Abstract
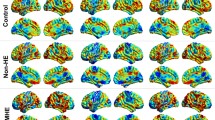
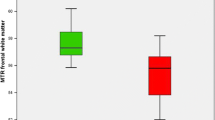
Wilson disease (WD) can manifest with hepatic or neuropsychiatric symptoms. Our understanding of the in vivo brain changes in WD, particularly in the hepatic phenotype, is limited. Thirty subjects with WD and 30 age- and gender-matched controls participated. WD group underwent neuropsychiatric assessment. Unified WD Rating Scale neurological exam scores were used to determine neurological (WDN, score > 0) and hepatic-only (WDH, score 0) subgroups. All subjects underwent 3 Tesla anatomical and resting-state functional MRI. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) were performed only in the WD group. Volumetric, DTI, and functional connectivity analyses were performed to determine between-group differences. WDN and WDH groups were matched in demographic and psychiatric profiles. The entire WD group compared to controls showed significant thinning in the bilateral superior frontal cortex. The WDN group compared to control and WDH groups showed prominent structural brain changes including significant striatal and thalamic atrophy, more subcortical hypointense lesions on SWI, and diminished white matter integrity in the bilateral anterior corona radiata and corpus callosum. However, the WDH group also showed significant white matter volume loss compared to controls. The functional connectivity between the frontostriatal nodes was significantly reduced in the WDN group, whereas that of the hippocampus was significantly increased in the WDH group compared to controls. In summary, structural and functional brain changes were present even in neurologically non-manifesting WD patients in this cross-sectional study. Longitudinal brain MRI scans may be useful as biomarkers for prognostication and optimization of treatment strategies in WD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bareš, M., Apps, R., Avanzino, L., Breska, A., D'Angelo, E., Filip, P., Gerwig, M., Ivry, R. B., Lawrenson, C. L., Louis, E. D., Lusk, N. A., Manto, M., Meck, W. H., Mitoma, H., & Petter, E. A. (2019). Consensus paper: Decoding the contributions of the cerebellum as a time machine. From neurons to clinical applications. Cerebellum (London, England), 18(2), 266–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-018-0979-5.
Bennett, J., & Hahn, S. H. (2011). Clinical molecular diagnosis of Wilson disease. Seminars in Liver Disease, 31(3), 233–238. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1286054.
Bruni, J. E., & Montemurro, D. G. (2009). Human Neuroanatomy: A text, brain atlas, and laboratory dissection guide (3rd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Chai, X. J., Castañón, A. N., Ongür, D., & Whitfield-Gabrieli, S. (2012). Anticorrelations in resting state networks without global signal regression. NeuroImage, 59(2), 1420–1428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.08.048.
Clarke, D. E., & Kuhl, E. A. (2014). DSM-5 cross-cutting symptom measures: A step towards the future of psychiatric care? World psychiatry : official journal of the World Psychiatric Association (WPA), 13(3), 314–316. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20154.
Conn, H. O. (1977). Trailmaking and number-connection tests in the assessment of mental state in portal systemic encephalopathy. The American Journal of Digestive Diseases, 22(6), 541–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01072510.
Constable, R. T., Ment, L. R., Vohr, B. R., Kesler, S. R., Fulbright, R. K., Lacadie, C., Delancy, S., Katz, K. H., Schneider, K. C., Schafer, R. J., Makuch, R. W., & Reiss, A. R. (2008). Prematurely born children demonstrate white matter microstructural differences at 12 years of age, relative to term control subjects: An investigation of group and gender effects. Pediatrics, 121(2), 306–316. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2007-0414.
Członkowska, A., Litwin, T., Dusek, P., Ferenci, P., Lutsenko, S., Medici, V., Rybakowski, J. K., Weiss, K. H., & Schilsky, M. L. (2018). Wilson disease. Nature reviews. Disease primers, 4(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-018-0018-3.
Członkowska, A., Tarnacka, B., Möller, J. C., Leinweber, B., Bandmann, O., Woimant, F., & Oertel, W. H. (2007). Unified Wilson's disease rating scale - a proposal for the neurological scoring of Wilson's disease patients. Neurologia i Neurochirurgia Polska, 41(1), 1–12.
Dale, A. M., Fischl, B., & Sereno, M. I. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage, 9(2), 179–194. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1998.0395.
Dusek, P., Smolinski, L., Redzia-Ogrodnik, B., Golebiowski, M., Skowronska, M., Poujois, A., Laurencin, C., Jastrzebska-Kurkowska, I., Litwin, T., & Członkowska, A. (2020). Semiquantitative scale for assessing brain MRI abnormalities in Wilson disease: A validation study. Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 35(6), 994–1001. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28018.
