Abstract
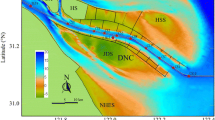
In-situ data from the summer cruise of 2010 in the west Taiwan Strait are used to study the spatial distribution of the Jiulongjiang River plume (JRP). The results show that in the 2 m layer, the JRP debouches into the west Taiwan Strait in the form of jets, with one branch through the Xiamen Bay (Xiamen JRP) and another through the channel between Jinmen and Weitou (JinWei JRP). Driven by the summer southwesterly monsoon, the upwelling-related Dongshan low temperature and high salinity water flows northeastward in the form of a jet as well. To a certain degree, the Dongshan low temperature and high salinity jet restricts the Xiamen JRP from spreading further offshore and drags the JinWei JRP northeastward at the same time. Meanwhile, a terrestrial dissolved organic matter (DOM) distribution model on the basis of molecular collision theory in thermodynamics and statistical physics is applied to analyze the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) turbidity data. The correlation coefficient of the theoretical model to the MODIS turbidity data reaches 0.96 (significant at a 95% level of confidence). The result clarifies the dynamic mechanism for the turbidity distribution characteristics. It is the salinity in macro-scale that plays a decisive role in the turbidity variability in the coastal water. This suggests that the satellite-derived turbidity data can be used as an indicator to show the spreading patterns of the JRP. Based on the turbidity data from 2003 to 2011, we conclude that there are four main spreading patterns of the JRP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chao S Y, Boicourt W C (1986). Onset of estuarine plumes. J Phys Oceanogr, 16(12): 2137–2149
Chen H, Hu J Y, Pan WR, Zeng G N, Chen Z Z, He Z G, Zhang C Y, Li H (2002). Underway measurement of sea surface temperature and salinity in the Taiwan Straits in August, 1999. Marine Science Bulletin, 4(1): 11–18
Chen J Q, Fu Z L, Li F X (1982). Study of upwelling in Minnan-Taiwan Bank. J Oceanogr Taiwan, 2(1): 5–13 (in Chinese)
Chen X H, Hu J Y, Pi Q L, Liu G P, Chen Z Z (2009). Densely underway measurement of surface temperature and salinity in Xiamen-Quanzhou near-shore area. Advances in Earth Science, 24(6): 629–635 (in Chinese)
Guo WD, Yang L Y, Hong H S, Stedmon C A, Wang F L, Xu J, Xie Y Y (2011). Assessing the dynamics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in a subtropical estuary using parallel factor analysis. Mar Chem, 124(1–4): 125–133
Hickey B, Geier S, Kachel N, MacFadyen A (2005). A bi-directional river plume: the Columbia in summer. Cont Shelf Res, 25(14): 1631–1656
Hong H S, Zhang C Y, Shang S L, Huang B Q, Li Y H, Li X D, Zhang S M (2009a). Inter annual variability of summer coastal upwelling in the Taiwan Strait. Cont Shelf Res, 29(2): 479–484
Hong H S, Zheng Q A, Hu J Y, Chen Z Z, Li C Y, Jiang YW, Wan ZW (2009b). Three-dimensional structure of a low salinity tongue in the southern Taiwan Strait observed in the summer of 2005. Acta Oceanol Sin, 28(4): 1–7
Huang Y C, LI Y, Shao H, Li Y H (2008). Seasonal variations of sea surface temperature, chlorophyll a and turbidity in Beibu Gulf, MODIS imagery study. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 47(6): 856–863
Kim H C, Yamaguchi H, Yoo S, Zhu J R, Okamura K, Kiyomoto Y, Tanaka K, Kim SW, Park T, Oh IS, Ishizaka J (2009). Distribution of Changjiang diluted water detected by satellite chlorophyll a and its interannual variation during 1998–2007. J Oceanogr, 65(1): 129–135
Kundu P K (1990). Fluid Mechanics. San Diego: Academic Press, 478–481
Libes S (2009). Introduction to Marine Biogeochemistry. San Diego: Academic Press, 208
Lie H J, Cho C H, Lee J H, Lee S (2003). Structure and eastward extension of the Changjiang River plume in the East China Sea. J Geophys Res, 108(C3 3077): 22, 1–14
Liu Y G, MacCready P, Hickey B M (2009a). Columbia River plume patterns in summer 2004 as revealed by a hindcast coastal ocean circulation model. Geophys Res Let, 36: L02601
Liu Y G, MacCready P, Hickey B M, Dever E P, Kosro P M, Banas N S (2009b). Evaluation of a coastal ocean circulation model for the Columbia River plume in 2004. J Geophys Res, 114(C2): C00B4
