Abstract
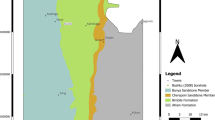
Groundwater levels are gradually declining in basins around the world due to anthropogenic and natural factors. Climate is not the only factor contributing to change in groundwater levels, population growth and economic progress are leading to increased water demand. Areas used for agricultural irrigation are expanding, necessitating the use of artificial groundwater recharge as a method to sustain pumping and enhance storage. The present study delineates potential locations of significant groundwater resources that already exist using a geostatistical approach as a method to identify potential groundwater recharge zones. The Multi-Influencing Factors (MIF) technique was applied to determine the relationship between different landscape and climatic factors that influence groundwater recharge. Factors include topography, climate, hydrogeology, population, economic change, and geology. Integration of these factors enabled the identification of potential locations of groundwater suitable for artificial recharge efforts based on weights derived through the MIF technique. We applied these weights to derive a groundwater recharge index (GRI) map. The map was delineated into three groundwater recharge zones classified by their potential areal coverage as a metric for recharge suitability, namely low, medium and high suitability, occupying areas of 8625 km2 (30.06%), 9082 km2 (31.65%), and 10,989 km2 (38.29%), respectively. Our findings have important implications for designing sustainable groundwater development and land-use plans for the coming century.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuzied SM, Alrefaee HA (2017) Mapping of groundwater prospective zones integrating remote sensing, geographic information systems and geophysical techniques in El-Qaà Plain area, Egypt. Hydrogeol J 25(7):2067–2088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1603-3
Adiat KAN, Nawawi MNM, Abdullah K (2012) Assessing the accuracy of GIS-based elementary multi criteria decision analysis as a spatial prediction tool---A case of predicting potential zones of sustainable groundwater resources. J Hydrol 440:75–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.03.028
Aguilar C, Zinnert JC, Polo MJ, Young DR (2012) NDVI as an indicator for changes in water availability to woody vegetation. Ecol Indic 23:290–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.04.008
Al Saud M (2010) Mapping potential areas for groundwater storage in wadi aurnah basin, western Arabian Peninsula, using remote sensing and geographic information system techniques. Hydrogeol J 18:1481–1495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-010-0598-9
Al-Abadi AM, Al-Temmeme AA, Al-Ghanimy MA (2016) A GIS-based combining of frequency ratio and index of entropy approaches for mapping groundwater availability zones at BadraeAl Al-GharbieTeeb areas, Iraq Sustain. Water Resour Manag 2(3):265–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-016-0056-5
Algaydi BA, Subyani AM, Hamza MH (2019) Investigation of groundwater potential zones in hard rock terrain, Wadi Na’man, Saudi Arabia. Groundwater 1:1. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12870
Anbazhagan S, Jothibasu A (2016) Geoinformatics in groundwater potential mapping and sustainable development: a case study from southern India. Hydrol Sci J 61(6):1109–1123. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2014.990966
Aniya M (1985) Landslide-susceptibility mapping in the amahata river basin, Japan. Ann Assoc Am Geogr 75(1):102–114. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8306.1985.tb00061.x
Arora B, Burrus M, Newcomer ME, Steefel CI, Carroll RWH, Dwivedi D et al (2020) Differential C-Q analysis: a new approach to inferring lateral transport and hydrologic transients within multiple reaches of a mountainous headwater catchment. Front Water 2:24. https://doi.org/10.3389/frwa.2020.00024
Arulbalaji P, Padmalal D, Sreelash K (2019) GIs and AHP techniques based delineation of groundwater potential zones: a case study from southern Western Ghats, Indai. Sci Rep 9(1):2082. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-38567-x
Ayazi MH, Pirasteh S, Arvin AKP, Pradhan B, Nikouravan B, Mansor S (2010) Disasters and risk reduction in groundwater: Zagros mountain southwest Iran using geo-informatics techniques. Dis Adv 3(1):51–57
Barik KK, Dalai PC, Goudo SP, Panda SR, Nandi D (2017) Delineation of groundwater potential zone in Baliguda Block of Kandhamal District, Odisha using geospatial technology approach. Int J Adv Remote Sens GIS 6(3):2068–2079. https://doi.org/10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.33
Bera K, Bandyopadhyay J (2011) Management of ground water using geoinformatics in Dwarkeswar watershed of Puruliya District. Indian Cartogr 31:265–270
Bera K, Banik P (2019), Multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) for surface water management plan, a case study of Kansachara sub-watershed, West Bengal, India. Water Supply 19(7):2156–2162. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2019.096
Bera K, Banik P (2022) Statistical Model based decadal Land Use/land cover change identification and prediction in & around West Bengal dry-land area. In: International journal of emerging technologies and innovative research (www.jetir.org), ISSN:2349–5162, Vol.9, Issue 4, page no.h90-h105, April-2022. https://doi.org/10.1729/Journal.30083
Bhunia GS, Samanta S, Pal.B, Memorial R, Agamkuan S (2012) Deciphering prospective groundwater zones of Morobe province, Papua New Guinea. Int J Eng Appl 2(3):752–766. www.ijera.com