Favrole, P., Chabriat, H., Guichard, J. P., & Woimant, F. (2006). Clinical correlates of cerebral water diffusion in Wilson disease. Neurology, 66(3), 384–389. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000196482.71636.7d.
Ferenci, P., Caca, K., Loudianos, G., Mieli-Vergani, G., Tanner, S., Sternlieb, I., Schilsky, M., Cox, D., & Berr, F. (2003). Diagnosis and phenotypic classification of Wilson disease. Liver international: official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver, 23(3), 139–142. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0676.2003.00824.x.
Fischl, B., & Dale, A. M. (2000). Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(20), 11050–11055. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.200033797.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., van der Kouwe, A., Killiany, R., Kennedy, D., Klaveness, S., Montillo, A., Makris, N., Rosen, B., & Dale, A. M. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: Automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33(3), 341–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00569-x.
Fischl, B., Sereno, M. I., & Dale, A. M. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. II: Inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. NeuroImage, 9(2), 195–207. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1998.0396.
Fritzsch, D., Reiss-Zimmermann, M., Trampel, R., Turner, R., Hoffmann, K. T., & Schäfer, A. (2014). Seven-tesla magnetic resonance imaging in Wilson disease using quantitative susceptibility mapping for measurement of copper accumulation. Investigative Radiology, 49(5), 299–306. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0000000000000010.
Gao, J., Brackley, S., & Mann, J. P. (2019). The global prevalence of Wilson disease from next- generation sequencing data. Genetics in medicine : official journal of the American College of Medical Genetics, 21(5), 1155–1163. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41436-018-0309-9.
García-García, R., Cruz-Gómez, Á. J., Mangas-Losada, A., Urios, A., Forn, C., Escudero-García, D., Kosenko, E., Ordoño, J. F., Tosca, J., Giner-Durán, R., Serra, M. A., Avila, C., Belloch, V., Felipo, V., & Montoliu, C. (2017). Reduced resting state connectivity and gray matter volume correlate with cognitive impairment in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. PLoS One, 12(10), e0186463. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186463.
García-García, R., Cruz-Gómez, Á. J., Urios, A., Mangas-Losada, A., Forn, C., Escudero-García, D., Kosenko, E., Torregrosa, I., Tosca, J., Giner-Durán, R., Serra, M. A., Avila, C., Belloch, V., Felipo, V., & Montoliu, C. (2018). Learning and memory impairments in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy are associated with structural and functional connectivity alterations in Hippocampus. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 9664. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27978-x.
Genovese, C. R., Lazar, N. A., & Nichols, T. (2002). Thresholding of statistical maps in functional neuroimaging using the false discovery rate. NeuroImage, 15(4), 870–878. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2001.1037.
Han, Y., Cheng, H., Toledo, J. B., Wang, X., Li, B., Han, Y., Wang, K., & Fan, Y. (2016). Impaired functional default mode network in patients with mild neurological Wilson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 30, 46–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.06.018.
Hermann, W. (2014). Morphological and functional imaging in neurological and non-neurological Wilson's patients. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1315, 24–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12343.
Hu, X., Chen, S., Huang, C. B., Qian, Y., & Yu, Y. (2017). Frequency-dependent changes in the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations in patients with Wilson's disease: A resting-state fMRI study. Metabolic Brain Disease, 32(3), 685–692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9946-3.
Hua, K., Zhang, J., Wakana, S., Jiang, H., Li, X., Reich, D. S., Calabresi, P. A., Pekar, J. J., van Zijl, P. C., & Mori, S. (2008). Tract probability maps in stereotaxic spaces: Analyses of white matter anatomy and tract-specific quantification. NeuroImage, 39(1), 336–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.053.
Jadav, R., Saini, J., Sinha, S., Bagepally, B., Rao, S., & Taly, A. B. (2013). Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and its clinical correlates in drug naïve Wilson's disease. Metabolic Brain Disease, 28(3), 455–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9407-1.
Jing, R., Han, Y., Cheng, H., Han, Y., Wang, K., Weintraub, D., & Fan, Y. (2019). Altered large- scale functional brain networks in neurological Wilson's disease. Brain imaging and behavior, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00066-y. advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00066-y.
Kalita, J., Kumar, V., Misra, U. K., & Bora, H. K. (2018). Memory and learning dysfunction following copper toxicity: Biochemical and Immunohistochemical basis. Molecular Neurobiology, 55(5), 3800–3811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0619-y.
Karantzoulis, S., Novitski, J., Gold, M., & Randolph, C. (2013). The repeatable battery for the assessment of neuropsychological status (RBANS): Utility in detection and characterization of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease. Archives of clinical neuropsychology: the official journal of the National Academy of Neuropsychologists, 28(8), 837–844. https://doi.org/10.1093/arclin/act057.
