Abstract
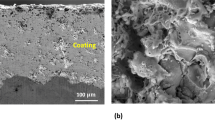
In this research, the erosion wear characterization of waste marble dust (an industrial/construction waste)-filled polyester composites is evaluated. The relative effect of the control factors on the erosion rate of the composites is experimentally and statistically evaluated using a statistical model based on the response surface method, and the mechanisms of erosion loss are studied from the worn surface morphologies taken using a scanning electron microscope. The analysis reveals that striking velocity, filler concentration, and impingement angle in that sequence are the significant control factors affecting the erosion rate of the composites. The erosion efficiency of the composites is calculated to ascertain the erosion behavior of the composites. Further, an analytical as well as predictive model working on neural networks, is used to predict the erosion rate of the composites at different levels of the individual control factors. Such composites are expected to be advantageous in wear-related applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Magnée, Generalized Law of Erosion: Application to Various Alloys and Intermetallics, Wear, 1995, 181–183(2), p 500–510
J. Cayer-Barrioz, D. Mazuyer, P. Kapsa, A. Chateauminois, and G. Robert, Abrasive Wear Micromechanisms of Oriented Polymers, Polymer (Guildf), 2004, 45(8), p 2729–2736
L. Jiang, C. He, J. Fu, and D. Chen, Wear Behavior of Straw Fiber-Reinforced Polyvinyl Chloride Composites under Simulated Acid Rain Conditions, Polym. Test., 2017, 62, p 373–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2017.07.028
O. Reynolds, XLII. On the Action of a Blast of Sand in Cutting Hard Material, Lond. Edinb., Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci., 1873, 46(307), p 337–343
S. Arjula and A.P. Harsha, Study of Erosion Efficiency of Polymers and Polymer Composites, Polym. Test., 2006, 25(2), p 188–196
M.A. Islam and Z.N. Farhat, Effect of Impact Angle and Velocity on Erosion of API, X42 Pipeline Steel under High Abrasive Feed Rate, Wear, 2014, 311(1–2), p 180–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2014.01.005
Y.I. Oka, H. Ohnogi, T. Hosokawa, and M. Matsumura, The Impact Angle Dependence of Erosion Damage Caused by Solid Particle Impact, Wear, 1997, 203–204, p 573–579
R. Rattan and J. Bijwe, Influence of Impingement Angle on Solid Particle Erosion of Carbon Fabric Reinforced Polyetherimide Composite, Wear, 2007, 262(5–6), p 568–574
S. Biswas and A. Satapathy, A Comparative Study on Erosion Characteristics of Red Mud Filled Bamboo-Epoxy and Glass-Epoxy Composites, Mater. Des., 2010, 31(4), p 1752–1767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.11.021
P.J. Mathias, W. Wu, K.C. Goretta, J.L. Routbort, D.P. Groppi, and K.R. Karasek, Solid Particle Erosion of a Graphite-Fiber-Reinforced Bismaleimide Polymer Composite, Wear, 1989, 135(1), p 161–169
A. Rout, A. Satapathy, S. Mantry, A. Sahoo, and T. Mohanty, Erosion Wear Performance Analysis of Polyester-GF-Granite Hybrid Composites Using the Taguchi Method, Procedia Eng., 2012, 38, p 1863–1882
J. Zahavi and G.F. Schmitt, Solid Particle Erosion of Reinforced Composite Materials, Wear, 1981, 71, p 179–190
E. Sarlin, M. Saarimäki, R. Sironen, M. Lindgren, S. Siljander, M. Kanerva, and J. Vuorinen, Erosive Wear of Filled Vinylester Composites in Water and Acidic Media at Elevated Temperature, Wear, 2017, 390–391, p 84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2017.07.011
