Abstract
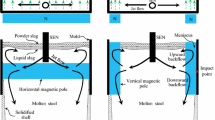
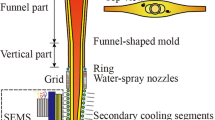
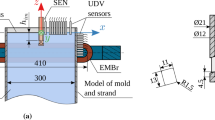
In the current study, a three-dimensinal (3D) numerical model is built to investigate the effect of a local-type electromagnetic brake (EMBr) on the fluid flow, heat transfer, and inclusion motion in slab continuous casting strands. The results indicate that the magnetic force affects the jet characteristics, including jet angle, turbulent kinetic energy, and its dissipation rate. To reduce the top surface velocity and stabilize the top surface, the magnetic flux intensity should be larger than a critical value. With a 0.39 T magnetic flux intensity, the top surface velocity and its fluctuation can be well controlled, and less slag is entrained. The motion of argon bubbles is also studied. More bubbles, especially >2.0-mm bubbles, escape from the top surface between the mold submerged entry nozzle (SEN) and \( \frac{1}{4} \) width for the case with a 0.39 T EMBr. This may push the top slag away and create an open “eye” on the top slag. Small bubbles (≤1 mm) tend to escape from one side of wide face no matter with or without EMBr, which is induced by the swirl flow from the SEN outport. EMBr has a little effect on the overall removal fraction of inclusions; however, it affects the local distribution of inclusion in the slab. With EMBr, more inclusions accumulate the region just below the surface, thus a worse subsurface quality, whereas the inner quality of the slab is better than that without EMBr. For heat transfer in the mold, the heat flux on the narrow face and the area of possible break-out zones can be reduced by using EMBr. Prevention of bias flow and/or asymmetrical flow in mold by EMBr is also concluded.







































Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Nagai, K. Suzuki, S. Kojima, and S. Kollberg: Iron Steel Eng., 1984, vol. 41, no. 5, pp. 41-47.
E. Takeuchi, Z. Masafumi, T. Takehiko, and S. Mizoguchi: Magnetohydrodynamics in Process Metallurgy, J. Szekely, J.W. Evans, K. Blazek, and N. El-Kaddah, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1992, p. 261.
M. Zeze, H. Harada, and E. Takeuchi: Steelmaking Conf. Proc., Dallas, TX, 1993, pp. 267-72.
K. Kariya, Y. Kitano, M. Kuga, A. Idogawa, and K. Sorimachi: Steelmaking Conf. Proc., Dallas, TX, 1994, pp. 53-58.
S.G. Kollberg and H.R. Hackl: Iron Steel Eng., 1996, vol. 6, pp. 24-28.
K. Okuyama: CAMP-ISIJ, 1999, vol. 12, p. 8321.
H. Harada, T. Toh, T. Ishii, K. Kaneko, and E. Takeuchi: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, no. 10, pp. 1236-44.
B. Li and F. Tsukihashi: ISIJ Int., 2006, vol. 46, no. 12, pp. 1833-38.
M. Cornelissen and R. Boom: Steel Res., 2003, vol. 74, no. 11, pp. 716-23.
K. Sorimachi and J. Hasunuma: Kawasaki Steel Technical Report, 1996, vol. 35, pp. 52-59.
A. Lehman, G. Tallback, and A. Rullgard: ABB Review, 1996, (1), pp. 4–10.
S. Kenichiro: Tetsu-to-Hagane, 1982, vol. 68, no. 11, p. S920.
S. Kollberg and P. Löfgren: Cahiers d’Infomations Techniques, 1980, vol. 102, no. 6, pp. S31-S40.
E. Takeuchi, T. Toh, H. Harada, M. Zeze, H. Tanaka, M. Hojo, T. Ishii, and K. Shigematsu: Nippon Steel Tech. Report, 1994, vol. 61, pp. 29-37.
A. Idogawa, Y. Kitano, and H. Tozawa: Kawasaki Steel Technical Report, 1996, vol. 35, pp. 74-81.
B. Li and F. Tsukihashi: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, no. 8, pp. 844-50.
H. Harada, E. Takeuchi, M. Zeze, and T. Ishii: Tetsu-to-Hagane, 2000, vol. 86, no. 4, pp. 278-84.
W. Cui: “EMBR, ElectroMagnetic Brake for Thin Slab Casters,” ABB Report, 2005, pp. 1–4.
E. Takeuchi and H. Harada: Int. Conf. on CFD in Mineral & Metal Processing and Power Generation, 1997, pp. 71–78.
H. Zhen, B. Li, and Z. Chang: Acta Metall. Sin., 2001, vol. 37, no. 8, pp. 877-81.
K. Cukierski and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 94-107.
A. Lehman, G. Tallback, S. Kollberg, and H. Hackl: Int. Symp. on Electromagnetic Proc. of Materials, Tokyo, Japan, 1994, p. 372.