Kozić, D., Svetel, M., Petrović, B., Dragasević, N., Semnic, R., & Kostić, V. S. (2003). MR imaging of the brain in patients with hepatic form of Wilson's disease. European Journal of Neurology, 10(5), 587–592. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1468-1331.2003.00661.x.
Lin, W., Chen, X., Gao, Y. Q., Yang, Z. T., Yang, W., & Chen, H. J. (2019). Hippocampal atrophy and functional connectivity disruption in cirrhotic patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metabolic Brain Disease, 34(6), 1519–1529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00457-6.
Litwin, T., Dzieżyc, K., Karliński, M., Chabik, G., Czepiel, W., & Członkowska, A. (2015). Early neurological worsening in patients with Wilson's disease. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 355(1–2), 162–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2015.06.010.
Litwin, T., Gromadzka, G., Członkowska, A., Gołębiowski, M., & Poniatowska, R. (2013). The effect of gender on brain MRI pathology in Wilson's disease. Metabolic Brain Disease, 28(1), 69–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9378-2.
Magalhaes, A. C., Caramelli, P., Menezes, J. R., Lo, L. S., Bacheschi, L. A., Barbosa, E. R., Rosemberg, L. A., & Magalhaes, A. (1994). Wilson's disease: MRI with clinical correlation. Neuroradiology, 36(2), 97–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588068.
Mosher, V., Swain, M. G., Pang, J., Kaplan, G. G., Sharkey, K. A., MacQueen, G. M., & Goodyear, B. G. (2017). Primary biliary cholangitis alters functional connections of the Brain's deep gray matter. Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology, 8(7), e107. https://doi.org/10.1038/ctg.2017.34.
Mosher, V., Swain, M., Pang, J., Kaplan, G., Sharkey, K., MacQueen, G., & Goodyear, B. G. (2019). Primary biliary cholangitis patients exhibit MRI changes in structure and function of interoceptive brain regions. PLoS One, 14(2), e0211906. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0211906.
Pal, A., & Prasad, R. (2014). Recent discoveries on the functions of astrocytes in the copper homeostasis of the brain: A brief update. Neurotoxicity Research, 26(1), 78–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-013-9453-9.
Papademetris, X., Jackowski, A. P., Schultz, R. T., Staib, L. H., & Duncan, J. S. (2001). Integrated intensity and point-feature nonrigid registration. Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention : MICCAI ... International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, 3216(2004), 763–770. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.2001.3216-763.
Papademetris, X., Jackowski, M. P., Rajeevan, N., DiStasio, M., Okuda, H., Constable, R. T., & Staib, L. H. (2006). BioImage suite: An integrated medical image analysis suite: An update. The insight journal, 2006, 209.
Prashanth, L. K., Taly, A. B., Sinha, S., Ravishankar, S., Arunodaya, G. R., Vasudev, M. K., & Swamy, H. S. (2005). Prognostic factors in patients presenting with severe neurological forms of Wilson's disease. QJM : Monthly Journal of the Association of Physicians, 98(8), 557–563. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hci095.
Randolph, C., Tierney, M. C., Mohr, E., & Chase, T. N. (1998). The repeatable battery for the assessment of neuropsychological status (RBANS): Preliminary clinical validity. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 20(3), 310–319. https://doi.org/10.1076/jcen.20.3.310.823.
Schilsky, M. L. (2017). Wilson disease: Diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up. Clinics in Liver Disease, 21(4), 755–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2017.06.011.
Shen, X., Tokoglu, F., Papademetris, X., & Constable, R. T. (2013). Groupwise whole-brain parcellation from resting-state fMRI data for network node identification. NeuroImage, 82, 403–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.081.
Sinha, S., Taly, A. B., Prashanth, L. K., Ravishankar, S., Arunodaya, G. R., & Vasudev, M. K. (2007). Sequential MRI changes in Wilson's disease with de-coppering therapy: A study of 50 patients. The British Journal of Radiology, 80(957), 744–749. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/48911350.
Smolinski, L., Litwin, T., Redzia-Ogrodnik, B., Dziezyc, K., Kurkowska-Jastrzebska, I., & Czlonkowska, A. (2019). Brain volume is related to neurological impairment and to copper overload in Wilson's disease. Neurological sciences : official journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology, 40(10), 2089–2095. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-03942-z.
Stezin, A., George, L., Jhunjhunwala, K., Lenka, A., Saini, J., Netravathi, M., Yadav, R., & Pal, P. K. (2016). Exploring cortical atrophy and its clinical and biochemical correlates in Wilson's disease using voxel based morphometry. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 30, 52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.06.017.
