Abstract
Background
The introduction of robotics in bariatric surgery is a novel development since the beginning of this century. The aim of this study is to compare surgical outcome of the robotic gastric bypass with the laparoscopic counterpart.
Methods
A retrospective study was conducted to compare the results of 100 fully robotic gastric bypasses (RGB) and 100 laparoscopic gastric bypasses (LGB) performed by a single surgeon. Surgical outcome was analysed by evaluating operation room time and surgical time, morbidity and mortality, and length of hospital stay.
Results
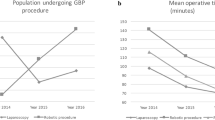
In the RGB and LGB group, respectively, 92 and 80 % of operated patients were female (p = 0.024). Mean age was 39 (range 20–62, SD 10.21) and 42 years (range 18–65, SD 11.87), respectively (p = 0.158). Mean BMI was 40 (range 35–47, SD 2.66) and 42 (range 35–56, SD 4.75), respectively (p < 0.05). Mean surgical time was 67 (range 39–210, SD 22.46) and 31 min (range 18–62, SD 9.12), respectively (p < 0.05). Mean operation room time was 117 (range 80–257, SD 30.13) and 66 min (range 38–101, SD 12.68), respectively (p < 0.05). The surgery-related 30-day morbidity rate was 5 % in both groups. Major morbidity (Clavien-Dindo class 3–4) was 3 and 1 %, respectively (p = 0.62). There was no mortality. Median hospital stay was two postoperative days in both groups. A learning curve developed after 25 procedures.
Conclusions
The RGB is a feasible procedure. Although more time is needed, a standardized technique results in fair operation times in the hands of an experienced surgeon.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mason E, Ito C. Gastric bypass in obesity. Surg Clin North Am. 1967;47:1345–54.
Wittgrove A, Clark G, Tremblay L. Laparoscopic gastric bypass, Roux-en-Y: preliminary report of five cases. Obes Surg. 1994;4:353–7.
Horgan S, Vanuno D. Robots in laparoscopic surgery. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2001;11(6):415–9.
Talamini M, Chapman S, Horgan S, et al. A prospective analysis of 211 robotic-assisted surgical procedures. Academic Robotics Group. Surg Endosc. 2003;17(10):1521–4.
Fourman M, Saber A. Robotic bariatric surgery: a systematic review. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2012;8(4):483–8.
Cirocchi R, Boselli C, Santoro A, et al. Current status of robotic bariatric surgery: a systematic review. BMC Surg. 2013;13:53.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien P. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240(2):205–13.
NIH Consensus Development Conference Panel for bariatric surgery, Bethesda, March 1991
Fried I, Yumuk V, Oppert J, et al. Interdisciplinary European guidelines on metabolic and bariatric surgery. Obes Facts. 2013;6(5):449–68.
Ramos A, Silva A, Ramos M, et al. Simplified gastric bypass: 13 years of experience and 12,000 patients operated. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2014;27 Suppl 1:2–8.
DeMaria E, Sugerman H, Kellum J, et al. Results of 281 consecutive total laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypasses to treat morbid obesity. Ann Surg. 2002;235(5):640–5. discussion 645-7.
Peterli R, Borbély Y, Kern B, et al. Early results of the Swiss Multicentre Bypass or Sleeve Study (SM-BOSS): a prospective randomized trial comparing laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Ann Surg. 2013;258(5):690–4. discussion 695.
Dillemans B, Sakran N, Van Cauwenberge S, et al. Standardization of the fully stapled laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for obesity reduces early immediate postoperative morbidity and mortality: a single center study on 2606 patients. Obes Surg. 2009;19(10):1355–64.
Dogan K, Kraaij L, Aarts E, et al. Fast-track bariatric surgery improves perioperative care and logistics compared to conventional care. Obes Surg. 2015;25(1):28–35.
Myers SR, McGuirl J, Wang J. Robot-assisted versus laparoscopic gastric bypass: comparison of short-term outcomes. Obes Surg. 2013;23(4):467–73.
Park C, Lam E, Walsh T, et al. Robotic-assisted Roux-en-Y gastric bypass performed in a community hospital setting: the future of bariatric surgery? Surg Endosc. 2011;25(10):3312–21.
