Abstract
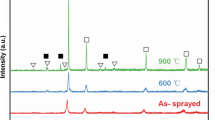
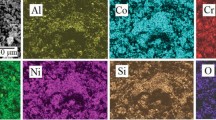
This study investigates the effect of annealing on the microstructural evolution, phase formation and tribological properties of CoCrFeNiW0.3 + 5 at.% C alloy prepared using atmospheric plasma spray. The annealing has a significant effect on microstructure evolution and tribological properties. The microstructure of the CoCrFeNiW0.3 + 5 at.% C alloy exhibits the lamellar microstructure. When the annealing temperature reaches 900 °C, the carbon dissolves in the chromium and forms Cr-rich carbides phase. The coarsening of grey phases is observed with the evolution of W-rich, and Cr-rich carbides as the temperature attain 1200 °C. Phase analysis results revealed that CoCrFeNiW0.3 + 5 at.% C alloy coating comprising of FCC solid solution phase, with Cr- and W-rich phase. As the annealing temperature increases from 900 to 1200 °C, more Cr- and W-rich phase evolved. The surface morphology results indicate the increase in the surface roughness value post-heat-treatment. The dilution level investigation reveals the strong metallurgical bonding between the coating and the substrate. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy reveal the formation of the oxidation state in detail. The average microhardness of the CoCrFeNiW0.3 + 5 at.% C alloy coating was found to be marginally decreased by increasing the annealing temperature, and the deposited coating microhardness was found to be 388.54 ± 14 HV0.2. The wear analysis test revealed a considerable decrease in wear resistance after heat treatment at 1200 °C. The wear volume rate of the as-deposited coating was found to be 7.88 × 10−5 mm3 N−1 m−1, and the coating annealed at 700, 900, and 1200 °C was 7.92 × 10−5, 8.02 × 10−5, 13.26 × 10−5 mm3 N−1 m−1, respectively.














Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
J.W. Yeh et al., Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6, p 299–303.
B. Cantor, Multicomponent and High Entropy Alloys, Entropy, 2014, 16, p 4749.
B.S. Murty, J.-W. Yeh, and S. Ranganathan, High-Entropy Alloys, 2nd ed. Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam, 2019, p 37–56
R. Feng, P.K. Liaw, M.C. Gao, and M. Widom, First-Principles Prediction of High-Entropy-Alloy Stability, Npj Comput Mater, 2017, 3(1), p 1–7.
G.U.O. Sheng and C.T. Liu, Phase Stability in High Entropy Alloys: Formation of Solid-Solution Phase or Amorphous Phase, Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int., 2011, 21(6), p 433–446.
J.-K. Xiao et al., Microstructure and Tribological Properties of Plasma-Sprayed Cocrfeni-Based High-Entropy Alloy Coatings under Dry and Oil-Lubricated Sliding Conditions, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2021, 30(4), p 926–936. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-021-01175-1
D. Wang et al., ‘Enhanced Creep Resistance of Ti30Al25Zr25Nb20 High-Entropy Alloy at Room Temperature, J. Alloys Compd., 2021, 885, p 161038.
A. Anupam et al., Understanding the Microstructural Evolution of High Entropy Alloy Coatings Manufactured by Atmospheric Plasma Spray Processing, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 505, p 144117.
A. Meghwal et al., Multiscale Mechanical Performance and Corrosion XXXinerali of Plasma-Sprayed AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings, J. Alloys Compd., 2021, 854, p 157140.
V. Soni, B. Gwalani, O.N. Senkov et al., Phase Stability as a Function of Temperature in a Refractory High-Entropy Alloy, J. of Mater. Res., 2018, 33, p 3235.
L.H. Tian et al., Microstructure and Wear Behavior of Atmospheric Plasma-Sprayed AlCoCrFeNiTi High-Entropy Alloy Coating, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25(12), p 5513–5521.
A.S.M. Ang, C.C. Berndt, and M.L. Sesso, Plasma-Sprayed High Entropy Alloys: Microstructure and Properties of AlCoCrFeNi and MnCoCrFeNi, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, 46(2), p 791–800.
L. Wei et al., Phase, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties Evaluation of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy During Mechanical Ball Milling, Intermetallics, 2021, 138, p 107310.
Lu. Jie et al., Oxidation Behavior of Gas-Atomised AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Powder at 900–1100 °C, Corros. Sci., 2021, 181, p 109257.
J.M. Zhu, H.M. Fu, H.F. Zhang et al., Microstructures and Compressive Properties of Multicomponent AlCoCrFeNiMox Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 6975–6979.
H. Liu, S. Sun, T. Zhang, G. Zhang, H. Yang, and J. Hao, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2021, 405, p 126522.
H. Kumar, S.G.K. Chandra Kumar, M. Manikandan, and S.S. Kamaraj, Laser Re-Melting of Atmospheric Plasma Sprayed High Entropy Alloy, Advanced Engineering of Materials Through Lasers. J. Radhakrishnan, S. Pathak Ed., Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2022, p 105–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-03830-3_5
J.M. Zhu, H.M. Fu, H.F. Zhang et al., Microstructure and Compressive Properties of Multiprincipal Component AlCoCrFeNiCx Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2011, 509, p 3476.
B.-S. Lou et al., Property Evaluation of TixZrNbTaFeBy High Entropy Alloy Coatings: Effect of Ti and B Contents, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2022, 434, p 128180.
