Abstract
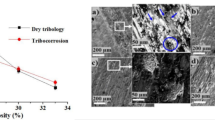
The application range of magnesium alloys is restricted because of poor tribological performance. The present study focuses on improving the tribological characteristics of magnesium Ze41A alloy by ball burnishing process. The lowest wear rate of 2.997 × (10)−3 mm3/m, CoF of 0.116 and interface temperature of 38 °C are obtained by ball burnishing process. The SEM examination at optimum burnishing condition reveals the oxidative wear mechanism, while the milled surface exhibited plastic deformation mechanism under similar wear conditions. The significant enhancement in tribological performance of magnesium Ze41A alloy is apparently due to the improvement in surface roughness and microhardness during ball burnishing process. The wear rate has been decreased by 51.22%, CoF by 72.58 and interfacial temperature by 39.68% at the optimum burnishing condition as compared to initial milling condition under similar wear conditions. Additionally, the tribological performance is evaluated by fuzzy interface system and the model found to estimate the results with an average absolute error of 4.92%.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Sachin, S. Narendranath and D. Chakradhar, Effect of Working Parameters on the Surface Integrity in Cryogenic Diamond Burnishing of 17–4 PH Stainless Steel with a Novel Diamond Burnishing Tool, J. Manuf. Process., 2019, 38, p 564–571.
G. Rotella, S. Rinaldi and L. Filice, Roller Burnishing of Ti6Al4V under Different Cooling/Lubrication Conditions and Tool Design: Effects on Surface Integrity, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2020, 106(1–2), p 431–440.
D.F. Silva-Álvarez et al., Improving the Surface Integrity of the CoCrMo Alloy by the Ball Burnishing Technique, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2020, 9(4), p 7592–7601.
T.T. Nguyen and L.H. Cao, Optimization of the BURNISHING Process for Energy Responses and Surface Properties, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., 2020, 21(6), p 1143–1152.
T.T. Nguyen, L.H. Cao, X.P. Dang, T.A. Nguyen and Q.H. Trinh, Multi-objective Optimization of the Flat Burnishing Process for Energy Efficiency and Surface Characteristics, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2019, 34(16), p 1888–1901.
G.V. Jagadeesh and S. Gangi Setti, A current Status of the Residual Stress Characterization by the Crystal Lattice Strain (Diffraction) Method, J. Struct. Chem., 2020, 61(2), p 262–273.
G. Devaraya, R. Shetty, S. Srinivas and V. Neelakanth, Wear Resistance Enhancement of Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V ) by Ball Burnishing Process, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2017, 6(1), p 13–32.
D.S. Rao, H.S. Hebbar, M. Komaraiah and U.N. Kempaiah, Investigations on the Effect of Ball Burnishing Parameters on Surface Hardness and Wear Resistance of HSLA Dual-Phase Steels, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2008, 23(3), p 295–302.
N.S.M. El-Tayeb, K.O. Low and P.V. Brevern, Influence of Roller Burnishing Contact width and Burnishing Orientation on Surface Quality and Tribological Behaviour of Aluminium 6061, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, 186, p 272–278.
K.O. Low and K.J. Wong, Influence of Ball Burnishing on Surface Quality and Tribological Characteristics of Polymers under dry Sliding Conditions, Tribol. Int., 2011, 44(2), p 144–153.
Ł Janczewski et al., Effects of Ball Burnishing on Surface Properties of Low Density Polyethylene, Tribol. Int., 2016, 93, p 36–42.
H. Hamadache, L. Laouar, N.E. Zeghib and K. Chaoui, Characteristics of Rb40 Steel Superficial Layer under Ball and Roller Burnishing, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2006, 180(1–3), p 130–136.
V.P. Kuznetsov, A.V. Makarov, S.G. Psakhie, R.A. Savrai, I.Y. Malygina and N.A. Davydova, Tribological Aspects in Nanostructuring Burnishing of Structural Steels, Phys. Mesomech., 2014, 17(4), p 250–264.
A. Dzierwa and A.P. Markopoulos, Influence of Ball-Burnishing Process on Surface Topography Parameters and Tribological Properties of Hardened Steel, Machines, 2019, 7(11), p 1–13.
N.S.M. El-Tayeb, K.O. Low and P.V. Brevern, Enhancement of Surface Quality and Tribological Properties using Ball Burnishing Process, Mach. Sci. Technol., 2008, 12(2), p 234–248.
N.S.M. El-Tayeb, K.O. Low and P.V. Brevern, On the Surface and Tribological Characteristics of Burnished Cylindrical Al-6061, Tribol. Int., 2009, 42(2), p 320–326.
N.S. Manam et al., Study of Corrosion in Biocompatible Metals for Implants: A Review, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 701, p 698–715.
G.V. Jagadeesh and S. Gangi Setti, Bio-Engineering and Bio-Design of New Generation Bioresorbable Implants, Indian J. Biochem. Biophys., 2021, 58, p 118–126.
Y.F. Zheng, X.N. Gu and F. Witte, Biodegradable Metals, Mater. Sci. Eng. R, 2014, 77, p 1–34.
Q. Chen and G.A. Thouas, Metallic Implant Biomaterials, Mater. Sci. Eng. R, 2015, 87, p 1–57.
X.N. Gu, X.H. Xie, N. Li, Y.F. Zheng and L. Qin, In Vitro and In Vivo Studies on a MG–Sr Binary Alloy System Developed as a New Kind of Biodegradable Metal, Acta Biomater., 2012, 8, p 2360–2374.
Y. Yang et al., Mg Bone Implant: Features, Developments and Perspectives, Mater. Des., 2020, 185, p 108259.
M. Geetha, A.K. Singh, R. Asokamani and A.K. Gogia, Ti Based Biomaterials, the Ultimate Choice for Orthopaedic Implants: A Review, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2009, 54, p 397–425.
