Abstract
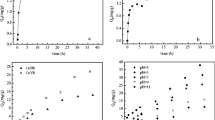
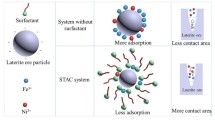
To shorten the bioleaching cycle of arsenic-containing gold concentrate, surfactants were used to promote the interaction between bacteria and ore to increase the arsenic leaching rate. Three different kinds of surfactants were used to evaluate the effects of surfactants on the growth of bacteria and arsenic leaching rate of arsenic-containing gold concentrate. The mechanism underlying surfactant enhancement was also studied. Results show that when relatively low-concentration surfactants are added to the medium, no significant difference is observed in the growth and Fe2+ oxidation ability of the bacteria compared with no surfactant in the medium. However, only the anionic surfactant calcium lignosulfonate and the nonionic surfactant Tween 80 are found to improve the arsenic leaching rates. Their optimum mass concentrations are 30 and 80 mg/L, respectively. At such optimum mass concentrations, the arsenic leaching rates are approximately 13.7% and 9.1% higher than those without the addition of surfactant, respectively. Mechanism research reveals that adding the anionic surfactant calcium lignosulfonate improves the percentage of bacterial adhesion on the mineral surface and decreases the surface tension in the leaching solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CUI Ri-cheng, YANG Hong-ying, ZHANG Gu-ping, MA Yu-rui, FAN Jin, LI Ke-feng. Biooxidation of high arsenic gold concentrate with arsenopyrite type [J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2008, 59(12): 3090–3094. (in Chinese)
LUO Zhi-xiong, ZHANG Guang-ji, FANG Zhao-heng. Bioleaching arsenic-containing gold concentrates with MLY and At.f [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(8):1342–1347. (in Chinese)
YANG Wei, QIN Wen-qing, LIU Rui-qiang, REN Yun-chao. Extraction of Au from high arsenic refractory gold concentrate by bacterial oxidation-cyanidation [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(5): 1151–1158. (in Chinese)
WIERTZ J V, MATEO M, ESCOBAR B. Mechanism of pyritecatalysis of As(III) oxidation in bioleaching solutions at 30 °C and 70 °C [J]. H Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 83(1/2/3/4): 35–39
MARQUEZ M, GASPAR J, BESSLER K E, MAGELA G. Process mineralogy of bacterial oxidized gold ore in Sao Bento Mine(Brasil) [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 83(1/4): 114–123.
BRIERLEY J A, BRIERLEY C L. Present and future commercial applications of biohydrometallurgy [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 59(2/3): 233–239.
SUN Li-xin, ZHANG Xu, TAN Wen-song, ZHU Ming-long. Effect of agitation on the biooxidation process of refractory gold concentrates by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 127–128: 99–103.
ARRASCUE M L, NIEKERK J V. Biooxidation of arsenopyriteconcentrate using BIOX process: Industrial experience in Tamboraque, Peru [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 83(1/2/3/4): 90–96.
JIANG Tao, LI Qian, YANG Yong-bin, LI Guang-hui, QIU Guan-zhou. Bio-oxidation of arsenopyrite [J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2008, 18(6): 1433–1438.
TORMA A E, GABRA G C. Effects of surface active agents on the oxidation of chalcopyrite by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1975, 1(4): 301–309.
ZHANG D C, ZHU L, LUO X G. Effect of nonionic surfactants in bacteria leaching of chalcopyrite at low temperature [J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog, 2008, 27(4): 540–543. (in Chinese)
OWUSU G, DREISINGER D B, PETERS E. Effect of surfactants on zinc and iron dissolution rates during oxidative leaching of sphalerite [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1995, 38(3): 315–319.
CHAI Li-yuan, CHEN Li-juan, HUANG Yan, SHU Yu-de, SU Yan-rong. Influence of surfactants on detoxification of chromium-containing slag by Achromobacter sp. CH-1 [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2009, 40(1): 41–47. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Cheng-gui, XIA Jin-lan, ZHANG Rui-yong, QIU Guan-zhou. Comparative study on effects of Tween-80 and sodium isobutyl-xanthate on growth andsulfur-oxidizing activities of Acidithiobacillus albertensis BY-05 [J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(4): 1003–1007.
GONG wen-qi, ZHANG xiao-zheng, LIU yan-ju. Influence of surfactants on leaching of phosphate ore with acidithiobacillus thiooxidans [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2007, 8(1): 61–64. (in Chinese)
AFZAL G M, OKIBE N, BARRIE J D. Attachment of acidophilic bacteria to solid surfaces: The significance of species and strain variations [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2007, 85(2/3/4): 72–80.
WU Ai-xiang, AI Chun-ming, WANG Yi-ming, LI Xi-wen. Surfactant accelerating leaching of copper ores [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2013, 5(6): 709–713. (in Chinese)
SUN Li-xin, ZHANG Xu, TAN Wen-song, ZHU Ming-long, LIU Rui-qiang, LI Chun-qiang. Rheology of pyrite slurry and its dispersant for the biooxidation process [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 104(2): 178–185.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(51104024, 51374043) supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(10JJ6019) supported by Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China; Project(10C0399) supported by Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department, China; Project(2014SK3182) supported by Hunan Provincial Science & Technology Department, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, F., Zhong, H., Jiang, Fm. et al. Influence of surfactants on bioleaching of arsenic-containing gold concentrate. J. Cent. South Univ. 21, 3963–3969 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2384-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2384-7