Abstract
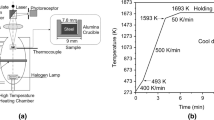
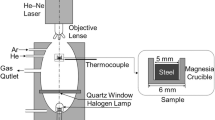
In this study, the precipitation, aggregation, and dissolution behaviors of TiN inclusions on the surface of liquid GCr15 bearing steel have been investigated by combining the observations of confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) and field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) with those obtained from energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) and theoretical analysis. The kinetic results show that the initial concentration of Ti and N are 0.0078 and 0.0049, respectively, the precipitation temperature is between 1640 K and 1680 K (1367 °C and 1407 °C), and the local cooling rate is between 0.5 and 10 K/s; TiN inclusion can precipitate only when the solid fraction is higher than 0.847 and its precipitation radius is between 1 and 6 μm. The precipitation radius of a TiN inclusion in the GCr15 bearing steel sheet can be reduced by decreasing the N content and increasing the cooling strength. The aggregation and densification of multi-particle aggregated TiN inclusions are verified by CLSM observation and theoretical analysis. The inclusions are aggregated by the cavity bridge force (CBF), and the aggregated TiN is formed by solid-phase sintering. The results of force analysis show that CBF plays a dominant role in the aggregation process of the inclusions. The atomic ratio of Ti and V obtained by EDS is 18:1, which may melt TiN and form the liquid inclusion at 1688 K (1415 °C) observed by CLSM. The theoretical analysis is conducted for the dissolution of the TiN inclusions observed by CLSM, which shows that the dissolution of the TiN inclusions is related to the size of the inclusions; the larger the size, the greater the dissolution rate. The long-strip TiN inclusion may be formed by the Ostwald ripening of two TiN inclusions. The TiN inclusions smaller than 3 μm in the GCr15 bearing steel may be formed by the dissolved Ti and N generated by the dissolution of TiN.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
[1] W. Ma, Y. Bao, and L. Zhao, and M. Wang: Int. J. Mine. Metall. Mater., 2014, vol. 21, pp. 234-39.
[2] Y. Liu, L. Zhang, and H. Duan, Y. Zhang, Y. Luo,and A. N. Conejo: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, vol. 47A, pp. 3015-25.
[3] H. Y. Liu, H. L. Wang, L. Li, J. Q. Zheng, Y. H. Li and X. Y. Zeng: Ironmak. and Steelmak., 2013, vol. 38: 53-58.
J. I. Takamura, and S. Mizoguchi: Proc. Int. Iron and Steel Congr., 6th, 1990, pp. 591–97.
[5] H. Ohta, R. Inoue, and H. Suito: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48, pp. 294-300.
[6] X. Yin, Y. Sun, Y. Yang, X. Bai, M. Barati, and A. Mclean, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47B, pp. 3274-84.
[7] W. Yan, Y. Shan, and K. Yang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 2147-58.
[8] S. Kanazawa, A. Nakashima, K. Okamoto, and K. Kanaya: Armaghan Danesh, 1975, vol. 61, pp. 130-40.
[9] Y. Tomita, N. Saito, T. Tsuzuk, Y. Tokunaga, and K. Okamo: ISIJ Int.,1994, vol. 34, pp. 829-35.
[10] M.A. Linaza, J.L. Romero, J.M. Rodriguez-Ibabe, and J.J.Urcola: Scr. Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 29, pp. 451-56.
H. Todoroki, and N. Shiga: Proceedings of the International Congress on Science and Technology of Steelmaking, ISIJ, Tokyo, Japan, 2008, pp. 121–24.
[12] K. Oikawa, H. Ohtani, K. Ishida, and T. Nishizawa: ISIJ Int., 1995, vol. 35, pp. 402-08.
[13] S. Mukae, K. Nishio, M. Katoh, and T. Isayama: Journal of the Japan Welding Society, 1985, vol. 3, pp. 567-74.
[14] H. Mabuchi, R. Uemori, and M. Fujioka: ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 39, pp. 1406-12.
[15] M. Fattahi, N. Nabhani, M. Hosseini, N. Arabian, E. Rahimi: Micron, 2013, vol. 45, pp. 107-14.
[16] P. Misra, S. Sridhar, and A.W. Cramb: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2001, vol. 32B, pp. 963-67.
[17] Y. Zhang, X. Li, and H. Ma: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47B, pp. 2148-56.
[18] X. Wan, B. Zhou, K. C. Nune, Y. Li, K. Wu, and G. Li: Science & Technology of Welding & Joining, 2016, vol. 22, pp. 343-52.
