Abstract
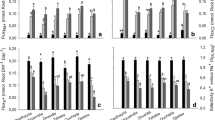
Salt stress perturbs a multitude of physiological processes such as photosynthesis and growth. To understand the biochemical changes associated with physiological and cellular adaptations to salinity, two lettuce varieties (Verte and Romaine) were grown in a hydroponics culture system supplemented with 0, 100 or 200 mM NaCl. Verte displayed better growth under 100 mM NaCl compared to Romaine, but both genotypes registered relatively similar reductions in growth under 200 mM NaCl treatment. Both varieties showed differences in net photosynthetic activity in the absence of salt and 8 days after salt treatment. These differences diminished subsequently under prolonged salt stress (14 days). Verte showed enhanced leaf proline and restricted total cations especially Na+, lesser malondialdehyde (MDA) formation and lignification in the roots under 100 mM NaCl salinity. Membrane damage estimated by electrolyte leakage increased with elevated salt concentrations in roots of both varieties, but Verte had significantly lower electrolyte leakage relative to Romaine under 100 mM NaCl. Moreover, Verte also accumulated greater levels of carotenoids under increasing NaCl concentrations compared to Romaine. Taken together, these findings suggest that the greater tolerance of Verte to 100 mM NaCl is related to the more restricted accumulation of total cations and toxic Na+ in the roots and enhanced levels of antioxidative metabolites in root and leaf tissue.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EL:
-
Electrolyte leakage
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- Pro:
-
Proline
References
Annalisa R, Patrizia P, Carlotta G, Graziano S, Antonio C, Daniela H (2002) Polyphenols in greenhouse and open-air-grown lettuce. Food Chem 79:337–342
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in chloroplasts phenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Ashraf M, McNeilly T (1990) Responses of four Brassica species to sodium chloride. Environ Exp Bot 30:475–487
Ashraf M, Naqvi M (1991) Growth and ion uptake of four Brassica species as affected by Na/Ca ratio in saline sand culture. Z Pflanzenemiihr Bodenkd 155:101–108
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Bhandal IS, Malik CP (1988) Potassium estimation, uptake and its role in the physiology and metabolism of flowering plants. Int Rev Cytol 10:205–224
Bilgin O, Baser I, Korkut KZ, Balkan A, Saglam N (2008) The impacts on seedling root growth of water and salinity stress in maize (zea mays indentata sturt.). Bulgarian J Agricul Sci 14:313–320
Blaha G, Stelzl U, Spahn CMT, Agrawal RK, Frank J, Nierhaus KH (2000) Preparation of functional ribosomal complexes and effect of buffer conditions on tRNA positions observed by cryoelectron microscopy. Methods Enzymol 317:292–309
Cachorro P, Ortiz A, Cerda A (1994) Implications of calcium nutrition on the response of Phaseolus vulgaris L. to salinity. Plant Soil 159:205–212
Cramer GR, Epstein E, Laûchli A (1989) Na–Ca interactions in barley seedlings: relationship to ion transport and growth. Plant Cell Environ 12:551–558
Delauney AJ, Verma DPS (1993) Proline biosynthesis and osmoregulation in plants. Plant J 4:215–223
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (2005) Effects of salinity on sodium content and photosynthetic responses of rice seedlings differing in salt tolerance. J Plant Physiol 157:54–58
Dubey RS (2005) Photosynthesis in plants under stressful conditions In: Photosynthesis Handbooks. CRC Press, New York, pp 717–718
El-Hendawy SE, Hu Y, Schmidhalter U (2005) Growth, ion content, gas exchange, and water relations of wheat genotypes differing in salt tolerances. Aust J Agric Res 56:123–134
Elkahoui S, Hernández JA, Abdelly C, Ghrir R, Limam F (2005) Effects of salt on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities of Catharanthus roseus suspension cells. Plant Sci 168:607–613
Grattan SR, Grieve CM (1993) Mineral nutrient acquisition and response by plants grown in saline environments. In: Handbook of plant and crop stress. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 203–226
Gross J (1991) Pigments in vegetables. Chlorophylls and carotenoids. Avi: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company Inc, New York
