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 27, 241 (2010).
P. Sharma, I.-H. Baek, Y.-W. Park, S.-C. Nam, J.-H. Park, S.-D. Park and S. Y Park, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 29, 249 (2012).
A. Zhao, A. Samanta P. Sarkar and R. Gupta, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 52, 6480 (2013).
R. Dey, R. Gupta and A. Samanta, Sep. Sci. Technol, 53, 2683 (2018).
E.S. Sanz-Pérez, M. Olivares-Marín, A. Arencibia, R. Sanz, G. Calleja and M. M. Maroto-Valer, Int. J Greenh. Gas Con., 17, 366 (2013).
Z. Liu, D. Pudasainee, Q. Liu and R. Gupta, Sep. Purif. Technol., 156, 259 (2015).
R. Kishor and A. K. Ghoshal, Chem. Eng. J., 300, 236 (2016).
T. Zhu, S. Yang, D. K. Choi and K. H. Row, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 27, 1910 (2010).
A. Boonpoke, S. Chiarakorn, N. Laosiripojana, S. Towprayoon and A. Chidthaisong, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 29, 89 (2012).
C. Chen, J. Kim and WS. Ahn, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 31, 1919 (2014).
C. Manianglung, R. M. Pacia and Y. S. Ko, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 36, 1267 (2019).
WJ. Son, J. S. Choi and WS. Ahn, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 113, 31 (2008).
C. Chen, S. T. Yang, W. S. Ahn and R. Ryoo, Chem. Commun., 24, 3627 (2009).
C. Chen, K. S. You, J. W Ahn and WS. Ahn, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 27, 1010 (2010).
X. Ma, X. Wang and C. Song, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 131, 5777 (2009).
A. Olea, E.S. Sanz-Perez, A. Arencibia, R. Sanz and G. Calleja, Adsorption, 19, 2 (2013).
Y K. Bae and O. H. Han, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 106, 304 (2007).
L. C. C. Silva, T. V. S. Reis, I. C. Cosentino, M. C. A. Fantini, J. R. Matos and R. E. Bruns, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 133, 1 (2010).
F. Kleitz, W. Schmidt and F. Schuth, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 65, 1 (2003).
B. Tian, X. Liu, C. Yu, F. Gao, Q. Luo, S. Xie, B. Tu and D. Zhao, Chem. Commun., 11, 1186 (2002).
T. L. Lai, Y.Y. Shu, Y. C. Lin, W.N. Chen and C.B. Wang, Mater. Lett., 63, 1693 (2009).
S.G.d. Avila, L.C.C. Silva and J.R. Matos, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 234, 277 (2016).
M. H. Yuan, L. Wang and R. T. Yang, Langmuir, 30, 8124 (2014).
D. Zhao, J. Feng, Q. Huo, N. Melosh, G. H. Fredrickson, B. F. Chmelka and G. D. Stucky, Science, 279, 548 (1998).
F. Berube and S. Kaliaguine, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 115, 469 (2008).
M. Barczak, K. Michalak-Zwierz, K. Gdula, K. Tyszczuk-Rotko, R. Dobrowolski and A. Dabrowski, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 211, 162 (2015).
M. S. Yilmaz and S. Piskin, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim., 121, 1255 (2015).
Z. Peng and J.-Y Hwang, Int. Mater. Rev., 60, 30 (2015).
L. F. Chen, C. K. Ong, C. P. Neo, V. V. Varadan and V. K. Varadan, Microwave electronics: Measurement and materials characterization, John Wiley & Sons. Ltd., USA (2004).
A.S. Mujumdar, Handbook of industrial drying, fourth Ed., CRC, Boca Raton (2006).
X. Xu, C. Song, J. M. Andresen, B. G. Miller and A. W. Scaroni, Energy Fuels, 16, 1463 (2002).
J. Liu, D. Cheng, Y Liu and Z. Wu, Energy Fuels, 27, 5416 (2013).
W. Klinthong, C. H. Huang and C. S. Tan, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 55, 6481 (2016).
X. Wang, X. Ma, C. Song, D. R. Locke, S. Siefert, R. E. Winans, J. Möllmer, M. Lange, A. Möller and R. Gläser, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 169, 103 (2013).
A. Heydari-Gorji and A. Sayari, Chem. Eng. J., 173, 72 (2011).
A. Samanta, A. Zhao, G. K. H. Shimizu, P. Sarkar and R. Gupta, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 51, 1438 (2012).
A. Sayari and Y. Belmabkhout, J. Am. Chem. Soc, 132, 6312 (2010).
G. Sartori and D. W. Savage, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam., 22, 239 (1983).
T. L. Donaldson, Y. N. Nguyen, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam., 19, 260 (1980).
Acknowledgements
Runa Dey is thankful to Indian Institute of Technology (Indian School of Mines), Dhanbad, India for financial support in the form of a research scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dey, R., Samanta, A. Microwave-synthesized high-performance mesoporous SBA-15 silica materials for CO2 capture. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 37, 1951–1962 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-020-0596-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-020-0596-0