K.H. Moon, H.K. Shin, B.J. Kim, J.Y. Chung, Y.S. Hwang and J.K. Yoon: ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 36, pp. S201-S203.
Y. Haiqi, W. Baofeng, L. Huiqin, and L. Jianchao: J. Mater. Process. Tech., 2008, vol. 202, nos. 1-3, pp. 179-87.
K. Ezaki, M. Kaneda, T. Tagawa, and H. Ozoe: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, no. 6, pp. 907-14.
K. Okazawa, I. Sawada, H. Harada, T. Toh, and E. Takeuchi: Tetsu-to- Hagane, 1998, vol. 84, no. 7, pp. 490-95.
Y. Delannoy, O. Widlund, and J. Etay: Int. Scientific Colloquium—Modelling for Electromagnetic Processing, Hannover, Germany, 2003, pp. 183-88.
T. Toh, H. Hasegawa and H. Harada: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, no. 10, pp. 1245-51.
B. Li, T. Okane, and T. Umeda: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, vol. 31B, pp. 1491-1503.
M. Morishita, M. Kogita, T. Nakaoka, and T. Miyake: Tetsu-to-Hagane, 2001, vol. 87, no. 4, pp. 167-74.
G. Xu and J. He: J. Northeastern Univ. (Natural Science), 2001, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 83-86.
Y. Hwang, P. Cha, H. Nam, K. Moon, and J. Yoon: ISIJ Int., 1997, vol. 37, no. 7, p. 659-67.
K. Deok-Soo, K. Woo-Seung, and C. Kee-Hyeon: ISIJ Int., 2000, vol. 40, no, 7, pp. 670-76.
M.Y. Ha, H.G. Lee, and S.H. Seong: J. Mater. Process. Tech., 2003, vol. 133, no. 3, pp. 322-39.
K.-G. Kang, H.-S. Ryou, and N.-K. Hur: Numer. Heat Tran. Part A, 2005, vol. 48, pp. 461-81.
K. Takatani: Magnetohydrodynamics, 1996, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 128-33.
Y.-S. Hwang, P.-R. Cha, H.-S. Nam, K.-H. Moon, and J.-K. Yoon: ISIJ Int., 1997, vol. 37, no. 7, pp. 659-67.
H. Cerber and J. Rachford: IEEE, 1996, vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 2541-46.
H. Trippelsdorf, R. Marraccini, and S. Kollberg: Int. Sci. Colloquium, Hannover, Germany, 2003, pp. 189-96.
Y. Wang and L. Zhang: AISTech 2009, St. Louis, MO, 2009.
H. Yu, B. Wang, H. Li, and J. Li: J. Mater. Process. Tech., 2008, vol. 202, pp. 179-87.
P. Gardin, J.Galpin, M. Regnier, and J. Radot: IEEE Trans. Magnetics, 1995, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 2088-91.
P. Gardin, J.-M. Galpin, M.-C. Regnier, and J.-P. Radot: Magnetohydrodynamics, 1996, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 189-95.
K. Takatani: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, no. 6, pp. 915-22.
FLUENT6.1-Mannual: Fluent. Inc., Lebanon, NH, Report, 2003.
N. Bessho, R. Yoda, H. Yamasaki, T. Fujii, T. Nozaki, and S. Takatori: Iron Steelmaker, 1991, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 39-44.
I. Sawada, H. Tanaka, and I. Takigawa: The Sixth International Iron and Steel Congress, Nagoya, Japan, 1990, vol. 3, pp. 334–47.
B.G. Thomas and L. Zhang: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, no. 10, pp. 1181-93.
L. Zhang, J. Aoki, and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2006, vol. 37B, pp. 361-79.
L. Zhang and S. Taniguchi: Int. Mater. Rev., 2000, vol. 45, no. 2, pp. 59-82.
R.H.M.G. Nabben, R.P.J. Duursma, A.A. Kamperman, and J.L. Lagerberg: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 1998, vol. 25, no. 5, pp. 403-06.
