Abstract
Objective
To investigate gene mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and K-RAS (Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene) in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and study the correlation with its protein expression and its clinical significance on gefitinib.
Methods
Detect the EGFR and K-RAS gene mutations status by gene sequencing and use the method of immunohistochemistry to detect EGFR and K-RAS protein expression.
Results
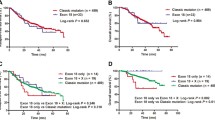
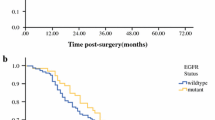
The frequency of EGFR mutations was 33%, mainly located in exon 19 and exon 21. The frequency of K-RAS mutations was 5.5%, mainly located in codon 12. There was no case which both had EGFR and K-RAS mutations, suggesting a mutually exclusive relationship between the two. EGFR mutations are more common in adenocarcinomas (particularly those with bronchioloalveolar features), nonsmokers and females. 16% were detected EGFR positive expression and had no correlation with EGFR mutation (P > 0.05), but had significant correlation with mutation in exon 19 (P < 0.05). The frequency of K-RAS positive expression was 52.5% and had no correlation with K-RAS mutation (P > 0.05). Twelve (8 cases were protein-negative) out of 15 gefitinib-treated NSCLC patients with disease control carry EGFR mutations.
Conclusion
EGFR protein expression has some correlation with exon 19 mutations. Combined detection of EGFR and K-RAS gene mutations can help clinicians to choose patients who may benefit from EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) and to predict the response and prognosis of gefitinib.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tamura K, Okamoto I, Kashii T, et al. Multicentre prospective phase II trial of gefitinib for advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: results of the West Japan Thoracic Oncology Group trial (WJTOG0403). Br J Cancer 2008; 98: 907–914.
Ahn MJ, Park BB, Ahn JS, et al. Are there any ethnic differences in molecular predictors of erlotinib efficacy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer? Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 3860–3866.
Parra HS, Cavina R, Latteri F, et al. Analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor expression as a predictive factor for response to gefitinib (’Iressa’, ZD1839) in non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 2004; 91: 208–212.
Tsao MS, Sakurada A, Cutz JC, et al. Erlotinib in lung cancer: molecular and clinical predictors of outcome. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 133–144.
Yin GH, Liu W, Liu GJ, et al. Comparison between EGFR and EGFR mutation in non-small cell lung cancer. Zhongguo Shi Yan Zhen Duan Xue Za Zhi 2009; 13: 200–202 (Chinese).
Pinter F, Papay J, Almasi A, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) high gene copy number and activating mutations in lung adenocarcinomas are not consistently accompanied by positivity for EGFR protein by standard immunohistochemistry. J Mol Diagn 2008; 10: 160–168.
Kim KS, Jeong JY, Kim YC, et al. Predictors of the response to gefitinib in refractory non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 2244–2251.
Kang SM, Kang HJ, Shin JH, et al. Identical epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in adenocarcinomatous and squamous cell carcinomatous components of adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung. Cancer 2007; 109: 581–587.
Dacic S, Flanagan M, Cieply K, et al. Significance of EGFR protein expression and gene amplification in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 2006; 125: 860–865.
Macarenco RS, Uphoff TS, Gilmer HF, et al. Salivary gland-type lung carcinomas: an EGFR immunohistochemical, molecular genetic and mutational analysis study. Mod Pathol 2008; 21: 1168–1175.
Li AR, Chitale D, Riely GJ, et al. EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: clinical testing experience and relationship to EGFR gene copy number and immunohistochemical expression. J Mol Diagn 2008; 10: 242–248.
Sun GY, Zhao XW, Li B, et al. Expression and clinical significance of epidermal growth factor receptor in female non-small-cell lung cancer. Zhongguo Ai Zheng Za Zhi 2007; 17: 380–384 (Chinese).
Massarelli E, M VG, Tang X, et al. KRAS mutation is an important predictor of resistance to therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 2890–2896.
Marchetti A, Milella M, Felicioni L, et al. Clinical Implications of KRAS Mutations in Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: An Important Role for mutations in Minor Clones. Neoplasia 2009; 11: 1084–1092.
Jang TW, Oak CH, Chang HK, et al. EGFR and KRAS mutations in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung. Korean J Intern Med 2009; 24: 48–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Luan, Hl., Sun, Ln., Dong, N. et al. Study of the correlation of EGFR and K-RAS gene mutations with its protein expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Oncol. Cancer Res. 7, 97–102 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11805-010-0502-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11805-010-0502-3