Abstract
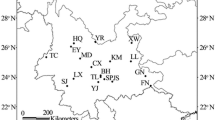
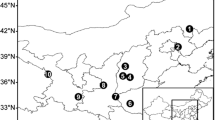
Pinus yunnanensis Franch. is an particular conifer tree species in Yunnan–Guizhou plateau in southwest China. The morphological and anatomical traits of needles are important to evaluate geographic variation and population dynamics of conifer species. Seedlings from seven populations of P. yunnanensis were analyzed, looking at 22 morphological and anatomical needle traits. The results showed that variations among and within populations were significantly different for all traits and the variance components within populations were generally higher than that among populations in the most tested needle traits. The proportions of three-needle fascicle were significantly different among populations. The traits related to needle size in both morphology and anatomy were positive with latitude and negative with annual temperature and precipitation. Ratio indices, including mesophyll area/vascular bundle area, mesophyll area/resin canals area, vascular bundle area/resin canals area and mesophyll area/(resin canals area and vascular bundle area), were negatively correlated with elevation and positively correlated with the annual mean temperature, showing some fitness feature for the populations. Needle traits were more significantly correlated with longitude than with other four environmental factors. Needle length was significantly correlated with almost all environmental factors. First four principal components accounted for 81.596 % of the variation with eigenvalues >1; the differences among populations were mainly dependent on needle width, stomatal density, section areas of vascular bundle, total resin canals, and mesophyll, as well as area ratio traits. Seven populations were divided into three categories by Euclidean distance. Variations in needle traits among the populations have shown systematic microevolution in terms of geographic impact on P. yunnanensis. This study would provide empirical data to characterize adaptation and genetic variation of P. yunnanensis, which would be helpful for management of genetic resources and reasonable utilization of them in future.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Androsiuk P, Kaczmarek Z, Urbaniak L (2011) The morphological traits of needles as markers of geographical differentiation in European Pinus sylvestris populations. Dendrobiology 65:3–16
Batos B, Vilotić D, Orlović S, Miljković D (2010) Inter and intra-population variation of leaf stomatal traits of Quercus robur L. in Northern Serbia. Arch Biol Sci 62:1125–1136
Boratynska K, Lewandowska D (2009) Differences among three populations of Pinus uliginosa and their relation to P. sylvestris has expressed by the needle characters. Dendrobiology 61:37–46
Eo JK, Hyun JO (2013) Comparative anatomy of the needles of Abies koreana and its related species. Turkish J Bot 37:553–560
Esteban LG, Martín JA, de Palacios P, Fernández FG, López R (2010) Adaptive anatomy of Pinus halepensis trees from different Mediterranean environments in Spain. Trees 24:19–30
Ghimire B, Lee C, Heo K (2014) Leaf anatomy and its implications for phylogenetic relationships in Taxaceae sl. J Plant Res 127:373–388
Grant DR (1977) Glacial style and ice limits, the Quaternary stratigraphic record, and changes of land and ocean level in the Atlantic Provinces, Canada. Géog Phys Quat 31:247–260
Gray JE, Holroyd GH, van der Lee FM, Bahrami AR, Sijmons PC, Woodward FI, Schuch W, Hetherington AM (2000) The HIC signalling pathway links CO2 perception to stomatal development. Nature 408:713–716
Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2005) Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int J Climatol 25:1965–1978
Huang RF (1993) The population heredity and evolution of P. yunnanensis. J Yunnan Univ 15:50–63
Jasińska AK, Boratyńska K, Sobierajska K, Romo A, Ok T, Kharat MBD, Boratyński A (2013) Relationships among Cedrus libani, C. brevifolia and C. atlantica has revealed by the morphological and anatomical needle characters. Plant Syst Evol 299:35–48
Jasinska AK, Boratynska K, Dering M, Sobierajska KI, Ok T, Romo A, Boratynski A (2014) Distance between south-European and south-west Asiatic refugial areas involved morphological differentiation: Pinus sylvestris case study. Plant Syst Evol 300:1487–1502
Jin ZZ, Peng J (2004) P. yunnanensis. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming, pp 1–167
Körner C (1989) The nutritional status of plants from high altitudes. Oecologia 81:379–391
Körner C (2007) The use of ‘altitude’ in ecological research. Trends Ecol Evol 22:569–574
Lavadinović V, Miletić Z, Lavadinović V, Isajev V (2011) Variability in magnesium concentration in needles of different Douglas-fir provenances. Forestry 17:74–79