S. Agarwal, J. Curtin, B. Duffy and S. Jaiswal, Biodegradable Magnesium Alloys for Orthopaedic Applications: A Review on Corrosion, Biocompatibility and Surface Modifications, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2016, 68, p 948–963.
D. Liu, D. Yang, X. Li and S. Hu, Mechanical Properties, Corrosion Resistance and Biocompatibilities of Degradable Mg-RE Alloys, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2018, 8(1), p 1538–1549.
R.I.M. Asri et al., Corrosion and Surface Modification on Biocompatible Metals: A Review, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2017, 77, p 1261–1274.
B.R. Sunil et al., In Vitro and In Vivo Studies of Biodegradable Fine Grained AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Produced by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2016, 59, p 356–367.
C. Taltavull, B. Torres, A.J. López and J. Rams, Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of AM50B Magnesium Alloy, Wear, 2013, 301, p 615–625.
S. Anbu Selvan and S. Ramanathan, Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of as-cast ZE41A Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Des., 2010, 31(4), p 1930–1936.
A.J. López, P. Rodrigo, B. Torres and J. Rams, Dry Sliding Wear Behaviour of ZE41A Magnesium Alloy, Wear, 2011, 271, p 2836–2844.
S.A. Selvan and S. Ramanathan, Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Hot Extruded ZE41A Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(7–8), p 1815–1820.
U. Elaiyarasan, V. Satheeshkumar and C. Senthilkumar, A Study on Wear Behaviour of Electrical Discharge-Coated Magnesium Alloy, J. Bio- Tribo-Corrosion, 2019, 5(1), p 1–9.
P. Rodrigo, M. Campo, B. Torres, M.D. Escalera, E. Otero and J. Rams, Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Al-SiC Composites Coatings on ZE41 Magnesium Alloy, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2009, 255(22), p 9174–9181.
S. García-Rodríguez et al., Wear Resistance of Stainless Steel Coatings on ZE41 Magnesium Alloy, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2018, 27(8), p 1615–1631.
L. Pezzato et al., Tribocorrosion Properties of PEO Coatings Produced on AZ91 Magnesium Alloy with Silicate- or Phosphate-Based Electrolytes, Coatings, 2018, 8(6), p 1–13.
L. Pezzato, K. Brunelli, S. Diodati, M. Pigato, M. Bonesso and M. Dabalà, Microstructural and Corrosion Properties of Hydroxyapatite Containing peo Coating Produced on az31 mg Alloy, Materials (Basel), 2021, 14(6), p 1–14.
M. Mohedano et al., Bioactive Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Coatings on Mg-Ca Alloy to Control Degradation Behaviour, Surf. Coatings Technol., 2017, 315, p 454–467.
R. Egala, G.V. Jagadeesh and S.G. Setti, Experimental Investigation and Prediction of Tribological Behavior of Unidirectional Short Castor Oil Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites, Friction, 2021, 9(2), p 250–272.
J. Leyva-Bravo, P. Chiñas-Sanchez, A. Hernandez-Rodriguez and G.G. Hernandez-Alba, Electrochemical Discharge Machining Modeling Through Different Soft Computing Approaches, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2020, 106(7–8), p 3587–3596.
A.A.D. Sarhan and N.S.M. El-Tayeb, Investigating the Surface Quality of the Burnished Brass C3605 - Fuzzy Rule-Based Approach, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2014, 71(5–8), p 1143–1150.
H. Basak and H.H. Goktas, Burnishing Process on al-Alloy and Optimization of Surface Roughness and Surface Hardness by Fuzzy Logic, Mater. Des., 2009, 30(4), p 1275–1281.
G.V. Jagadeesh and S.G. Setti, An Experimental Study on the Surface Finish of Ball Burnished Magnesium (Rare Earth Base) Alloy, Mater. Today Proc., 2019, 18, p 4711–4716.
Z. Yu Zhou et al., Wear Behavior of 7075-Aluminum After Ultrasonic-Assisted Surface Burnishing, J. Manuf. Process., 2020, 51, p 1–9.
B.B. Buldum and S.C. Cagan, Study of Ball Burnishing Process on the Surface Roughness and Microhardness of AZ91D Alloy, Exp. Tech., 2018, 42(2), p 233–241.
J.T. Maximov, G.V. Duncheva, A.P. Anchev, N. Ganev, I.M. Amudjev and V.P. Dunchev, Effect of Slide Burnishing Method on the Surface Integrity of AISI 316Ti Chromium–Nickel Steel, J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng., 2018, 40(4), p 1–14.
K. Mittal, A. Jain, K.S. Vaisla, O. Castillo and J. Kacprzyk, A comprehensive Review on Type 2 Fuzzy Logic Applications: Past, Present and Future, Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell., 2020, 95, p 103916.
A. Heidarzadeh, Ö.M. Testik, G. Güleryüz and R.V. Barenji, Development of a Fuzzy Logic Based Model to Elucidate the Effect of FSW Parameters on the Ultimate Tensile Strength and Elongation of Pure Copper Joints, J. Manuf. Process., 2020, 53(February), p 250–259.
S.K. Gugulothu, A Novel Assessment Study on a Dynamic Analysis of Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing Performance: A Taguchi-Fuzzy Based Approach Optimization, Transp. Eng., 2020, 2, p 100033.
Funding
No funds, grants or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jagadeesh, G.V., Gangi Setti, S. Tribological Performance Evaluation of Ball Burnished Magnesium Alloy for Bioresorbable Implant Applications. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 1170–1186 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06228-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06228-8