H. Kumar, G.A. Bhaduri, S.G.K. Manikandan, M. Kamaraj, and S. Shiva, Microstructural Characterization and Tribological Properties of Atmospheric Plasma Sprayed High Entropy Alloy Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2022, 31(6), p 1956–1974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-022-01422-z
T. Xu, Y. Lu, Z. Cao, T. Wang, and T. Li, Effects of Ta Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCu0.5FeNi High-Entropy Alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2019, 28(12), p 7642–7648.
A. Vyas, J. Menghani, and H. Natu, Influence of WC Particle on the Metallurgical, Mechanical, and Corrosion Behavior of AlFeCuCrCoNi-WCx High-Entropy Alloy Coatings, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021, 30, p 2449–2461.
M. El Garah, S. Achache, A. Michau et al., AlTiTaZr(-N) Medium-Entropy Films Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering with a Combinatorial Approach, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021, 30, p 4063–4071.
J. Mahaffey, A. Vackel, S. Whetten et al., Structure Evolution and Corrosion Performance of CoCrFeMnNi High Entropy Alloy Coatings Produced Via Plasma Spray and Cold Spray, J. Therm. Spray Tech., 2022, 31, p 1143–1154.
M. Löbel, T. Lindner, T. Mehner et al., Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of AlCrFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings Prepared by HVAF and HVOF, J. Therm. Spray Tech., 2022, 31, p 247–255.
L. Hou et al., Mechanical Properties Improvement of CoCrFeMnNiB0.1 High Entropy Alloy through Annealing Design, Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc., 2020, 79(2), p 100–105.
J.H. Zhao et al., On the Microstructure and Erosion-Corrosion Resistance of AlCrFeCoNiCu High-Entropy Alloy Via Annealing Treatment, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2016, 32(12), p 1271–1275.
P. Patel et al., Microstructural and Tribological Behavior of Thermal Spray CrMnFeCoNi High Entropy Alloy Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2022, 31, p 1285–1301.
R.W. Gray, M.B. Welch, and R.O. Ragsdale, A Study of 4-Substituted Acetanilide Complexes of Nickel (II) and Cobalt (II) Perchlorates, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 1969, 3, p 17–20.
A.N. Mansour, Characterisation of Slightly Hydrated Ni(OH)2 by XPS, Surf. Sci. Spectra, 1994, 3, p 247.
M.C. Biesinger et al., Resolving Surface Chemical States in XPS Analysis of First Row Transition Metals, Oxides and Hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 257, p 2717.
S. Dhara, A.C. Rastogi, and B.K. Das, Growth, Magnetic Properties and the Effect of Cobalt Addition in Metal-Organic Chemical Vapour Deposited (MOCVD) Gamma Iron Oxide Thin Films for Magnetic Recording Applications, Bull. Mater. Sci., 1994, 17(4), p 367–387.
G.A. Bhaduri and L. Šiller, Nickel Nanoparticles Catalyse Reversible Hydration of Carbon Dioxide for Mineralization Carbon Capture and Storage, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2013, 3(5), p 1234–1239.
Z. Song, J. Hrbek, and R. Osgood, Formation of TiO2 Nanoparticles by Reactive-Layer-Assisted Deposition and Characterization by XPS and STM, Nano Lett., 2005, 5(7), p 1327–1332.
M. Kazemnejadi, Z. Sharafi, B. Mahmoudi et al., Magnetic Fe–Cr–Ni Oxide Alloy Nano-Belts Prepared from the Chemical Decomposition of a Stainless Steel Screw (a top-down approach): An Efficient and Cheap Catalyst for Multicomponent Reactions, J. Iran Chem. Soc., 2020, 17, p 777.
Y. Zhang, W. Li, L.J. France, Z. Chen, Q. Zeng, D. Guo, and X. Li, Annealing Strategies for the Improvement of Low-Temperature NH3-Selective Catalytic Reduction Activity of CrMnO x Catalysts, ACS Omega, 2019, 4(5), p 8681–8692.
D.K. Nguyen, H. Lee, and I.T. Kim, Synthesis and Thermochromic Properties of Cr-Doped Al2O3 for a Reversible Thermochromic Sensor, Materials, 2017, 10(5), p 476.
S. Kumar, S. Baruah, and A. Puzari, Poly(p-phenylenediamine)-Based Nanocomposites with Metal Oxide Nanoparticle for Optoelectronic and Magneto-Optic Application, Polym. Bull., 2020, 77, p 441–457.
S. Sarkar, S. Mukherjee, C.S. Kumar, and A.K. Nath, Effects of Heat Treatment on Microstructure, Mechanical and Corrosion Properties of 15–5 PH Stainless Steel Parts Built by Selective Laser Melting Process, Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 50, p 279–294.
H. Li, J. Li, C. Yan, X. Zhang, and D. Xiong, Microstructure and Tribological Properties of Plasma-Sprayed Al0.2Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti-Ag Composite Coating from 25 to 750 °C, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2020, 29(3), p 1640–1649.
M.A.G. Soler and F. Qu, Raman Spectroscopy of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles BT-Raman Spectroscopy for Nanomaterials Characterisation, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 2012, p 379–416
A. Motallebzadeh, S.A.A. Dilawary, E. Atar et al., High-Temperature Oxidation of Stellite 12 Hardfacings: Effect of Mo on Characteristics of Oxide Scale, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2019, 28, p 463–474.
Acknowledgments
This study is funded by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) under project no. (ISRO/RES/3/844/19-20). The authors appreciate ISRO's sponsorship. The authors thank IIT Jammu's Central Instrumentation Facility (CIF) for providing the characterization facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, H., Bhaduri, G.A., Manikandan, S.G.K. et al. Effect of Annealing on Microstructural and Tribological Properties of CoCrFeNiW0.3 + 5 at.% C High Entropy Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 6293–6306 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07547-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07547-0