Abstract
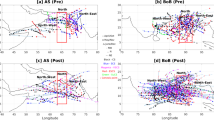
Characteristics of cyclones and explosively developing cyclones (or ‘bombs’) over the Southern Ocean in austral summer (December, January and February) from 2004 to 2008 are analyzed by using the Final Analysis (FNL) data produced by the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) of the United States. Statistical results show that both cyclones and explosively developing cyclones frequently develop in January, and most of them occur within the latitudinal zone between 55°S and 70°S. These cyclones gradually approach the Antarctic Continent from December to February. Generally cyclones and bombs move east-southeastward with some exceptions of northeastward movement. The lifetime of cyclones is around 2–6 d, and the horizontal scale is about 1000 km. Explosive cyclones have the lifetime of about 1 week with the horizontal scale reaching up to 3000 km. Compared with cyclones developed in the Northern Hemisphere, cyclones over the southern ocean have much higher occurrence frequency, lower central pressure and larger horizontal scale, which may be caused by the unique geographical features of the Southern Hemisphere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carleton, A. M., 1979. A synoptic climatology of satellite-observed extratropical cyclone activity for the Southern Hemisphere winter. Archiv für Meteorologie, Geophysik und Bioklimatologie, B27: 265–279.
Carleton, A. M., and Fitch, M., 1993. Synoptic aspects of Antarctic mesocyclones. Journal of Geohpysical Research, 98: 12 997–13 018.
Chen, J. N., Le, K. T., Jia, C. M., and Peng, Y., 2000. The change of the frequency of cyclone occurrence in the southern hemisphere influence on SST in the East Pacific and Southern Oscillation. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 22(3): 86–93.
Chen, S. J., Kuo, Y. H., Zhang, P. Z., and Bai, Q. F., 1991. Synoptic climatology of cyclogenesis over East Asia, 1958–1987. Monthly Weather Review, 119: 1407–1418.
Jones, D. A., and Simmonds, I., 1993. Time and space spectral analyses of Southern Hemisphere sea level pressure variability. Monthly Weather Review, 121: 661–672.
Lim, E.-P., and Simmonds, I., 2002. Explosive cyclone development in the Southern Hemisphere and a comparison with Northern Hemisphere events. Monthly Weather Review, 130: 2188–2209.
Qu, W. Z., Chen, X. R., Shen, R. S., and Wang, H. G., 2001. Some characteristics of general circulation at sea level of the Southern Hemisphere. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai and Bohai Seas, 19(1): 9–16.
Roebber, P. J., 1984. Statistical Analysis and Updated Climatology of Explosive Cyclones. Monthly Weather Review, 112: 1577–1589.
Sanders, F., 1986. Explosive cyclogenesi in the west-central North Atlantic Ocean, 1981–84. Part I: Composite structure and mean behavior. Monthly Weather Review, 114: 1781–1794.
Sanders, F., and Gyakum, J. R., 1980. Synoptic-dynamic climatology of the ‘bomb’. Monthly Weather Review, 108: 1589–1606.
Simmonds, I., and Keay, K., 2000a. Variability of Southern Hemisphere extratropical cyclones behavior, 1958–97. Journal of Climate, 13: 550–561.
Simmonds, I., and Keay, K., 2000b. Mean Southern Hemisphere extratropical cyclones behavior in the 40-year NCEP-NCAR reanalysis. Journal of Climate, 13: 873–885.
Simmonds, I., Keay, K., and Lim, E.-P., 2003. Synoptic activity in the seas around Antarctica. Monthly Weather Review, 131: 272–288.
Sinclair, M. R., 1995. A climatology of cyclogenesis for the Southern Hemisphere. Monthly Weather Review, 123: 1601–1919.
Streten, N. A., and Troup, A. J., 1973. A synoptic climatology of satellite-observed cloud vortices over the southern hemisphere. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 99: 56–72.
Taljaard, J. J., 1967. Development, distribution, and movement of cyclones and anticyclones in the Southern Hemisphere during the IGY. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 6: 973–987.
Van Loon, H., 1965. A climatological study of the atmospheric circulation in the Southern Hemisphere during the IGY, Part I: 1 July 1957–31 March 1958. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 4: 479–491.
Wang, C. C., and Rogers, J. C., 2001. A composite study of explosive cyclogenesis in different sectors of the North Atlantic. Part I: Cyclone structure and evolution. Monthly Weather Review, 129: 1481–1499.
Yoshida, A., and Asuma, Y., 2004. Structures and environment of explosively developing extratropical cyclones in the Northwestern Pacific region. Monthly Weather Review, 132: 1121–1142.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, N., Fu, G. & Kuo, YH. Statistical characteristics of austral summer cyclones in Southern Ocean. J. Ocean Univ. China 11, 118–128 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-012-1828-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-012-1828-7