Abstract
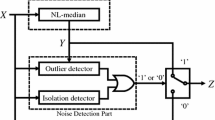
A predictive-based adaptive switching median filter for impulse noise removal using neural network-based noise detector (PASMF) is presented. The PASMF has a noise detector stage and a noise filtering stage. The noise detector implemented using feed forward neural network detects impulse noises in the corrupted image. The filter is a modified median filter, which removes detected impulse noise from the image. In contrast to the standard median filter, the PASMF computes the median value after predicting the appropriate values for neighboring corrupted pixels of the current central pixel in the filtering window. The results show that the PASMF gives better performance visually as well as in terms of different performance measures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gonzalez R.C., Woods R.E.: Digital Image Processing. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (2008)
Jain A.K.: Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing, Original Edition. Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River (1989)
Chanda B., Majumder D.D.: Digital Image Processing and Analysis. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (2008)
Ko S.J., Lee Y.H.: Center weighted median filters and their application to image enhancement. In: IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 38(9), 984–993 (1991)
Bovik A.: Handbook of Image and Video Processing. Academic, New York (2000)
Eng H.-L., Ma K.-K.: Noise adaptive soft-switching median filter. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10(2), 242–251 (2001)
Zhang S., Karim M.A.: A new impulse detector for switching median filters. In: IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 9(4), 360–363 (2002)
Chen T., Ma K.K., Chen L.H.: Tri-state median filter for image denoising. In: IEEE Trans. Image Process. 8(12), 1834–1838 (1999)
Luo W.: An efficient detail-preserving approach for removing impulse noise in images. In: IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 13(7), 413–417 (2006)
Dong Y., Xu S.: A new directional weighted median filter for removal of random-value impulse noise. In: IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 14(3), 193–196 (2007)
Kang C.C., Wang W.J.: Modified switching median filter with one more noise detector for impulse noise removal. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 63, 998–1004 (2009)
Salomon D.: Data Compression: The Complete Reference, pp. 240–241. Springer, Berlin (2000)
Wang Z., Bovik A.C.: A universal image quality index. In: IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 9(3), 81–84 (2002)
Nair, M.S., Raju, G.: A new fuzzy-based decision algorithm for high-density impulse noise removal. Signal Image Video Process. doi:10.1007/s11760-010-0186-4
Wang Z., Bovik A.C., Sheikh H.R., Simoncelli E.P.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. In: IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Ng P.-E., Ma K.-K.: A switching median filter with boundary discriminative noise detection for extremely corrupted images. In: IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(6), 1506–1516 (2006)
Dong Y., Chan R.H., Xu S.: A detection statistic for random-valued impulse noise. In: IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16(4), 1112–1120 (2007)
Yüksel M.E., Besd E.: A simple neuro-fuzzy impulse detector for efficient blur reduction of impulse noise removal operators for digital images. In: IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 12(6), 854–865 (2004)
Yüksel M.E.: A hybrid neuro-fuzzy filter for edge preserving restoration of images corrupted by impulse noise. In: IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(4), 928–936 (2006)
Kaliraj G., Baskar S.: An Efficient approach for the removal of impulse noise from the corrupted image using neural network based impulse detector. Image Vis. Comput. 28, 458–466 (2010)
Akkoul S., Ledee R., Leconge R., Harba R.: A new adaptive switching median filter. In: IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(6), 587–590 (2010)
Garnett R., Huegerich T., Chui C., He W.: A universal noise removal algorithm with an impulse detector. In: IEEE Trans. Image Process 14(11), 1747–1754 (2005)
Schulte S., Nachtegael M., De Witte V., Van der Weken D., Kerre E.E.: A fuzzy impulse noise detection and reduction method. In: IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(5), 1153–1162 (2006)
Bigand A., Colot O.: Fuzzy filter based on interval-valued fuzzy sets for image filtering. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 161, 96–117 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, M.S., Shankar, V. Predictive-based adaptive switching median filter for impulse noise removal using neural network-based noise detector. SIViP 7, 1041–1070 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-012-0310-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-012-0310-8