H.B.M. Schulte, R.H.M.G. Nabben, D.W. Van der Plas, and D. Trizenberg: Rev. Metall.-Paris, 1997, vol. 1997, no. 6, pp. 751-60.
Q. Yuan, S. Sivaramakrishnan, S.P. Vanka, and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35B, pp. 967-82.
K. Cukierski and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 94-106.
L. Zhang, S. Yang, X. Wang, K. Cai, J. Li, X. Wan, and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2007, vol. 38B, pp. 63-83.
L. Zhang, Y. Wang, and X. Zuo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 534-50.
L.J. Mika and B.G. Thomas: Modeling and Control of Casting and Welding Processes—IV, A.F. Giamei and G.J. Abbaschian, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1988, pp. 459-69.
T. Kouji, T. Yoshinori, M. Hideo, and N. Kenzi: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, no. 10, pp. 1252-61.
B.G. Thomas, Q. Yuan, S. Sivaramakrishnan, and S.P. Vanka: J. Metals: JOM-e, 2002. http://www.tms.org/pubs/journals/JOM/0201/Thomas/Thomas-0201.html.
B.G. Thomas: 3rd Int. Cong. on the Sc. and Tech. of Steelmaking, AIST, Warrandale, PA, 2005, pp. 847-63.
R. Chaudhary, G.-g. Lee, B.G. Thomas, and S.-H. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 870-84.
M. Yemmou, M.A.A. Azouni, and P. Casses: J. Cryst. Growth, 1993, vol. 128, no. 4, pp. 1130-36.
J.K. Kim and P.K. Rohatgi: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1998, vol. 29B, pp. 351-75.
D.M. Stefanescu and A.V. Catalina: ISIJ Int., 1998, vol. 38, no. 5, pp. 503-05.
Y. Wang, X. Zuo, L. Zhang, S. Li, A. Dong, and L.N.W. Damoah: Proc. of AISTech 2010 Iron & Steel Technology Conference and Exposition, vol. II, AIST, Warrendale, PA, 2010, pp. 793–806.
H. Turkoglu and B. Farouk: ASME Winter Annual Meeting, Dallas, TX, 1990, vol. 100, pp. 31–38.
Y. Wang, X. Zuo, and L. Zhang: 7th International Conference on Clean Steel, Budapest, Hungary, 2007, pp. 161-71.
X. Tian, B. Li, and J. He: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2009, vol. 40B, pp. 596-604.
H. Bai and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2001, vol. 32B, pp. 253-67.
L. Zhang and B.G. Thomas: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 271-91.
M.B. Assar, P.H. Dauby, and G.D. Lawson: Steelmaking Conf. Proc., ISS, Warrendale, PA, 2000, vol. 83, pp. 397-411.
Y. Wang and G. Wen: “Slab Casting Quality Control”, Chongqing University, Report, 2006.
D.V.V.D. Plas, C. Platvoet, B. Debiesme, J.-P. Radot, and J.-M. Galpin: 2nd European Continuous Casting Conf., Düsseldorf, Germany, 1994, pp. 109-18.
K. Takatani, K. Nakai, N. Kasai, T. Watanabe, and H. Nakajima: ISIJ Int., 1989, vol. 29, no. 12, pp. 1063-68.
Y. Satou, N. Baba, N. Kasai, A. Mutou, and M. Hanao: AISTech 2009, St. Louis, MO, 2009.
H. Tozawa: Steel Times, 1999, vol. 227, no. 4, pp. 125-27.
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the UM Research Board Grant, Laboratory of Green Process Metallurgy and Modeling (GPMM), Material Research Center (MRC), and the Intelligent Systems Center (ISC) at Missouri University of Science and Technology (Missouri S&T).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 22, 2009.
Appendix
Appendix
The value of k and ε value on the backflow zone of the calculation bottom is important for the result if k-ε turbulence model is applied as discussed in Section III–B–2. Also, the value of solute concentration on the backflow zone will affect the solute transportation. In order to adjust the k, ε and concentration values on the backflow of the bottom. A program was designed to update these values for each step. The main scheme of the program is,
-
1.
Scan the center line on the bottom and obtain the information, for example v, k, ε, and c from the line;
-
2.
Determine the values that can be applied to the backflow zone;
-
3.
Initialize the value to backflow zone and update them at every iteration.
The flow chart of the program is given in Figure 40.
The code and explanation are given as follows



Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhang, L. Fluid Flow-Related Transport Phenomena in Steel Slab Continuous Casting Strands under Electromagnetic Brake. Metall Mater Trans B 42, 1319–1351 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-011-9554-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-011-9554-x