M. Fang, F. Liu, X. Min, Z. Huang, Y. Liu, X. Wu, C. Tang, L. Zhang, and F. Peng, Effect of Temperature on Solid Particle Impact Erosion Wear Mechanism of 5 Mol% Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramics, Ceram. Int., 2015, 41(5), p 6807–6811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.01.128
A. Kishore and G.B. Sridhar, On Evaluating Erosion by Sand Particles in Polythene System without and with Ceramic Particles, Polym. Test., 2002, 21(4), p 473–477
A. Patnaik, A. Satapathy, S.S. Mahapatra, and R.R. Dash, Tribo-Performance of Polyester Hybrid Composites: Damage Assessment and Parameter Optimization Using Taguchi Design, Mater. Des., 2009, 30(1), p 57–67
H. Arabnejad, S.A. Shirazi, B.S. McLaury, H.J. Subramani, and L.D. Rhyne, The Effect of Erodent Particle Hardness on the Erosion of Stainless Steel, Wear, 2015, 332–333, p 1098–1103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2015.01.017
B. Ghiban, C.A. Safta, M. Ion, C.E. Crângaşu, and M.C. Grecu, Structural Aspects of Silt Erosion Resistant Materials Used in Hydraulic Machines Manufacturing, Energy Procedia, 2017, 112, p 75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.1064
K. Friedrich, Polymer Composites for Tribological Applications, Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res., 2018, 1(1), p 3–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aiepr.2018.05.001
P.J. Slikkerveer and F.J. Touwslager, Erosion of Elastomeric Protective Coatings, Wear, 1999, 236(1–2), p 189–198
R. Kaundal, Role of Process Variables on the Solid Particle Erosion of Polymer Composites: A Critical Review, Silicon, 2014, 6(1), p 5–20
A. Purohit and A. Satapathy, Development and Characterization of Epoxy-Based Composites Filled with Linz–Donawitz Sludge, J. Compos. Mater., 2017, 51(7), p 899–911
S. Ray, A.K. Rout, A.K. Sahoo, and I. After, Glass-Epoxy Composites Filled with Marble, UPB Sci. Bull. Ser. B, 2018, 80(4), p 181–196
C.B. Ng, B.J. Ash, L.S. Schadler, and R.W. Siegel, A Study of the Mechanical and Permeability Properties of Nano-TiO2 Filled Epoxy Composites, Adv. Compos. Lett., 2001, 10(3), p 101–111
R.K. Nayak, Influence of Seawater Aging on Mechanical Properties of Nano-Al2O3 Embedded Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Nanocomposites, Constr. Build. Mater., 2019, 221, p 12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.043
K. Friedrich, Z. Zhang, and A.K. Schlarb, Effects of Various Fillers on the Sliding Wear of Polymer Composites, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2005, 65(15-16 SPEC. ISS.), p 2329–2343
Krishna, B. Suresha, S.S. Kallesh, and R. Hemanth, Effect of Fillers on Erosive Wear Behavior of Polyoxymethylene/Polytetrafluoroethylene Blend and Their Composites: A Statistical Approach, Indian J. Adv. Chem. Sci., 2016, 1, p 45–51
K. Tanaka, Effects of Various Fillers on the Friction and Wear of PTFE-Based Composites, Frict. Wear Polym. Compos., 1986, https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-42524-9.50009-0
J. Abenojar, M.A. Martínez, F. Velasco, V. Pascual-Sánchez, and J.M. Martín-Martínez, Effect of Boron Carbide Filler on the Curing and Mechanical Properties of an Epoxy Resin, J. Adhes., 2009, 85(4–5), p 216–238
J. Abenojar, J.C. del Real, M.A. Martinez, and M.C. de Santayana, Effect of Silane Treatment on SiC Particles Used as Reinforcement in Epoxy Resins, J. Adhes., 2009, 85(6), p 287–301
J. Abenojar, J. Tutor, Y. Ballesteros, J.C. Real, and M.A. Martínez, Erosion-Wear, Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Silica Filled Epoxy Nanocomposites, Compos. Part B, 2017, 120, p 42–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.03.047
