Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of electroacupuncture (EA) treatment on the expression of cyclooxygenase (COX) 2 and microglia in spinal cord by using rat model of neuropathic pain, and to probe into the relationship between COX 2 and microglia.
Methods
The rats were randomly divided into 6 groups, including normal control group, model group, sham group, EA 1 group (distant acupoints + local acupoints), EA 2 group (local acupoints), and EA 3 group (distant acupoints). Thermal withdrawal latencies were evaluated at 1 day preoperatively and 3, 5 and 7 days postoperatively. At 7 days postoperatively, the spinal COX 2 mRNA was detected by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. Double immunofluorescent staining technology was applied to screen and verify the relationship between altered COX 2 and microglia.
Results
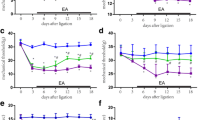
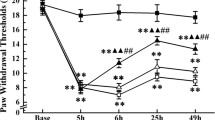
Compared with the model group, thermal withdrawal latencies increased after EA treatment (P<0.01). The expressions of COX 2 mRNA were up-regulated in spinal cord of rat on day 7 after surgery (P<0.05). Compared with the model group, EA stimulation (EA 1 and EA 2 groups) reversed the up-regulation of COX 2 mRNA expression (P<0.05). EA 1 and EA 2 groups might have better treatment effect compared with the EA 3 group. Fluorescent images displayed COX 2 and microglia expressed at common areas.
Conclusions
EA was effective in analgesic and anti-inflammatory. EA has decreased the expression of spinal COX 2 mRNA in the trend of the therapeutic effect of "distant acupoints + local acupoints", and "local acupoints" intervention may be superior to that of "distant acupoints" intervention. Microglia may be related to the formation of COX 2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhuo M, Wu G, Wu LJ. Neuronal and microglial mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Mol Brain 2011;4:31–42.
Smith WL, Garavito RM, DeWitt DL. Prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthases (cyclooxygenases)-1 and-2. J Biol Chem 1996;271:33157–33160.
McAdam BF, Mardini IA, Habib A, Burke A, Lawson JA, Kapoor S, et al. Effect of regulated expression of human cyclooxygenase isoforms on eicosanoid and isoeicosanoid production in inflammation. J Clin Invest 2000;105:1473–1482.
Willingale HL, Gardiner NJ, McLymont N, Giblett S, Grubb BD. Prostanoids synthesized by cyclo-oxygenase isoforms in rat spinal cord and their contribution to the development of neuronal hyperexcitability. Br J Pharmacol 1997;122:1593–1604.
Seybold VS, Jia YP, Abrahams LG. Cyclo-oxygenase-2 contributes to central sensitization in rats with peripheral inflammation. Pain 2003;105:47–55.
Omair A, Holden M, Lie BA, Reikeras O, Brox JI. Treatment outcome of chronic low back pain and radiographic lumbar disc degeneration are associated with inflammatory and matrix degrading gene variants: a prospective genetic association study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2013;14:105–113.
Zhou XY, Xu YY, Xie ZH, Xu JP, Bi JZ. The research progress of inflammatory response and nervous system degenerative disease. Chin J Gerontol (Chin) 2012;32:196–199.
Streit WJ, Mrak RE, Griffin WS. Microglia and neuroinflammation: a pathological perspective. J Neuroinflammation 2004;1:14–17.
Tsuda M, Inoue K, Salter MW. Neuropathic pain and spinal microglia: a big problem from molecules in "small" glia. Trends Neurosci 2005;28:101–107.
Ji RR, Suter MR. p38 MAPK, microglial signaling, and neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 2007;3:33–41.
Zhao LY, Jiang HL, Ren XJ, Tu Y. Effects of electroacupuncture on pain-related behaviors and pathologic changes on spinal nerve root and dorsal root ganglion in rat model of lumbar disc herniation. J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2014;37:551–555.
International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP). IASP guidelines for the use of animals in research. Retrieved September 07, 2016. Available at:http://www.iasp-pain.org/ Education/Content.aspx?ItemNumber=1217
Jiang HL, Yu X, Ren XJ, Fang TY, Tu Y. Effect of electroacupuncture at distal-proximal acupoint combinations on spinal interleukin-1 beta in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Tradit Chin Med Sci 2015;2:45–51.
Zhang LF, ed. Experimental acupuncture science. Beijing: Chemical Industry Publisher; 2010:219–224.
Zhang YQ, Ji GC, Wu GC, Zhao ZQ. Excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists and electroacupuncture synergetically inhibit carrageenan-induced behavioral hyperalgesia and spinal fos expression in rats. Pain 2002;99:525–535.
Long XQ, Jiang HL, Ren XJ, Ji LL, Tu Y. Development of researches on mechanisms of acupoint combination for some disorders in nerve-humoral-immunological modulation. Acupunct Res 2015;40:314–318.
Jiang HL, Ji LL, Ren XJ, Long, Tu Y. Exploration of acupuncture prescriptions for chronic low back pain: a review of ancient and modern literature. J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2015;38:280–283.
Yermakova A, O'Banion MK. Cyclooxygenases in the central nervous system: implications for treatment of neurological disorders. Curr Pharm Des 2000;6:1755–1776.
Miyamoto H, Saura R, Doita M, Kurosaka M, Mizuno K. The role of cyclooxygenase-2 in lumbar disc herniation. Spine 2002;27:2477–2483.
Banati RB, Gehrmann J, Schubert P, Kreutzberg GW. Cytotoxicity of microglia. Glia 1993;7:111–118.
Ji RR, Strichartz G. Cell signaling and the genesis of neuropathic pain. Sci STKE 2004;252:reE14.
Di Y, Li WY. Research advances in the role microglia`s surface receptors in neuropathic pain. Med Recapitu 2013;19:1108–1111.
Henry CJ, Huang Y, Wynne A, Hanke M, Himler J, Bailey MT, et al. Minocycline attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation, sickness behavior, and anhedonia. J Neuroinflammation 2008;5:15–28.
Lin LL, Wartmann M, Lin AY, Knopf JL, Seth A, Davis RJ. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell 1993;72:269–278.
Samad TA, Moore KA, Sapirstein A, Billet S, Allchorne A, Poole S, et al. Interleukin-1 beta-mediated induction of COX-2 in the CNS contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Nature 2001;410:471–475.
Zhang F, Vadakkan KI, Kim SS, Wu LJ, Shang Y, Zhuo M. Selective activation of microglia in spinal cord but not higher cortical regions following nerve injury in adult mouse. Mol Pain 2008;4:15–30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Project of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, China (No. JYB22-JS022)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, Ll., Guo, Mw., Ren, Xj. et al. Effects of electroacupuncture intervention on expression of cyclooxygenase 2 and microglia in spinal cord in rat model of neuropathic pain. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 23, 786–792 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2606-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2606-y