[19] L. Yang, G. Cheng, S. Li, M.Zhao, and G. Feng: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 1901-05.
[20] Q. Tian, G. Wang, Y. Zhao, J. Li, and Q. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, vol. 49B, pp. 1149-64.
[21] H. Suito, H. Ohta: ISIJ Int., 2006, vol. 46, pp. 33-41.
[22] G.M. Gulliver: Metallic Alloys, Griffen, London, 1922.
[23] E. Scheil: Zeitschrift Metallkunde, 1942, vol. 34, pp. 70-72.
[24] E. Gao, G. Zou, W. Wang, F. Ma, and X. Luo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 48B, pp. 1014-23.
[25] Y. Won, B. G. Thomas: Metall. Mater.Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 1755-67.
[26] F. Huang, J. Zhang, X. Wang, S. Wang, Y. Fang, and Y. Yu.: J. Iron Steel Res., 2008, vol. 20, pp. 14-19.(in Chinese).
[27] K. Sasai: ISIJ Int., 2016, vol. 56, pp. 1013-22.
[28] K. Sasai: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 2780-89.
[29] M. Nakamoto, T. Tanaka, M. Suzuki, K. Taguchi, Y. Tsukaguchi, and T. Yamamoto: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 1195-203.
[30] R. N. Lumley, T. B. Sercombe, and G. M. Schaffer: Metall. Mater.Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30A, pp. 457-63.
[31] C. Xuan, A. V. Karasev, P. G. Jönsson, and K. Nakajima: Steel Res. Int., 2016, vol. 87, pp. 1-9.
[32] K. Wu: Principles of Metallurgical Transport, 1th ed., Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2011, pp. 7.
[33] Y. Sui, G. Sun, Y. Zhao, C. Wang, M. Guo, and M. Zhang: J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing., 2014, vol. 36, pp. 1174-82.
[34] L. Zhang, C. Guo, W. Yang, Y. Ren, H. Ling: Metall. Mater.Trans. B, 2018, vol. 49B, pp. 803-11.
W. Ostwald: Lehrbuch der Allgemeinen Chemie, 1896, Vol. 2.
[36] W. Ostwald: Zeitschrift Für Physikalische Chemie, 1897, vol. 22, pp. 289-330.
[37] R. Tadmor: J. Phys. Cond. Mat., 2001,vol. 13, pp. 195-202.
[38] I. M. Lifshitz, and V.V. Slyozov: J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1961, vol. 19, pp. 35-50.
[39] C. Wagner: Zeitschrift für Elektrochemie, 1961, vol. 65, pp. 581-91.
[40] H. B. Aaron: Metal Sci.,1968, vol. 2, pp. 192-93.
[41] L. Cheng, E. Hawbolt, and T. Meadowcroft: Metall. Mater.Trans. A, 2000, vol. 31A, pp. 1907-16.
[42] J. Moon, C. Lee, S. Uhm, and J. Lee: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 1053-61.
[43] T. Hong, and T. Debroy: Metall. Mater.Trans. B, 2003, vol. 34B, pp. 267-269.
[44] T. Hong, and T. Debroy: Ironmak. and Steelmak., 2001, vol. 28, pp. 450-54.
[45] T. Hong, and T. Debroy: Scr. Mater.,2001, vol. 44, pp. 847-52.
[46] M.J. Whelan: Met. Sci. J., 1969, vol. 3, pp. 95-97.
Y. Jin, and S. Du: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2016, published online, pp. 1–6.
[48] S. Lee, Y. Oh, and K. Yi: Mater. Trans., 2002, vol. 43, pp. 518-22.
[49] Y. Chen, Y. Bao, M. Wang, X. Cai, L. Wang, and L. Zhao: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 2215-20.
[50] P. Chen, C. Zhu, G. Li, Y. Dong, and Z. Zhang: ISIJ Int., 2017, vol. 57, pp. 1019-28.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully express their appreciation to Natural Science Foundation of China (51634004); The Union Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Marine Equipment and Applications—University of Science and Technology Liaoning (SKLMEA - USTL - 201706); The Open Project Foundation of the Key Laboratory of Electromagnetic Process Material, Northeastern University, China (NEU - EPM - 001); and Natural Science Foundation of China (51474125) for supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 9, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Q., Wang, G., Shang, D. et al. In Situ Observation of the Precipitation, Aggregation, and Dissolution Behaviors of TiN Inclusion on the Surface of Liquid GCr15 Bearing Steel. Metall Mater Trans B 49, 3137–3150 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1411-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1411-8