Strauss, E., Sherman, E. M. S., & Spreen, O. (2006). A compendium of neuropsychological tests: Administration, norms, and commentary (3rd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Südmeyer, M., Saleh, A., Wojtecki, L., Cohnen, M., Gross, J., Ploner, M., Hefter, H., Timmermann, L., & Schnitzler, A. (2006). Wilson's disease tremor is associated with magnetic resonance imaging lesions in basal ganglia structures. Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 21(12), 2134–2139. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21136.
Tarnacka, B., Szeszkowski, W., Buettner, J., Gołebiowski, M., Gromadzka, G., & Członkowska, A. (2009). Heterozygous carriers for Wilson's disease--magnetic spectroscopy changes in the brain. Metabolic Brain Disease, 24(3), 463–468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-009-9145-6.
Terwel, D., Löschmann, Y. N., Schmidt, H. H., Schöler, H. R., Cantz, T., & Heneka, M. T. (2011). Neuroinflammatory and behavioural changes in the Atp7B mutant mouse model of Wilson's disease. Journal of Neurochemistry, 118(1), 105–112. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07278.x.
Tombaugh, T. N. (2004). Trail making test a and B: Normative data stratified by age and education. Archives of clinical neuropsychology : the official journal of the National Academy of Neuropsychologists, 19(2), 203–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0887-6177(03)00039-8.
Tombaugh, T. N., Kozak, J., & Rees, L. (1999). Normative data stratified by age and education for two measures of verbal fluency: FAS and animal naming. Archives of clinical neuropsychology : the official journal of the National Academy of Neuropsychologists, 14(2), 167–177.
Torres, D. S., Abrantes, J., & Brandão-Mello, C. E. (2013). Cognitive assessment of patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy in Brazil. Metabolic Brain Disease, 28(3), 473–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9405-3.
Wakana, S., Caprihan, A., Panzenboeck, M. M., Fallon, J. H., Perry, M., Gollub, R. L., Hua, K., Zhang, J., Jiang, H., Dubey, P., Blitz, A., van Zijl, P., & Mori, S. (2007). Reproducibility of quantitative tractography methods applied to cerebral white matter. NeuroImage, 36(3), 630–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.02.049.
Walshe, J. M., & Yealland, M. (1993). Chelation treatment of neurological Wilson's disease. The Quarterly Journal of Medicine, 86(3), 197–204.
Whitfield-Gabrieli, S., & Nieto-Castanon, A. (2012). Conn: A functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connectivity, 2(3), 125–141. https://doi.org/10.1089/brain.2012.0073.
Yang, J., Li, X., Yang, R., Yu, X., Yu, C., Qian, Y., & Yu, Y. (2015). Susceptibility-weighted imaging manifestations in the brain of Wilson's disease patients. PLoS One, 10(4), e0125100. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125100.
Zhou, X. X., Li, X. H., Qin, H., Li, G. D., Huang, H. W., Liang, Y. Y., Liang, X. L., & Pu, X. Y. (2016). Diffusion tensor imaging of the extracorticospinal network in the brains of patients with Wilson disease. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 362, 292–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2016.02.006.
Zhong, W., Huang, Z., & Tang, X. (2019). A study of brain MRI characteristics and clinical features in 76 cases of Wilson's disease. Journal of clinical neuroscience: official journal of the Neurosurgical Society of Australasia, 59, 167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2018.10.096.
Zou, L., Song, Y., Zhou, X., Chu, J., & Tang, X. (2019). Regional morphometric abnormalities and clinical relevance in Wilson's disease. Movement disorders: official journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 34(4), 545–554. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27641.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Wilson Disease Association for their help with participant recruitment.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported through the grants from the Jack Levin Foundation, The Rachel and Drew Katz Foundation and the Albert Family to the Yale University School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conceptualization and design: ST, DR, MLS, RTC. Data collection: KN, AVR, JA. Data analysis and interpretation: ST, JA, KN, AVR, MS, AP, RTC. Supervision of the study procedures: ST, DR, RTC, MLS. Drafting the manuscript: ST. All authors contributed to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors Tinaz, Arora, Nalamada, Vives-Rodriguez, Sezgin, Robakis, Patel, and Constable declare that they have no conflict of interest. Author Schilsky received grant funding from Alexion and GMPO.
Ethical approval
All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 457 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tinaz, S., Arora, J., Nalamada, K. et al. Structural and functional brain changes in hepatic and neurological Wilson disease. Brain Imaging and Behavior 15, 2269–2282 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00420-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00420-5