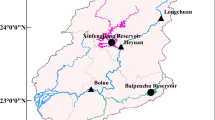
Abstract
Flooding is the most prevalent and costly natural disaster in the world and building reservoirs is one of the major structural measures for flood control and management. In this paper, a framework was proposed to evaluate functions of reservoirs′ locations and magnitudes on daily peak flow attenuation for a large basin of China, namely Ganjiang River Basin. In this study, the Xinanjiang model was adopted to simulate inflows of the reservoirs and flood hydrographs of all sub-catchments of the basin, and simple reservoir operation rules were established for calculating outflows of the reservoirs. Four reservoirs scenarios were established to analyze reservoirs′ locations on daily peak flow attenuation. The results showed that: 1) reservoirs attenuated the peak discharges for all simulated floods, when the flood storage capacities increase as new reservoirs were built, the peak discharge attenuation by reservoirs showed an increasing tendency both in absolute and relative measures; 2) reservoirs attenuated more peak discharge relatively for small floods than for large ones; 3) reservoirs reduced the peak discharge more efficiently for the floods with single peak or multi peaks with main peak occurred first; and 4) effect of upstream reservoirs on peak attenuation decreased from upper reaches to lower reaches; upstream and midstream reservoirs played important roles in decreasing peak discharge both at middle and lower reaches, and downstream reservoirs had less effect on large peak discharge attenuation at outlet of the basin. The proposed framework of evaluating functions of multiple reservoirs′ storage capacities and locations on peak attenuation is valuable for flood control planning and management at basin scale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acreman M C, Farquharson F A K, McCartney M P et al., 2000. Managed Flood Releases from Reservoirs: Issues and Guidance. Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, Wallingford, UK.
Ayalew T B, Krajewski W F, Mantilla R, 2013. Exploring the effect of reservoir storage on peak discharge frequency. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 18(12): 1697–1708. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000721
Bao H J, Zhao L N, He Y et al., 2011. Coupling ensemble weather predictions based on TIGGE database with Grid-Xinanjiang Model for flood forecast. Advances in Geosciences, 29 (6): 61–67. doi: 10.5194/adgeo-29-61-2011
Chen Y W, Tsai J P, Chang L C et al., 2014. The development of a real-time flooding operation model in the Tseng-Wen Reservoir. Hydrology Research, 45(3): 490–503. doi: 10.2166/nh.2013.301
Cheng C T, Chau K W, 2001. Fuzzy iteration methodology for reservoir flood control operation. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 37(5): 1381–1388. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-1688.2001.tb03646.x
Cheng C T, Chau K W, 2004. Flood control management system for reservoirs. Environmental Modelling & Software, 19(12): 1141–1150. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2003.12.004
Cheng C T, Zhao M Y, Chau K W et al., 2006. Using genetic algorithm and TOPSIS for Xinanjiang model calibration with a single procedure. Journal of Hydrology, 316(1–4): 129–140. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.04.022
Chou F N F, Wu C W, 2015. Stage-wise optimizing operating rules for flood control in a multi-purpose reservoir. Journal of Hydrology, 521: 245–260. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.11.073
Connaughton J, King N, Dong L et al., 2014. Comparing simple flood reservoir operation rules. Water, 6(9): 2717–2731. doi: 10.3390/w6092717
De Paes R P, Brandão J L B, 2013. Flood control in the Cuiabá River Basin, Brazil, with multipurpose reservoir operation. Water Resources Management, 27(11): 3929–3944. doi: 10.1007/s11269-013-0388-y
Dittmann R, Froehlich F, Pohl R et al., 2009. Optimum multiobjective reservoir operation with emphasis on flood control and ecology. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 9(6): 1973–1980. doi: 10.5194/nhess-9-1973-2009
Ford D T, Killen J R, 1995. PC-based decision-support system for Trinity River, Texas. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 121(5): 375–381. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(1995)121:5(375)
Hickey J T, Bond M V, Patton T K et al., 2003. Reservoir simulations of synthetic rain floods for the Sacramento and San Joaquin river basins. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 129(6): 443–457. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2003)129:6(443)
Jenicek M, 2008. Modelling the effect of small reservoirs on flood regime in the Chomutovka river basin. In: Brilly M and Šraj M. XXIVth Conference of the Danubian Countries on the Hydrological Forecasting and Hydrological Bases of Water Management. Slovenian National Committee for the IHP UNESCO, Ljubljana, 1–7.