A.H. Awad and M.H. Abdellatif, Assessment of Mechanical and Physical Properties of LDPE Reinforced with Marble Dust, Compos. Part B Eng., 2019, 173(March), p 106948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.106948
P.K. Padhi and A. Satapathy, Analysis of Sliding Wear Characteristics of BFS Filled Composites Using an Experimental Design Approach Integrated with ANN, Tribol. Trans., 2013, 56(5), p 789–796
A.H. Awad, A. Aly Abd El-Wahab, R. El-Gamsy, and M.H. Abdel-latif, A Study of Some Thermal and Mechanical Properties of HDPE Blend with Marble and Granite Dust, Ain Shams Eng. J., 2019, 10(2), p 353–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2018.08.005
S.K. Nayak, A. Satapathy, and S. Mantry, Processing and Wear Response Study of Glass-Polyester Composites with Waste Marble Dust as Particulate Filler, Polym. Compos., 2019, 2020, p 1–11
S.K. Nayak, A. Satapathy, and S. Mantry, Wear Characteristics of Glass-Polyester-Based Hybrid Composites: A Parametric Analysis Using Response Surface Method and Fuzzy Logic, Polym. Compos., 2020, 41(9), p 3687–3697
S.K. Nayak and A. Satapathy, Wear Analysis of Waste Marble Dust-Filled Polymer Composites with an Integrated Approach Based on Design of Experiments and Neural Computation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol., 2019, 234, p 1–11
S.K. Nayak and A. Satapathy, Development and Characterization of Polymer-Based Composites Filled with Micro-Sized Waste Marble Dust. Polym. Polym. Compos., 2020, p 1–12
A. Purohit and A. Satapathy, Epoxy matrix composites filled with micro-sized LD sludge: wear characterization and analysis, in IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (2016), p. 012006 (1–8)
R. Sundarakannan, V. Arumugaprabu, V. Manikandan, and R. Deepak Joel Johnson, Tribo performance studies on redmud filled pineapple fiber composite, in IConAMMA 2018 Tribo, Materials Today: Proceedings (Elsevier Ltd., 2018), pp. 1225–1234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.437
S. Biswas, A. Satapathy, and A. Patnaik, A comparative study on wear behavior of copper slag filled bamboo-epoxy and glass-epoxy composites, in International Conference on “Advancements in Polymeric Materials” (APM-2010) (Bhubaneswar, India, 20–22 February 2010, 2010), pp. 1–5.
P. Kumar Padhi and A. Satapathy, Solid Particle Erosion Behavior of BFS-Filled Epoxy-SGF Composites Using Taguchi’s Experimental Design and ANN, Tribol. Trans., 2014, 57(3), p 396–407
A. Purohit and A. Satapathy, A study on erosion wear performance of Linz–Donawitz sludge filled polypropylene matrix composites, in International Conference on Mechanical Materials and Renewable Energy, IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 377, no. 1 (2018), p. 012045 (1–5)
A. Patnaik, A. Satapathy, S.S. Mahapatra, and R.R. Dash, Modeling and Prediction of Erosion Response of Glass Reinforced Polyester-Flyash Composites, J. Reinf. Plast. Compos., 2009, 28(5), p 513–536
A. Rout, A. Satapathy, S. Mantry, A. Sahoo, and T. Mohanty, Erosion wear performance analysis of polyester-GF-granite hybrid composites using the Taguchi method, in Procedia Engineering, International Conference on Modelling Optimization and Computing-2012 (Tamilnadu, India, 10–11 April 2012) (Elsevier Ltd., 2012), pp. 1863–1882
J.J. Mathavan and A. Patnaik, Analysis of Wear Properties of Granite Dust Filled Polymer Composite for Wind Turbine Blade, Results Mater., 2020, 5, p 100073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinma.2020.100073
N. Soni and P.M. Bhargava, Experimental Investigation and Numerical Simulation of Marble Dust Filled Aramid Fibre Reinforced Epoxy Composite for Wind Turbine Blade Application, Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Technol., 2017, 6(1), p 23–31