Hagen M, Inan I, Pugin F, et al. The da Vinci surgical system in digestive surgery. Rev Med Suisse. 2007;3(117):1622–6.
Benizri E, Renaud M, Reibel N, et al. Perioperative outcomes after totally robotic gastric bypass: a prospective nonrandomized controlled study. Am J Surg. 2013;206(2):145–51.
Buchs N, Morel P, Azagury D, et al. Laparoscopic versus robotic Roux-En-Y gastric bypass: lessons and long-term follow-up learned from a large prospective monocentric study. Obes Surg. 2014;24(12):2031–9.
Yu S, Clapp B, Lee M, et al. Robotic assistance provides excellent outcomes during the learning curve for laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: results from 100 robotic-assisted gastric bypasses. Am J Surg. 2006;192(6):746–9.
Ayloo S, Addeo P, Shah G, et al. Robot-assisted hybrid laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: surgical technique and early outcomes. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2010;20(10):847–50.
Artuso D, Wayne M, Grossi R. Use of robotics during laparoscopic gastric bypass for morbid obesity. JSLS. 2005;9(3):266–8.
Mohr C, Nadzam G, Alami R, et al. Totally robotic laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric bypass: results from 75 patients. Obes Surg. 2006;16(6):690–6.
Hagen M, Pugin F, Chassot G, et al. Reducing cost of surgery by avoiding complications: the model of robotic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2012;22(1):52–61.
Hubens G, Balliu L, Ruppert M, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass procedure performed with the da Vinci robot system: is it worth it? Surg Endosc. 2008;22(7):1690–6.
Bailey J, Hayden J, Davis P, et al. Robotic versus laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) in obese adults ages 18 to 65 years: a systematic review and economic analysis. Surg Endosc. 2014;28(2):414–26.
Sanchez B, Mohr C, Morton J, et al. Comparison of totally robotic laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and traditional laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2005;1(6):549–54.
Scozzari G, Rebecchi F, Millo P, et al. Robot-assisted gastrojejunal anastomosis does not improve the results of the laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Endosc. 2011;25(2):597–603.
Snyder B, Wilson T, Leong B, et al. Robotic-assisted Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: minimizing morbidity and mortality. Obes Surg. 2010;20(3):265–70.
Buchs NC, Morel P, Azagury DE, et al. Laparoscopic versus robotic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: lessons and long-term follow-up learned from a large prospective monocentric study. Obes Surg. 2014;24(12):2031–9. doi:10.1007/s11695-014-1335-6.
Tieu K, Allison N, Snyder B, et al. Robotic-assisted Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: update from 2 high-volume centers. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2013;9(2):284–8.
Moser F, Horgan S. Robotically assisted bariatric surgery. Am J Surg. 2004;188(4A Suppl):38S–44.
Deng J, Lourié D. 100 robotic-assisted laparoscopic gastric bypasses at a community hospital. Am Surg. 2008;74(10):1022–5.
Bindal V, Gonzalez-Heredia R, Masrur M, Elli EF. Technique evolution, learning curve, and outcomes of 200 robot-assisted gastric bypass procedures: a 5-year experience.Obes Surg. 2014;14.
Bindal V, Bhatia P, Dudeja U, et al. Review of contemporary role of robotics in bariatric surgery. Surg Endosc. 2015;29(1):1–8.
Toro J, Lin E, Patel A. Review of robotics in foregut and bariatric surgery. J Minim Access Surg. 2015;11(1):16–21.
Buchs N, Pugin F, Bucher P, et al. Learning curve for robot-assisted Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Endosc. 2012;26(4):1116–21.
Renaud M, Reibel N, Zarnegar R, et al. Multifactorial analysis of the learning curve for totally robotic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 2013;23(11):1753–60.
Lawson E, Curet M, Sanchez B, et al. Postural ergonomics during robotic and laparoscopic gastric bypass surgery: a pilot project. Robot Surg. 2007;1(1):61–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smeenk, R.M., van ‘t Hof, G., Elsten, E. et al. The Results of 100 Robotic Versus 100 Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass Procedures: a Single High Volume Centre Experience. OBES SURG 26, 1266–1273 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-015-1933-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-015-1933-y