Abstract
Objective
To investigate the therapeutic effect of gentisic acid (GA) on rheumatoid arthritis (RA) based on the miR-19b-3p/RAF1 axis.
Methods
The cell counting kit-8 method was used to detect the growth inhibitory effect of different concentrations of GA on MH7A cells, and the drug concentration of GA was determined in the experiment. The quantificational real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to detect the expression of miR-19b-3p and RAF1. RAF1, extracellular regulated protein kinases1/2 (ERK1/2) and phospho-ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2) were examined by Western blotting. Three methods (dual-luciferase assay, qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis) were used to verify miR-19b-3p targeting RAF1. Flow cytometry was performed to detect MH7A cell apoptosis. Transwell and wound healing assays were used to determine the invasion and migration capacities of MH7A cells.
Results
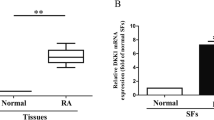
The growth of MH7A cells was gradually inhibited with increasing GA concentration. When the GA concentration exceeded 80 mmol/L, GA was significantly cytotoxic to MH7A cells, so the half maximal inhibitory concentration of GA for MH7A cells was calculated as 67.019 mmol/L. GA upregulated miR-19b-3p expression, downregulated RAF1 expression, inhibited ERK1/2 phosphorylation, induced MH7A cell apoptosis and suppressed MH7A cell invasion and migration (P<0.05 or P<0.01). RAF1 was identified as the target of miR-19b-3p and reversed inhibitory effects on miR-19b-3p expression (P<0.05 or P<0.01). The miR-19b-3p inhibitor upregulated RAF1 expression and ERK1/2 phosphorylation, suppressed MH7A cell apoptosis and induced MH7A cell invasion and migration (P<0.01).
Conclusion
GA regulated miR-19b-3p/RAF1 axis to mediate ERK pathway and inhibit the development of RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kong XY, Wen CP. On research progress of Western and Chinese medicine treatment on pre-rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Integr Med 2019;25:643–647.
Yang M, Guo MY, Luo Y, Yun MD, Yan J, Liu T, et al. Effect of artemisia annua extract on treating active rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Chin J Integr Med 2017;23:496–503.
Rezaeepoor M, Pourjafar M, Tahamoli-Roudsari A, Basiri Z, Hajilooi M, Solgi G. Altered expression of microRNAs may predict therapeutic response in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Int Immunopharmacol 2020;83:106404.
Tavasolian F, Hosseini AZ, Soudi S, Naderi M. miRNA-146a improves immunomodulatory effects of MSC-derived exosomes in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Gene Ther 2020;20:297–312.
Lenert A, Fardo DW. Detecting novel microRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis with gene-based association testing. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2017;35:586–592.
Pauley KM, Satoh M, Chan AL, Bubb MR, Reeves WH, Chan EK. Upregulated miR-146a expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther 2008;10:R101.
Dong L, Wang X, Tan J, Li H, Qian W, Chen J, et al. Decreased expression of microRNA-21 correlates with the imbalance of Th17 and Treg cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Cell Mol Med 2014;18:2213–2224.
Wang Y, Zheng F, Gao G, Yan S, Zhang L, Wang L, et al. MiR-548a-3p regulates inflammatory response via TLR4/NF- κ B signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. J Cell Biochem 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26659
Jin S, Chen H, Li Y, Zhong H, Sun W, Wang J, et al. Maresin 1 improves the Treg/Th17 imbalance in rheumatoid arthritis through miR-21. Ann Rheum Dis 2018;77:1644–1652.
Romo-García MF, Bastian Y, Zapata-Zuñiga M, Macías-Segura N, Castillo-Ortiz JD, Lara-Ramírez EE, et al. Identification of putative miRNA biomarkers in early rheumatoid arthritis by genome-wide microarray profiling: a pilot study. Gene 2019;720:144081.
Nishikawa M, Myoui A, Tomita T, Takahi K, Nampei A, Yoshikawa H. Prevention of the onset and progression of collagen-induced arthritis in rats by the potent p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor FR167653. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:2670–2681.
