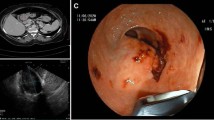
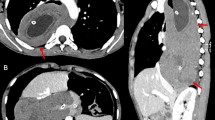
Abstract
Alport–leiomyomatosis syndrome is an extremely rare condition occurring at a young age in which Alport syndrome coexists with diffuse leiomyomatosis of the digestive tract (primarily the esophagus). Most patients with diffuse esophageal leiomyomatosis require esophagectomy of variable extents. A 20-year-old man with Alport–leiomyomatosis syndrome was diagnosed with dysphasia and hematuria in childhood. Although he underwent partial esophagogastrectomy at 8 years of age, extremely severe gastroesophageal reflux symptoms were noted postoperatively. He was diagnosed with refractory severe reflux esophagitis associated with diffuse leiomyomatosis and esophagogastric anastomosis, for which he underwent subtotal esophagectomy, gastric tube reconstruction, and esophagogastric anastomosis in the left neck. The postoperative course was generally good, and he had no postoperative reflux symptoms. To achieve long-term control of symptoms, the lesion must be removed completely; nevertheless, unnecessarily extensive esophagectomy should be avoided.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uliana V, Marcocci E, Mucciolo M, Meloni I, Izzi C, Manno C, et al. Alport syndrome and leiomyomatosis: the first deletion extending beyond COL4A6 intron 2. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011;26:717–24.
Hasstedt SJ, Atkin CL. X-linked inheritance of Alport syndrome: family P revisited. Am J Hum Genet. 1983;35:1241–51.
Pajari H, Kääriäinen H, Muhonen T, Koskimies O. Alport's syndrome in 78 patients: epidemiological and clinical study. Acta Paediatr. 1996;85:1300–6.
Persson U, Hertz JM, Wieslander J, Segelmark M. Alport syndrome in southern Sweden. Clin Nephrol. 2005;64:85–90.
García-Torres R, Orozco L. Alport-leiomyomatosis syndrome: an update. Am J Kidney Dis. 1993;22:641–8.
Ulíbarri JI, González-Madroño A, Villar NG, González P, González B, Mancha A, et al. CONUT: a tool for controlling nutritional status. First validation in a hospital population. Nutr Hosp. 2005;20:38–45.
Ziogas IA, Mylonas KS, Tsoulfas G, Spartalis E, Zavras N, Nikiteas N, et al. Diffuse esophageal leiomyomatosis in pediatric patients: a systematic review and quality of evidence assessment. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1676507.
Dagbert F, Pelascini E, Pasquer A, Gincul R, Mion F, Poncet G, et al. Extensive preoperative workup in diffuse esophageal leiomyomatosis associated with Alport syndrome influences surgical treatment: a case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;10:183–6.
Sousa RG, Figueiredo PC, Pinto-Marques P, Meira T, Novais LA, Vieira AI, et al. An unusual cause of pseudoachalasia: the Alport syndrome-diffuse leiomyomatosis association. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;25:1352–7.
Antignac C, Zhou J, Sanak M, Cochat P, Roussel B, Deschenes G, et al. Alport syndrome and diffuse leiomyomatosis: deletions in the 5' end of the COL4A5 collagen gene. Kidney Int. 1992;42:1178–83.
Savige J, Gregory M, Gross O, Kashtan C, Ding J, Flinter F. Expert guidelines for the management of Alport syndrome and thin basement membrane nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;24:364–75.
Jais JP, Knebelmann B, Giatras I, De Marchi M, Rizzoni G, Renieri A, et al. X-linked Alport syndrome: natural history and genotype-phenotype correlations in girls and women belonging to 195 families: a “European Community Alport Syndrome Concerted Action” study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:2603–10.
Nochaiwong S, Ruengorn C, Awiphan R, Koyratkoson K, Chaisai C, Noppakun K, et al. The association between proton pump inhibitor use and the risk of adverse kidney outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018;33:331–42.
Garritano S, Irino T, Scandavini CM, Tsekrekos A, Lundell L, Rouvelas I. Long-term functional outcomes after replacement of the esophagus in pediatric patients: a systematic literature review. J Pediatr Surg. 2017;52:1398–408.
Irino T, Tsekrekos A, Coppola A, Scandavini CM, Shetye A, Lundell L, et al. Long-term functional outcomes after replacement of the esophagus with gastric, colonic, or jejunal conduits: a systematic literature review. Dis Esophagus. 2017;30:1–11.
Acknowledgements
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Shigeki Yamaguchi received honoraria from Johnson & Johnson, Covidien Japan Inc., Terumo Corp., and Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and received a research grant from Sysmex Corp.
Informed consent
For this report, we obtained informed consent from the patient.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aoyama, J., Miyawaki, Y., Kato, T. et al. Alport–leiomyomatosis syndrome requiring subtotal esophagectomy for refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease after childhood partial esophagogastrectomy: a case report. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 68, 199–203 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-019-01255-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-019-01255-8