Abstract
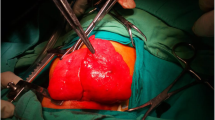
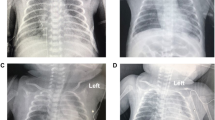
Congenital lobar overinflation is characterized by disruption of bronchopulmonary development which produces lobar or segmental bronchial abnormalities and overinflation of normal lung tissue. This is a 44-year old man, never smoker, who presents dyspnea every time he arrived in highlands, marked decreased breathing sounds and hyperresonance in the left hemithorax. Imaging studies suggested left upper lobe overinflation. The affected area was resected resulting in symptoms improvement. Accepted treatment is resection, however conservative management has been proposed for asymptomatic patients because cases of spontaneous improvement have been described. We recommend close monitoring and resection if symptoms or overinflation progress.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pariente G, Aviram M, Landau D, Hershkovitz R. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital lobar emphysema: case report and review of the literature. J Ultrasound Med. 2009;28(8):1081–4.
Mei-Zahav M, Konen O, Manson D, Langer JC. Is congenital lobar emphysema a surgical disease? J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41:1058–61.
Demir OF, Hangul M, Kose M. Congenital lobar emphysema: diagnosis and treatment options. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:921–8.
King N, Ramesh SS, Essandoh M, Merritt RE. Near complete obliteration of the left hemithorax by congenital lobar emphysema in an adult. Ann Thoracic Surg. 2017;104(5):e369.
PérezRuiz E, Caro Aguilera P, MorenoMedinilla E, PérezFrías FJ, HermosoTorregrosa C. Hiperinsuflación lobar congénita: manejo conservador como alternativa terapéutica. Anal Pediatr. 2014;81(81):45–8.
Dillman JR, Sanchez R, Ladino-Torres MF, Yarram SG, Strouse PJ, Lucaya J. Expanding upon the unilateral hyperlucent hemithorax in children. RadioGraphics. 2011;31:723–41.
Berend N, Woolcock AJ, Marlin GE. Relationship between bronchial and arterial diameters in normal human lungs. Thorax. 1979;34:354–8.
Minira B, Anna M, Aigul B. Case of congenital lobar lung emphysema. J Histol Histopathol. 2014;1:13.
Sadaqat M, Malik JA, Karim R. Congenital Lobar Emphysema in an adult. Lung India. 2011;28(1):67–9.
Sasieta HC, Nichols FC, Kuzo RS, Boland JM, Utz JP. Congenital Lobar Emphysema in an Adult. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;194(3):377–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have a conflict of interest regarding the subject of this article, however one of the authors (SIM) belonged to the Advisory Board and has received fees for Lectures from Ethicon, Medtronic, AstraZeneca y Roche S.A.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández, A., Martínez, S.I., Prada, G. et al. Management of congenital lobar overinflation in an adult. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 69, 163–167 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-020-01444-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-020-01444-w