Liu Y G, Weisberg R H (2007). Ocean currents and sea surface heights estimated across the West Florida Shelf. J Phys Oceanogr, 37(6): 1697–1713
Luo Z B, Pan W R, Li L, Zhang G R (2011). Salinity fronts at Jiulongjiang Estuary. IEEE Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering (RSETE), 3449–3454
Luo Z B, Pan W R, Li L, Zhang G R (2012). The study on three-dimensional numerical model and fronts of the Jiulong Estuary and the Xiamen Bay. Acta Oceanol Sin, 31(4): 55–64
MacCready P, Banas N S, Hickey B M, Dever E P, Liu Y G (2009). A model study of tide- and wind-induced mixing in the Columbia River Estuary and plume. Cont Shelf Res, 29(1): 278–291
Mao H L, Gan Z J, Lan S F (1963). A preliminary study of the Yangtze diluted water and its mixing processing. Oceanologia ET Limnologia Sinica, 5(3): 183–206 (in Chinese)
Ortner P B, Lee T N, Milne P J, Zika R G, Clarke M E, Podesta G P, Swart P K, Tester P A, Atkinson L P, Johnson W R (1995). Mississippi River flood water that reached the Gulf Stream. J Geophys Res, 100(C7): 13595–13601
Rong Z R, Li M (2012). Tidal effects on the bulge region of Changjiang River plume. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci, 97(20): 149–160
Schiller R V, Kourafalou V H, Hogan P, Walker N D (2011). The dynamics of the Mississippi River plume-impact of topography, wind and offshore forcing on the fate of plume waters. J Geophys Res, 116(C6): C06029
Shi W, Wang M H (2009). Satellite observations of flood-driven Mississippi River Plume in the spring of 2008. Geophys Res Lett, 36(7): L07607
Wang X C, Chen R F, Gardner G B (2004). Sources and transport of dissolved and particulate organic carbon in the Mississippi River estuary and adjacent coastal waters of the northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar Chem, 89(1–4): 241–256
Wu H, Zhu J R, Shen J, Wang H (2011). Tidal modulation on the Changjiang River plume in summer. J Geophys Res, 116(C8): C08017
Zhang C Y, Hong H S, Hu C M, Shang S L (2011). Evolution of a coastal upwelling event during summer 2004 in the southern Taiwan Strait. Acta Oceanol Sin, 30(1): 1–6
Zhang Y H, Wang WQ, Huang Z Q (1999). Salinity fronts and chemical behavior of nutrient in Jiulongjiang Estuary. Marine Environmental Science, 18(4): 1–7 (in Chinese)
Zheng Q A, Chen Q, Zhao H H, Shi J X, Cao Y, Wang D (2008). A statistic-thermodynamic model for the DOM degradation in the estuary. Geophys Res Lett, 35(6): L06604
Zheng Q A, Clemente-Colon P, Yan X H, Liu W T (2004). Satellite synthetic aperture radar detection of Delaware Bay plumes: Jet-like feature analysis. J Geophys Res, 109(C3): C03031
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Daifeng Wang is a Ph.D Candidate in the College of Ocean and Earth Sciences, Xiamen University, China. Her current research interests focus on river plume.
Dr. Quan’an Zheng is a Senior Research Scientist of the Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Science, University of Maryland, USA, and a Guest Chair Professor of Xiamen University, China. His research interests are ocean remote sensing (including physics, data interpretation, applications, and laboratory simulation), ocean surface processes (including wind friction, wave spectra, skin layer physics, and surfactant effects), upper ocean dynamics (including internal wave dynamics and ocean-atmospheric coupling), mesoscale ocean dynamics, and solitary waves in the atmosphere and ocean.
Dr. Jianyu Hu obtained his Ph.D degree (2001) in physical oceanography from Tohoku University of Japan and Ph.D degree (2002) in environmental science from Xiamen University of China. He is now a professor in State Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science and Department of Physical Oceanography at Xiamen University, focusing on the study of regional environmental oceanography.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Zheng, Q. & Hu, J. Jet-like features of Jiulongjiang River plume discharging into the west Taiwan Strait. Front. Earth Sci. 7, 282–294 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-013-0372-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-013-0372-0