Abstract
Background
We designed a study to compare ventilation characteristics performed in morbidly obese patients by medical students via the facemask to that via the LMA Supreme®.
Methods
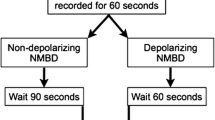
This prospective, randomized, crossover study included 31 ASA I–III morbidly patients showing difficult mask ventilation predictors. After induction of anesthesia, ten medical students with no previous clinical experience in airway management, clinically educated to facemask ventilation maneuvers, and theoretically educated to laryngeal mask use were supervised by a senior anesthesiologist during performance of 60 s facemask and LMA Supreme® ventilation in a randomly assigned order. Ventilation quality and difficulty were measured using an original score calculated as the sum of seven indicators (0 = no ventilation and complications, 12 = optimal and safe ventilation) and a visual analog scale (VAS; 0 = no difficult–100 = impossible), respectively. Values are presented as means (standard deviation) or medians [extremes].
Results
Mean age and body mass index of the patients were 39 years (12 years) and 44 kg m−2 (7 kg m−2), respectively. One patient was excluded because of ventilation difficulty experienced by the senior anesthesiologist. Medical students successfully established ventilation with the LMA Supreme® in all the 30 patients after a delay of 21 s (9 s) compared to 34 s (14 s) with the facemask (P < 0.05). Failure of ventilation occurred in four patients with the facemask. Ventilation quality score was superior and ventilation difficulty (VAS 0–100) was inferior with the LMA Supreme® than with the facemask (11 [10–12] and 9 [0–45] versus 5 [1–12] and 50 [5–100]); both P < 0.05, respectively.
Conclusions
We showed that the LMA Supreme™ placed in novice hands systematically promoted easier ventilation of better quality than the facemask in morbidly obese patients showing difficult mask ventilation predictors. Our data suggest that the LMA Supreme™ could be considered as a standard airway management tool for both elective and rescue airway management of morbidly obese patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation. International consensus on cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care science with treatment recommendations. Part 4: advanced life support. Resuscitation. 2005;67:213–47.
Nolan JP, Deakin CD, Soar J, et al. European resuscitation council guidelines for resuscitation 2005: section 4. Adult advanced life support. Resuscitation. 2005;67:S39–86.
Langeron O, Masso E, Huraux C, et al. Prediction of difficult mask ventilation. Anesthesiology. 2000;92:1229–36.
Kheterpal S, Han R, Tremper KK, et al. Incidence and predictors of difficult and impossible mask ventilation. Anesthesiology. 2006;105:885–91.
Han R, Tremper KK, Kheterpal S, et al. Grading scale for mask ventilation. Anesthesiology. 2004;101:267.
Combes X, Le Roux B, Suen P, et al. Unanticipated difficult airway in anesthetized patients: prospective validation of a management algorithm. Anesthesiology. 2004;100:1146–50.
Wharton NM, Gibbison B, Gabbott DA, et al. I-gel insertion by novices in manikins and patients. Anaesthesia. 2008;63:991–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Support for this work was provided solely from departmental sources.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdi, W., Dhonneur, G., Amathieu, R. et al. LMA Supreme™ Versus Facemask Ventilation Performed by Novices: A Comparative Study in Morbidly Obese Patients Showing Difficult Ventilation Predictors. OBES SURG 19, 1624–1630 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-009-9953-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-009-9953-0