N. Senthilkumar, T. Tamizharasan, and S. Gobikannan, Application of Response Surface Methodology and Firefly Algorithm for Optimizing Multiple Responses in Turning AISI, 1045 Steel, Arab. J. Sci. Eng., 2014, 39(11), p 8015–8030
R. Calfee and D. Piontkowski, Design and analysis of experiments, in Handbook of Reading Research, ed. by Heath Rushing, Andrew Karl, James Wisnowski, 2013 edn (SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina, 2016)
C.P. Koshy, P.K. Rajendrakumar, and M.V. Thottackkad, Evaluation of the Tribological and Thermo-Physical Properties of Coconut Oil Added with MoS2 Nanoparticles at Elevated Temperatures, Wear, 2015, 330–331(January), p 288–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2014.12.044
A. Kumar, V. Kumar, and J. Kumar, Multi-Response Optimization of Process Parameters Based on Response Surface Methodology for Pure Titanium Using WEDM Process, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2013, 68(9–12), p 2645–2668
M. Hanief and M.F. Wani, Modeling and Prediction of Surface Roughness for Running-in Wear Using Gauss-Newton Algorithm and ANN, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 357, p 1573–1577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.10.052
J. Adamowski and C. Karapataki, Comparison of Multivariate Regression and Artificial Neural Networks for Peak Urban Water-Demand Forecasting : Evaluation of Different ANN Learning Algorithms, J. Hydrol. Eng., 2010, 15, p 729–743
G. Sundararajan, M. Roy, and B. Venkataraman, Erosion Efficiency—A New Parameter to Characterize the Dominant Erosion Micromechanism, Wear, 1990, 140(2), p 369–381
A.P. Harsha, U.S. Tewari, and B. Venkatraman, Solid Particle Erosion Behaviour of Various Polyaryletherketone Composites, Wear, 2003, 254(7–8), p 693–712
H. Jena, A.K. Pradhan, and M.K. Pandit, Study of Solid Particle Erosion Wear Behavior of Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composite with Cenosphere Filler, Adv. Polym. Technol., 2018, 37(3), p 761–769
G.P. Tilly, Erosion Caused by Airborne Particles, Wear, 1969, 14(1), p 63–79
T. Sinmazcelik and I. Taskiran, Erosive Wear Behaviour of Polyphenylenesulphide (PPS) Composites, Mater. Des., 2007, 28, p 2471–2477
A.P. Harsha and A.A. Thakre, Investigation on Solid Particle Erosion Behaviour of Polyetherimide and Its Composites, Wear, 2007, 262(7–8), p 807–818
A.P. Harsha and S.K. Jha, Erosive Wear Studies of Epoxy-Based Composites at Normal Incidence, Wear, 2008, 265, p 1129–1135
N.M. Barkoula, J. Gremmels, and J. Karger-Kocsis, Dependence of Solid Particle Erosion on the Cross-Link Density in an Epoxy Resin Modified by Hygrothermally Decomposed Polyurethane, Wear, 2001, 247(1), p 100–108
M. Yogesh and A.N. Hari-Rao, Erosion Wear Response of Pineapple Leaf Fiber (PALF) Reinforced Vinylester Composites Filled With Redmud: An Alumina Plant Waste, Int. J. Eng. Dev. Res., 2018, 6(1), p 734–746
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This invited article is part of a special topical focus in the Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance on Surface Engineering. The issue was organized by Dr. M.K. Banerjee, Malaviya National Institute of Technology, Jaipur.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nayak, S.K., Satapathy, A. & Mantry, S. Parametric Analysis for Erosion Wear of Waste Marble Dust-Filled Polyester Using Response Surface Method and Neural Networks. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 3942–3954 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05595-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05595-6