Abstract
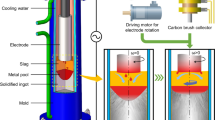
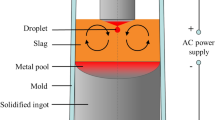
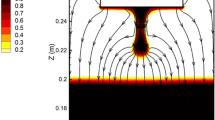
This paper presents a numerical method to investigate the shape of tip and melt rate of an electrode during electroslag remelting process. The interactions between flow, temperature, and electromagnetic fields are taken into account. A dynamic mesh-based approach is employed to model the dynamic formation of the shape of electrode tip. The effect of slag properties such as thermal and electrical conductivities on the melt rate and electrode immersion depth is discussed. The thermal conductivity of slag has a dominant influence on the heat transfer in the system, hence on melt rate of electrode. The melt rate decreases with increasing thermal conductivity of slag. The electrical conductivity of slag governs the electric current path that in turn influences flow and temperature fields. The melting of electrode is a quite unstable process due to the complex interaction between the melt rate, immersion depth, and shape of electrode tip. Therefore, a numerical adaptation of electrode position in the slag has been implemented in order to achieve steady state melting. In fact, the melt rate, immersion depth, and shape of electrode tip are interdependent parameters of process. The generated power in the system is found to be dependent on both immersion depth and shape of electrode tip. In other words, the same amount of power was generated for the systems where the shapes of tip and immersion depth were different. Furthermore, it was observed that the shape of electrode tip is very similar for the systems running with the same ratio of power generation to melt rate. Comparison between simulations and experimental results was made to verify the numerical model.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Hoyle: Electroslag Processes, Applied Science Publishers, London, 1983.
E. J. Pickering: ISIJ Int., 2013, vol. 53, pp. 935–49.
G. Hoyle: 6th International Vacuum Metallurgy Conference on Special Melting, San Diego, 1979, pp. 624–40.
W. Holzgruber: 5th International Symposium on Electroslag and Other Special Melting Technologies, Pittsburgh, 1974, pp. 70–91.
A. Mitchell: Perspective in Metallurgical Development Conference, Sheffield, England, 1984, pp. 89–98.
F.S. Suarez, J.E. Roberts, and L.D Schley: 5th International Symposium on Electroslag and Other Special Melting Technologies, Pittsburgh, 1974, pp. 126–45.
A. Mitchell: Electric Furnace Steelmaking Conference, ISS, Warrendale, PA, 1985, p. 212.
A. Kharicha, E. Karimi-Sibaki, M. Wu, and A. Ludwig: International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Austin, 2013, pp. 95–99.
D.K. Melgaard, J.J. Beaman, and G.J. Shelmidine: U.S. Patent 7,180,931 B1, 2007.
D.K. Melgaard, G.J. Shelmidine, and B.K. Damkroger: U.S. Patent 6,496,530 B2, 2002.
D.K. Melgaard, R.L. Williamson, and J.J. Beaman: JOM, 1998, vol. 50 pp. 13–17.
A. Kharicha, M. Wu, and A. Ludwig: International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Austin, 2013, pp. 145–50.
M. A. Maulvault: Ph.D. Thesis, MIT, 1967, pp. 80–85.
A. Mitchell, S. Joshi and J. Cameron: Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 561–67.
J. Mendrykowski, J.J. Poveromo, J. Szekely and A. Mitchell: Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 4, pp. 1761–68.
T. Kishida, K. Yamaguchi, T. Tomioka, and T. Ichihara: Electr. Steel, 1974, vol. 45, pp. 219–27.
K. H. Tacke and K. Schwerdtfeger: Arch. Eisenhüttenwesen, 1981, vol. 52, pp. 137–42.
A. Jardy, D. Ablitzer and J.F. Wadier: Metall. Trans. B, 1991, vol. 22, pp. 111–20.
J. Yanke, K. Fezi, M. Fahrmann, and M.J.M. Krane: International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Austin, 2013, pp. 47–55.