Rubbert-Roth A. New kinase inhibitors. Z Rheumatol 2012;71:479–484.
Joshi R, Gangabhagirathi R, Venu S, Adhikari S, Mukherjee T. Antioxidant activity and free radical scavenging reactions of gentisic acid: in-vitro and pulse radiolysis studies. Free Radic Res 2012;46:11–20.
Han X, Guo J, Gao Y, Zhan J, You Y, Huang W. Gentisic acid prevents diet-induced obesity in mice by accelerating the thermogenesis of brown adipose tissue. Food Funct 2021;12:1262–1270.
Roseman S, Dorfman A. Effect of gentisic acid and related compounds on bovine testicular hyaluronidase. J Biol Chem 1952;199:345–355.
Zhang Q, Peng W, Wei S, Wei D, Li R, Liu J, et al. Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu Decoction possesses anti-arthritic effects on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats via suppression of inflammatory reactions, inhibition of invasion & migration and induction of apoptosis in synovial fibroblasts. Biomed Pharmacother 2019;118:109367.
Shen Y, Teng L, Qu Y, Liu J, Zhu X, Chen S, et al. Anti-proliferation and anti-inflammation effects of corilagin in rheumatoid arthritis by downregulating NF-κ B and MAPK signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol 2022;284:114791.
Wang J, Yan S, Yang J, Lu H, Xu D, Wang Z. Non-coding RNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: from bench to bedside. Front Immunol 2019;10:3129.
McInnes IB, Schett G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2017;389:2328–2337.
Kim M, Kim J, Shin YK, Kim KY. Gentisic acid stimulates keratinocyte proliferation through ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Int J Med Sci 2020;17:626–631.
Abedi F, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H. A review on gentisic acid as a plant derived phenolic acid and metabolite of aspirin: comprehensive pharmacology, toxicology, and some pharmaceutical aspects. Phytother Res 2020;34:729–741.
Evangelatos G, Fragoulis GE, Koulouri V, Lambrou GI. MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: from pathogenesis to clinical impact. Autoimmun Rev 2019;18:102391.
Metzinger-Le Meuth V, Burtey S, Maitrias P, Massy ZA, Metzinger L. microRNAs in the pathophysiology of CKD-MBD: biomarkers and innovative drugs. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2017;1863:337–345.
Chen JQ, Papp G, Szodoray P, Zeher M. The role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev 2016;15:1171–1180.
Chen XM, Zhao Y, Wu XD, Wang MJ, Yu H, Lu JJ, et al. Novel findings from determination of common expressed plasma exosomal microRNAs in patients with psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis vulgaris, rheumatoid arthritis, and gouty arthritis. Discov Med 2019;28:47–68.
Malemud CJ. Negative regulators of JAK/STAT signaling in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci 2017;18:484.
Lin K, Su HY, Jiang LF, Chu TG, Li Z, Chen XL, et al. Influences of miR-320a on proliferation and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis through targeting MAPK-ERK 1/2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2019;23:1907–1914.
Lechuga CG, Simón-Carrasco L, Jacob HK, Drosten M. Genetic validation of cell proliferation via ras-independent activation of the RAf/MEK/ERK pathway. Methods Mol Biol 2017;1487:269–276.
Li R, Cai L, Tang WJ, Lei C, Hu CM, Yu F. Apoptotic effect of geniposide on fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis via inhibiting ERK signal pathway in vitro. Inflammation 2016;39:30–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ding D wrote the paper, Dong XJ applied for funds, Zhang Q designed the experiments, Zeng FJ finished the experiments, Cai MX analyzed the data, Gan Y submitted the manuscript, and all authors approved the submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Supported by a grant from Zunyi Science and Technology Bureau, China (No. [2019]194)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, D., Zhang, Q., Zeng, Fj. et al. Mechanism of Gentisic Acid on Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on miR-19b-3p/RAF1 Axis. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 29, 508–516 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-022-3723-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-022-3723-4