Jordan F M, Boillat J, Schleiss A J, 2012. Optimization of the flood protection effect of a hydropower multi-reservoir system. International Journal of River Basin Management, 10(1): 65–72. doi: 10.1080/15715124.2011.650868
Kumar D N, Baliarsingh F, Raju K S, 2010. Optimal reservoir operation for flood control using folded dynamic programming. Water Resources Management, 24(6): 1045–1064.doi: 10.1007/s11269-009-9485-3
Lee K, Chang C, Yang M et al., 2001. Reservoir attenuation of floods from ungauged basins. Hydrological Science Journal, 46(3): 349–362. doi: 10.1080/02626660109492831
Li H, Zhang Y, Chiew F et al., 2009. Predicting runoff in ungauged catchments by using Xinanjiang model with MODIS leaf area index. Journal of Hydrology, 370(1–4): 155–162. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.03.003
Li H, Zhang Y, Vaze J et al., 2012. Separating effects of vegetation change and climate variability using hydrological modelling and sensitivity-based approaches. Journal of Hydrology, 420(7): 403–418. doi: 10.1007/s11431-012-4859-9
López-Moreno J I, Beguería S, García-Ruiz J M, 2002. Influence of the Yesa Reservoir on floods of the Aragón River, central Spanish Pyrenees. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 6(4): 753–762. doi: 10.5194/hess-6-753-2002
Luo J G, Qi Y T, Xi J C et al., 2015. A hybrid multi-objective PSO-EDA algorithm for reservoir flood control operation. Applied Soft Computing, 34: 526–538. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.05.036
Nash J E, Sutcliffe J V, 1970. River flow forecasting through conceptual models: Part 1. A discussion of principles. Journal of Hydrology, 10(3): 282–290. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(70) 90255-6
Ngo L L, Madsen H, Rosbjerg D et al., 2008. Implementation and comparison of reservoir operation strategies for the Hoa Binh Reservoir, Vietnam using the Mike 11 Model. Water Resources Management, 22(4): 457–472. doi: 10.1007/s11269-007-9172-1
Song X M, Kong F Z, Zhan C H et al., 2012. Hybrid optimization rainfall–runoff simulation based on Xinanjiang model and artificial neural network. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 17(9): 1033–1041. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000548
Schultz B, 2002. Role of dams in irrigations, drainage and flood control. International Journal of Water Resources Development, 18(1): 147–162. doi: 10.1080/07900620220121710
Seibert S P, Skublics D, Ehret U, 2014. The potential of coordinated reservoir operation for flood mitigation in large basins: a case study on the Bavarian Danube using coupled hydrological-hydrodynamic models. Journal of Hydrology, 517(1): 1128–1144. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.06.048
Shi P, Chen C, Srinivasan R et al., 2011. Evaluating the SWAT model for hydrological modeling in the Xixian Watershed and a comparison with the XAJ model. Water Resources Management, 25(10): 2595–2612. doi: 10.1007/s11269-011-9828-8
Simonovic S P, 2002. Two new non-structural measures for sustainable management of floods. Water International, 27(1): 38–46. doi: 10.1080/02508060208686976
Wang G Q, Xu Z X, 2011. Assessment on the function of reservoirs for flood control during typhoon seasons based on a distributed hydrological model. Hydrological Processes, 25(16): 2506–2517. doi: 10.1002/hyp.8023
WMO (World Meteorological Organization), 2006. Environmental Aspects of Integrated flood Management, APFM Technical Document No.3, Flood Management Policy Series. Geneva: Associated Programme on Flood Management, World Meteorological Organization, WMO, No.1009.
Wu Y, Chen J, Sivakumar B, 2007. Numerical modeling of operation and hydrologic effects of Xinfengjiang Reservoir in southern China. In: Oxley L et al. (eds). MODSIM 2007 International Congress on Modeling and Simulation. Modeling and Simulation Society of Australia and New Zealand, 1561–1567.
Xu J, 1990. Downstream hydrological effects of reservoirs built in mountainous areas and their environmental influences. In: Sinniger O et al. (eds). Hydrology in Mountainous Regions. II Artificial Reservoirs: Water and Slopes. Wallingford: IAHS Publication, 194: 187–194.
Xu C Y, Singh V P, 2001. Evaluation and generalization of temperature-based methods for calculating evaporation. Hydrological Processes, 15(2): 305–319. doi: 10.1002/hyp.119
Yang D, Koike T, Tanizawa H, 2004. Application of a distributed hydrological model and weather radar observations for flood management in the upper Tone River of Japan. Hydrological Processes, 18(16): 3119–3132. doi: 10.1002/hyp.5752
Yao C, Li Z, Bao H et al., 2009. Application of a developed Grid-Xinanjiang Model to Chinese watersheds for flood forecasting purpose. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 14(9): 923–934. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000067
Zhang D, Zhang L, Guan Y et al., 2012. Sensitivity analysis of Xinanjiang rainfall-runoff model parameters: a case study in Lianghui, Zhejiang Province, China. Hydrology Research, 43(1–2): 123–134. doi: 10.2166/nh.2011.131
Zhang Y, You Q, Lin H et al., 2015. Analysis of dry/wet conditions in the Gan River Basin, China, and their association with large-scale atmospheric circulation. Global and Planetary Change, 133: 309–317. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2015.09.005
Zhao R, 1992. The Xinanjiang model applied in China. Journal of Hydrology, 135 (1–4): 371–381. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(92)90096-E
Zhao R, Zhuang Y, Fang L et al., 1980. The Xinanjiang Model. Hydrological Forecasting. Wallingford: IAHS Publication, 129: 351–356.
Zhou Y L, Guo S L, Liu P et al., 2014. Joint operation and dynamic control of flood limiting water levels for mixed cascade reservoir systems. Journal of Hydrology, 519(3): 248–257. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.07.029
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of Commonwealth and Specialized Programs for Scientific Research, Ministry of Water Resources of China (No. 200901042)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, J., Zheng, D., Xu, Y. et al. Evaluating functions of reservoirs′ storage capacities and locations on daily peak attenuation for Ganjiang River Basin using Xinanjiang model. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 26, 789–802 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-016-0838-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-016-0838-6