Abstract
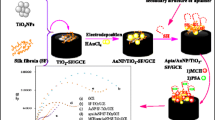
An impedimetric aptasensor has been used to study the effect of charge transfer on the binding of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) to its aptamer. Full understanding of this mechanism will be beneficial to further improve its sensitivity for PSA detection in human semen at physiologically relevant concentrations. Bare gold electrodes (SPAuEs) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs)-coated screen-printed carbon ink electrodes (AuNPs/SPCEs) were coated with aptamer solution at various concentrations and the sensor response to increasing PSA concentration in buffer solution examined. AuNPs were deposited onto carbon electrodes in 10 cycles. AuNPs/SPCEs were then coated with a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of 16-mercaptohexadecanoic acid prior to aptamer immobilization at dose of 5 μg mL−1. The results indicate that anisotropic AuNPs/SPCEs outperform bare gold electrodes in terms of decreased amount of aptamer bunches as well as the number of intermediate PSA-aptamer complexes formed on the electrode surface. The key finding is that the fabricated aptasensor is sensitive enough [limit of detection (LoD) 1.95 ng mL−1] for early diagnosis of prostate cancer and displays linear response in the physiologically relevant concentration range (0 ng mL−1 to 10 ng mL−1), as shown by the calibration curve of the relative change in electron transfer resistance (ΔR CT) versus PSA concentration when aptamer/SAM/AuNPs/SPCEs were exposed to buffer containing PSA at different concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Diet, Nutrition, Physical Activity and Prostate Cancer (World Cancer Research Fund, 2014). http://www.wcrf. org/sites/default/files/Prostate-Cancer-2014-Report.pdf. Accessed 1 Sept 2016
S.P. Balk, J. Clin. Oncol. 21, 383 (2003).
R.P. Gallagher and N. Fleshner, CMAJ 159, 807 (1998).
J.A. Ludwig and J.N. Weinstein, Nat. Rev. Cancer 5, 845 (2005).
G. Botchorishvili, M.P. Matikainen, and H. Lilja, Curr. Opin. Urol. 19, 221 (2009).
M.J. Barry, Clin. Pract. 344, 1373 (2001).
P. Gunnar Aus, J.-E. Damber, A. Khatami, H. Lilja, J. Stranne, and J. Hugosson, Am. Med. Assoc. 165, 1857 (2005).
A.D. Ellington and J.W. Szostak, Nature 346, 818 (1990).
M. Mascini, Aptamers in Bioanalysis (New York: Wiley, 2009), pp. 3–5.
K.M. Song, S. Lee, and C. Ban, Sensors 12, 612 (2012).
M. Famulok, Acc. Chem. Res. 33, 591 (2000)
J.J. Li, X. Fang, and W. Tan, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 292, 31 (2002).
C.A. Savran, S.M. Knudsen, A.D. Ellington, and S.R. Manalis, Anal. Chem. 76, 3194 (2004).
C. Tuerk and L. Gold, Science 249, 505 (1990).
A.-E. Radi, Int. J. Electrochem. 2011, 1 (2011).
M.M. Costa, M. Guix, P. Kara, and A. De Escosura-mu, Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 1715 (2010).
Z. Yang, B. Kasprzyk-Hordern, S. Goggins, C. G. Frost, and P. Estrela, Analyst 140, 2628 (2015)
A. Santos, J.J. Davis, and P.R. Bueno, J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. S7, 1 (2014).
D.W. Kimmel, G. LeBlanc, M.E. Meschievitz, and D.E. Clifferl, Anal. Chem. 84, 685 (2012).
E. Katz and I. Willner, Electroanalysis 15, 913 (2003).
Z. Chen, Y. Lei, X. Chen, Z. Wang, and J. Liu, Biosens. Bioelectron. 36, 35 (2012).
T. Lien, N. Xuan Viet, and M. Chikae, J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2, 2 (2011).
L.T.N. Truong, M. Chikae, Y. Ukita, and Y. Takamura, Talanta 85, 2576 (2011).
T.T.N. Lien, Y. Takamura, E. Tamiya, and M.C. Vestergaard, Anal. Chim. Acta 892, 69 (2015).
N. Savory, K. Abe, K. Sode, and K. Ikebukuro, Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 1386 (2010).
P. Jolly, N. Formisano, J. Tkáč, P. Kasák, C.G. Frost, and P. Estrela, Sens. Actuators B Chem. 209, 306 (2015).
B. Liu, L. Lu, E. Hua, S. Jiang, and G. Xie, Microchim. Acta 178, 163 (2012).
P. Jolly, N. Formisano, and P. Estrela, Chem. Pap. 69, 77 (2015).
Y. Shamoo, Encycl. Life Sci. 1 (2002)
S.J. Ding, B.W. Chang, C.C. Wu, M.F. Lai, and H.C. Chang, Anal. Chim. Acta 554, 43 (2005).
M.I. Prodromidis, Electrochim. Acta 55, 4227 (2010).
B. Pejcic and R. De Marco, Electrochim. Acta 51, 6217 (2006).
G. Tsekenis, G. Garifallou, F. Davis, P.A. Millner, T.D. Gibson, and S.P.J. Higson, Anal. Chem. 80, 2058 (2008).
R. Elshafey, C. Tlili, A. Abulrob, A.C. Tavares, and M. Zourob, Biosens. Bioelectron. 39, 220 (2013).
E.C. Rama, M.B. González-García, and A. Costa-García, Sens. Actuators B Chem. 201, 567 (2014).
F. Rohrbach, H. Karadeniz, A. Erdem, M. Famulok, and G. Mayer, Anal. Biochem. 421, 454 (2012).
M. Peeters, B. Van Grinsven, T.J. Cleij, K.L. Jiménez-Monroy, P. Cornelis, E. Pérez-Ruiz, G. Wackers, R. Thoelen, W. De Ceuninck, J. Lammertyn, and P. Wagner, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 10316 (2015).
Acknowledgements
This research is funded by the Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED, Grant No. 103.99-2012.12) and The Flemish Interuniversity Council (VLIR-UOS, Grant No. ZEIN2013RIP022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Do, T.T.N., Van Phi, T., Nguy, T.P. et al. Anisotropic In Situ-Coated AuNPs on Screen-Printed Carbon Surface for Enhanced Prostate-Specific Antigen Impedimetric Aptasensor. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 3542–3552 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5187-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5187-9