Abstract
Objective
To observe the efficacy of acupuncture at points of Shaoyang meridians plus moving cupping on neck and shoulder for migraine.
Methods
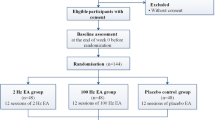
A total of 64 migraine cases were randomly allocated into an observation group and a control group, 32 cases in each group. Random number table method was used in allocation. Acupuncture at points of Shaoyang meridians and cupping on neck and shoulder were used for cases in the observation group, which contain acupuncture 5 times a week and cupping once a week. Oral flunarizine hydrochloride capsules were used for cases in the control group, 10 mg for each dose, 1 dose a day. 2 weeks constitutes a course of treatment. The patients were treated for two courses of treatment in both groups. After that, the changes of visual analogue scale (VAS) and the migraine disability assessment questionnaire (MIDAS) were observed, as well as the clinical efficacy.
Results
The total effective rate and recovery and marked effective rate in the observation group were 93.8% and 71.0% respectively, versus 78.1% and 43.8% in the control group, showing statistical significant differences (both P<0.05). There were significant decreases in VAS and MIDAS scores after treatments in both groups (both P<0.05). VAS and MIDAS scores in the observation group were significantly different from those in the control group (both P<0.05).
Conclusion
Combining acupuncture at points of Shaoyang meridians and cupping on neck and shoulder can relieve headache and reduce influence of migraine on life. It can produce a better efficacy than oral flunarizine hydrochloride capsules in treating migraine patients.
摘要
目的
观察针刺少阳经穴联合颈肩部走罐治疗偏头痛的临床疗效。
方法
将64例患者按随机数字表法分 为观察组和对照组, 每组32例。观察组予针刺少阳经穴联合颈肩部走罐治疗, 每星期针刺5次, 走罐1次; 对照组 予口服盐酸氟桂利嗪胶囊, 10 mg/次, 1次/ d。两组均以治疗2个星期为1个疗程, 共治疗2个疗程。观察治疗前后视 觉模拟量表(VAS)评分及偏头痛残疾程度评估问卷(MIDAS)评分, 并比较临床疗效。
结果
观察组的总有效率及愈 显率分别为93.8%和71.9%, 高于对照组的78.1%和43.8%, 组间差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。治疗后两组的VAS 及MIDAS评分均下降, 与本组治疗前差异有统计学意义(均P<0.05), 两组间差异亦有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。
结论
针刺少阳经穴联合颈肩部走罐治疗偏头痛疗效确切, 能减轻患者疼痛, 降低偏头痛对生活的影响, 其疗效优 于口服盐酸氟桂利嗪胶囊。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen H, Hao WY, Li LB, Wan XH, Cui LY, Shang YY. The study of cochlea and retrocochlear auditory pathway in migraineurs. Zhongguo Tengtong Yixue Zazhi, 2016, 22(4): 272–276, 280.
Feng YT. Clinical effect on migraine treated with acupoint implantation. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2016, 36(4): 373–375.
Dong XL, Wang YR. Research progress on the mechanism of acupuncture treatment of migraine. Zhongguo Zhongyi Jizheng, 2015, 24(6): 1039–1041.
Li J. Mechanisms and clinical analysis of cupping treatment in pain. Zhonghua Zhenjiu Dianzi Zazhi, 2013, 2(4): 176–178.
Yu SY. New classification and diagnosis of cephalagra. Yishi Jinxiu Zazhi, 2005, 28(7): 1–3.
Zhou ZB, Yu SY. Migraine related assessment tool. Zhongguo Tengtong Yixue Zazhi, 2015, 21(4): 241–244.
Lü YH. Migraine related life quality assessment tool. Guoji Shenjingbingxue Shenjing Waikexue Zazhi, 2011, 38(1): 91–94.
Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China. Guiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2002: 105–109.
Yu S, Liu R, Zhao G, Yang X, Qiao X, Feng J, Fang Y, Cao X, He M, Steiner T. The prevalence and burden of primary headaches in China: a population-based door-to-door survey. Headache, 2012, 52(4): 582–591.
Ye XJ, Hu XY. Research progress on the mechanism of acupuncture treatment of migraine. Guowai Yixue (Shenjingbingxue Shenjing Waikexue Fence), 2005, 32(3): 125–127.
Zhang GJ, Li RS, Jin WZ, Yan QH, Ren TT, Wang W, Li MR, Guo J, Li YQ. Clinical study on the curative effect of the continuous radiofrequency treatment of chronic migraine in butterfly palatal ganglion. Zhongguo Tengtong Yixue Zazhi, 2016, 22(2): 144–147.
Qin Z, Cheng K, Meng H, Wang J, Zhai LJ. Correlation study between the distribution of pain points in the head of migraine patients and the study on the correlation between the distribution of pain points in the head. Zhongguo Zhongyi Jichu Yixue Zazhi, 2015, 21(8): 994–995, 1013.
Geng H, Huang Y. Penetration acupuncture of head points in the treatment of migraine: clinical observation of 23 cases. Zhenjiu Linchuang Zazhi, 2011, 27(10): 36–37.
Cai YY, Wang S. Therapeutic effect of point-through-point acupuncture on migraine and its effects on brain blood flow velocity. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2006, 26(3): 177–179.
Lin HB, Yu BS, Chang XR, Liu M, Liu WA. Clinical observation of short-term effect of acupuncture on the treatment of migraine and the speed of cerebral blood flow. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2013, 28(3): 846–848.
Zhang HF, Chang XR, Liu M, Liu WA. Clinical study of acupuncture specific acupoint on Shaoyang meridians on the change of recent VAS score migraine headache intensity and MSQ score with migraine patients. Shizhen Guoyi Guoyao, 2013, 24(7): 1663–1665.
Liang RH, Zhang SP, Xie YH. Study on the effects of pinprick on cerebral neuronal metabolism in patients with chronic migraines. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2016, 34(54): 918–920.
Hong YF, Qu JX, Wang B, Li H, He YC. The effect of moving cupping therapy on nonspecific low back pain. Zhongguo Kangfu Yixue Zazhi, 2006, 21(4): 340–343.
Wu F, Lan L, Zeng F, Liang FR. Scale application in the research of acupuncture for migraine. Shizhen Guoyi Guoyao, 2013, 24(10): 2558–2561.
Stewart WF, Lipton RB, Dowson AJ, Sawyer J. Development and testing of the migraine disability assessment (MIDAS) questionnaire to assess headacherelated disability. Neurology, 2001, 56 (Suppl 1): S20–S28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Fl., Bi, Dy. Clinical observation on acupuncture at points of Shaoyang meridians plus moving cupping on the neck and shoulder for migraine. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 15, 377–381 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-017-1031-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-017-1031-x
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Cupping Therapy
- Moving Cupping Therapy
- Migraine Disorders
- Shaoyang Meridians
- Visual Analogue Scale
- Pain Measurement