Legoshchina O, Neverova O, Bykov A (2013) Variability of the anatomical structure of Picea obovata Ledeb. Needles under the influence of emissions from the industrial zone of Kemerovo. Contemp Probl Ecol 6:555–560
López R, Climent J, Gil L (2010) Intraspecific variation and plasticity in growth and foliar morphology along a climate gradient in the Canary Island pine. Trees 24:343–350
Mao JF, Wang XR (2011) Distinct niche divergence characterizes the homoploid hybrid speciation of Pinus densata on the Tibetan Plateau. Am Nat 177:424–439
Nikolić B, Bojović S, Marin P (2013) Variability of morpho-anatomical characteristics of the needles of Picea omorika from natural populations in Serbia. Plant Biosyst 10:1080–1126
Nobis MP, Traiser C, Roth-Nebelsick A (2012) Latitudinal variation in morphological traits of the genus Pinus and its relation to environmental and phylogenetic signals. Plant Ecol Divers 5:1–11
Rehfeldt G (1991) A model of genetic variation for Pinus ponderosa in the Inland Northwest (USA): applications in gene resource management. Can J For Res 21:1491–1500
Schlichting CD (1986) The evolution of phenotypic plasticity in plants. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 17:667–693
Sękiewicz K, Sękiewicz M, Jasińska A, Boratyńska K, Iszkuło G, Romo A, Boratyński A (2013) Morphological diversity and structure of West Mediterranean Abies species. Plant Biosyst 147:125–134
Tao JR, Kong ZC (1973) The fossil florule and sporo-pollen assemblage of the shang-in coal series of Erhyuan, Yunnan. Acta Bot Sin 15:120–126
Tiwari SP, Kumar P, Yadav D, Chauhan DK (2013) Comparative morphological, epidermal, and anatomical studies of Pinus roxburghii needles at different altitudes in the North-West Indian Himalayas. Turkish J Bot 37:65–73
Walter R, Epperson BK (2005) Geographic pattern of genetic diversity in Pinus resinosa: contact zone between descendants of glacial refugia. Am J Bot 92:92–100
Wang WM (1996) A palynological survey of Neogene strata in Xiao Long Tan basin, Yunnan province of south China. Acta Bot Sin 38:743–748
Wang CM, Wang J, Jiang HQ (2003) A Study on the comparative morphology of Pinus yunnanensis needles under different habitats. J Southwest For Coll 23:4–7
Wang CM, Wang J, Jiang HQ (2004) A Study on the Comparative Anatomy of Pinus yunnanensis Needles under Different Habitats. J Southwest For Coll 24:1–5
Wei W, Li GQ, Xu YL, Chen S, Lv XH, Cai NH (2012) Correlation between the temperature variation and the growth in height and basal diameter of seedling Pinus Yunnanensis. J Yunnan Univ (Natural Sciences Edition) 34:356–361
Wheeler B (2010) lmPerm: permutation tests for linear models. R package, version 1.0-1. http://CRAN.R-project.org/packagep=lmPerm
Woo KS, Fins L, McDonald GI, Wenny DL, Eramian A (2002) Effects of nursery environment on needle morphology of Pinus monticola Dougl. and implications for tree improvement programs. New For 24:113–129
Wu YS, Xiao JY (1991) A preliminary study on vegetation and climate changes in DianChi Lake area in the last 40000 years. Acta Bot Sin 33:450–458
Xing FQ, Mao JF, Meng JX, Dai JF, Zhao W, Liu H, Xing Z, Zhang H, Wang X, Li Y (2014) Needle morphological evidence of the homoploid hybrid origin of Pinus densata based on analysis of artificial hybrids and the putative parents, Pinus tabuliformis and Pinus yunnanensis. Ecol Evol 4:1890–1902
Xu B, Tao W (2006) Application of a hand-held slicing method for wood species identification. China Wood Ind 20:41–43
Zhang SB, Guan ZJ, Sun M, Zhang JJ, Cao KF, Hu H (2012) Evolutionary association of stomatal traits with leaf vein density in Paphiopedilum, Orchidaceae. Plos One 7:e40080
Zhao CM, Chen LT, Ma F, Yao BQ, Liu JQ (2008) Altitudinal differences in the leaf fitness of juvenile and mature alpine spruce trees (Picea crassifolia). Tree Physiol 28:133–141
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Hu-Wei Yuan, Li-Ming Wang, Fang-Qun Ouyang and Fang-Qian Xing for their kind help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project funding: This study was finically supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31070591) and Special National Forestry Public Welfare Industry Research (201104022) and the support of Southwest Forestry University.
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com.
Corresponding editor: Hu Yanbo.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Mao, J., Chen, Z. et al. Genetic structure of needle morphological and anatomical traits of Pinus yunnanensis . J. For. Res. 27, 13–25 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-015-0133-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-015-0133-x