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Mol Biol 51:463–499
He T, Cramer GR (1993) Salt tolerance of rapid-cycling Brassica species in relation to potassium/sodium ratio and selectivity at the whole plant and callus levels. J Plant Nutr 16:1263–1277
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Hermann K (1976) Flavonols and flavones in food plants: a review. J Food Technol 11:433–448
Hernandez JA, Aguilar AB, Portillo B, López-Gómez E, Mataix Beneyto J, García-Legaz MF (2003) The effect of calcium on the antioxidant enzymes from salt-treated loquat and anger plants. Funct Plant Biol 30:1127–1137
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif Agric Exp Station Circ (Berkley) 347:1–32
Huang J, Bhinu VS, Li X, Dallal Bashi Z, Zhou R, Hannoufa A (2009) Pleiotropic changes in Arabidopsis f5h and sct mutants revealed by large-scale gene expression and metabolite analysis. Planta 230:1057–1069
Inze′ D, van Montagu M (1995) Oxidative stress in plants. Curr Opin Biotechnol 6:153–158
Johnson DW, Smith SE, Dobrenz AK (1992) Genetic and phenotypic relationships in response to NaCl at different developmental stages in alfalfa. Theor Appl Genet 83:833–838
Ke D, Saltveit ME (1988) Plant hormone interaction and phenolic metabolism in the regulation of russet spotting in iceberg lettuce. Plant Physiol 88:1136–1140
Kim HJ, Fonseca JM, Choi JH, Kubota C, Kwon DY (2008) Salt in irrigation water affects the nutritional and visual properties of Romaine lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). J Agric Food Chem 56:3772–3776
Kotchoni SO, Kuhns C, Ditzer A, Kirch HH, Bartels D (2006) Overexpression of different aldehyde dehydrogenase genes in Arabidopsis thaliana confers tolerance to abiotic stress and protects plants against lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress. Plant Cell Environ 29:1033–1048
Kuiper PJC (1985) Environmental changes and lipid metabolism of higher plants. Physiol Plant 64:118–122
Liu X, Ardo S, Bunning M, Parry J, Zhou K, Stushnoff C (2007) Total phenolic content and DPPH radical scavenging activity of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) grown in Colorado. Food Sci Technol 40:552–557
M’rah S, Ouerghi Z, Berthomieu C, Havaux M, Jungas C, Hajji M, Grignon C, Lachaâl M (2006) Effects of NaCl on the growth, ion accumulation and photosynthetic parameters of Thellungiella halophila. J Plant Physiol 163:1022–1031
Mahmoudi H, Huang J, Gruber MY, Kaddour R, Lachaâl M, Ouerghi Z, Hannoufa A (2010) The impact of genotype and salinity on physiological function, secondary metabolite accumulation, and antioxidative responses in lettuce. J Agric Food Chem 58:5122–5130
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic Press, London
Nasri N, Kaddour R, Rabhi M, Plassard C, Lachaal M (2010) Effect of salinity on germination, phytase activity and phytate content in lettuce seedling. Act Physiol Plant doi 10.1007/s11738-010-0625-4
Nicolle C, Carnat A, Fraisse D, Lamaison JL, Rock E, Michel H, Amouroux P, Remesy C (2004) Characterisation and variation of antioxidant micronutrients in lettuce (Lactuca sativa folium). J Sci Food Agric 84:2061–2069
Sairam RK, Deshmukh PS, Saxena DC (1998) Role of antioxidant system in wheat genotypes tolerance to water stress. Biol Plant 41:387–394
Shin JH, Kim SR, An G (2009) Rice aldehyde dehydrogenase7 is needed for seed maturation and viability. Plant Physiol 149:905–915
Stepien P, Klobus G (2006) Water relations and photosynthesis in Cucumis sativus L. leaves under salt stress. Biol Plant 50:610–616
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:503–527
Wyn Jones RG, Brady CJ, Spears J (1979) Ionic and osmotic relations in plant cells. In: Recent Advances in the Biochemistry of Cereals. Academic Press, London, pp 63–103
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Aroca.
The authors Hela Mahmoudi and Rym Kaddour contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoudi, H., Kaddour, R., Huang, J. et al. Varied tolerance to NaCl salinity is related to biochemical changes in two contrasting lettuce genotypes. Acta Physiol Plant 33, 1613–1622 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0696-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0696-2