A. Kharicha, M. Wu and A. Ludwig: ISIJ, 2014, vol. 54, pp. 1621–28.
A. Mitchell, G. Beynon: Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 3333–45.
M. Kawakami, K. Nagata, M. Yamamura, N. Sakata, Y. Miyashita and K.S. Goto, Testsu- to-Hagane,1977, vol. 63, p. 220.
A. Kharicha, A. Ludwig, and M. Wu: EPD Congress, San Diego, 2011, pp. 771–78.
A. Kharicha, M. Wu, A. Ludwig, M. Ramprecht, H. Holzgruber: CFD modeling and simulation in materials, Wiley Florida, 2012, pp.139–46.
V. Weber, A. Jardy, B. Dussoubs, D. Ablitzer, S. Ryberon, V. Schmitt, S. Hans and H. Poisson: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2009, vol. 40B, pp. 271–80.
H. Song and N. Ida: IEEE Trans. Magn., 1991, vol. 27, pp. 4012–15.
T. Esch and F. R. Menter: Turbulence Heat and Mass Transfer Conference, Antalya, Turkey, 2003.
F.R. Menter: AIAA J., 1994, vol. 32, pp. 1598–605.
F. R. Menter, M. Kuntz and R. Langtry: Turbul. Heat Mass Transf., 2003, vol. 4, pp. 625–32.
Fluent 14.5 User’s Guide, Fluent Inc., 2012.
A. Menendez Blanco and J. M. Fernandez Oro: Comput. Fluids, 2012, vol. 57, pp.138–50.
G. Lame and B.P. Clapeyron: Ann. Chem. Phys., 1831, vol. 47, pp. 250–56.
L.I. Rubinstein: The Stefan Problem, American Mathematical Society, Providence USA, 1971.
K.C. Mills and B.J. Keene: Int. Met. Rev., 1981, vol. 1, pp. 21–69.
M. Hajduk and T.E. Gammal: Stahl Eisen, 1979, vol. 99, p. 113.
K.M. Kelkar, S.V. Patankar, S.K. Srivatsa, R.S. Minisandram, D.G. Evans, J.J. deBarbadillo, R.H. Smith, R.C. Helmink, A. Mitchell, and H.A. Sizek: International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Austin, 2013, pp. 3–12.
A.D. Patel: International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Nancy, France, 2011, pp. 49–56.
S.F. Medina and M.P. de Andres: Ironmak. Steelmak., 1987, vol. 14, pp.110–21.
E. Karimi-Sibaki, A. Kharicha, M. Wu, and A. Ludwig: International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Austin, 2013, pp. 13–19.
E. Karimi-Sibaki, A. Kharicha, M. Wu, and A. Ludwig: Ingot Casting Rolling Forging Conference, Milan, Italy, 2014.
H. Holzgruber, W. Holzgruber, A. Scheriau, M. Knabl, M. Kubin, J. Korp, and R Pierer: International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Nancy, France, 2011, pp. 57–64.
M. Hugo, B. Dussoubs, A. Jardy, J. Escaffre, and H. Poisson: International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Austin, 2013, pp. 79–85.
A. Kharicha, A. Ludwig and M. Wu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 413–414, pp. 129–34.
E. Karimi-Sibaki, A. Kharicha, J. Korp, M. Wu, and A. Ludwig: Met. Trans. Forum, vol. 790, p. 396, 2014.
A. Kharicha, W. Schützenhöfer, A. Ludwig, R. Tanzer and M. Wu: Steel Res. Int., 2008, vol. 79, pp. 632–36.
R. Taylor and K.C. Mills: Arch. Eisenhüttenwesen, 1982, vol. 53, pp. 55–63.
M. Choudhary and J. Szekely: Ironmak. Steelmak., 1981, vol. 5, pp. 225-32.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support by the Austrian Federal Ministry of Economy, Family and Youth and the National Foundation for Research, Technology and Development within the framework of the Christian Doppler Laboratory for Advanced Process Simulation of Solidification and Melting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted December 3, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karimi-Sibaki, E., Kharicha, A., Bohacek, J. et al. A Dynamic Mesh-Based Approach to Model Melting and Shape of an ESR Electrode. Metall Mater Trans B 46, 2049–2061 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-015-0384-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-015-0384-0