Brunet P, Clément R, Bouvier C (2010) Monitoring soil water content and deficit using Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT)—a case study in the Cevennes area, France. J Hydrol 380(1–2):146–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.10.032
CGWB (2020) Central Ground water board, ministry of jalshakti, department of water resources, river development & ganga rejevenation government of India, Ground Water Year Book of West Bengal & Andaman & Nicobar Islands (2019–2020), Report: Series ‘D’No. 284
Chen W, Pradhan B, Li S (2019) Novel hybrid integration approach of bagging-based fisher’s linear discriminant function for groundwater potential analysis. Nat Resour Res 28:1239–1258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09465-w
Chowdhury A, Jha MK, Chowdary VM (2010) Delineation of groundwater recharge zones and identification of artificial recharge sites in west medinipur district, West Bengal using RS, GIS and MCDM techniques. Environ Earth Sci 59(6):1209–1222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0110-9
Chung CJF, Fabbri AG (2003) Validation of spatial prediction models for landslide hazard mapping. Nat Hazards 30:451–472. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NHAZ.0000007172.62651.2b
Corona CR, Gurdak JJ, Dickinson JE, Ferré TPA, Maurer EP (2017) Climate variability and vadose zone controls on damping of transient recharge. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.08.028
Das N, Mukhopadhyay S (2018) Application of multi-criteria decision making technique for the assessment of groundwater potential zones: a study on Birbhum district, West Bengal, India. Environ Develop Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0227-7
Dinesan VP, Gopinatha G, Ashitha MK (2015) Application of geoinformatics for the delineation of groundwater prospects zones—a case study for Melattur Grama panchayat in Kerala, India. In: International conference on water resources, Coastal and Ocean Engineering (ICWRCOE ‘15). Aquatic Procedia, vol 4, pp 1389–1396 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqpro.2015.02.180
Dinesh PK, Gopinath G, Seralathan P (2007) Application of remote sensing and GIS for the demarcation of groundwater potential zones of a river basin in Kerala, southwest cost of India. Int J Remote Sens 28(24):5583–5601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2016.11.006
Dwivedi D, Mital U, Faybishenko B, Dafflon B, Varadharajan C, Agarwal D et al (2021) Imputation of contiguous gaps and extremes of Subhourly groundwater time series using random forests. J Mach Learn Model Comput. https://doi.org/10.1615/JMachLearnModelComput.2021038774
Elbeih SF (2015) An overview of integrated remote sensing and GIS for groundwater mapping in Egypt. Ain Shams Eng J 6(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2014.08.008
Ercanoglu M, Gokceoglu C (2002) Assessment of landslide susceptibility for a landslide prone area (north of Yenice, NW Turkey) by fuzzy approach. Environ Geol 41:720–730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-001-0454-2
Ettazarini S (2007) Groundwater potential index: a strategically conceived tool for water research in fractured aquifers. Environ Geol 52:477–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0481-0
Ettazarizini S, El Mahmouhi N (2004) Vulnerability mapping of the turonian limestone aquifer in the phosphate plateau (Morocco). Environ Geol 46:113–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-1022-3
Fagbohun BJ (2018) Integrating GIS and multi influencing factor technique for delineation of potential groundwater recharge zones in parts of Ilesha Schist Belt, Southwestern Nigeria. Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7229-5
Greenbaum D (1989) Hydrogeological applications of remote sensing in areas of crystalline basement. Paper presented at the In: Proc Groundwater Exploration and Development in Crystalline Basement Aquifers, Zimbabwe
Gyeltshen S, Tran VT, Gunda GKT, Kannaujiya S, Chatterjee RS, Hampatiray PK (2019) Groundwater potential zones using combination of geospatial technology and geophysical approach: case study in Dehradun, India. Hydrol Sci J. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2019.1688334
Haridas VR, Aravindan S, Girish G (1998) Remote sensing and its applications for groundwater favorable area identification. Q J Geol Assoc Res Centre 6:18–22
Hofkes EH, Visscher JT (1986) Artificial groundwater recharge for water supply of medium size communities in developing countries. In International reference centre for community water supply and sanitation, The Hague, The Netherlands. www.samsamwate r.com. Accessed June 25, 2017.
Jhariya DC, Kumar T, Gobinath M, Diwan P, Kishore N (2016) Assessment of groundwater potential zone using remote sensing, GIS and multi-criteria decision analysis techniques. J Geol Soc India 88:481–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-016-0511-9
Jothibasu A, Anbazhagan S (2016) Modeling groundwater probability index in Ponnaiyar River basin of South India using analytic hierarchy process. Model Earth Syst Environ 2:109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-016-0174
Kaliraj S, Chandrasekar N, Magesh NS (2014) Identification of potential groundwater recharge zones in vaigai upper basin, Tamil Nadu, using GIS-based analytical hierarchical process (AHP) technique. Arab J Geosci 7:1385–1401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0849-x
Khodaei K, Nassery HR (2013) Groundwater exploration using remote sensing and geographic information systems in a semi-arid area (Southwest of Urmieh, Northwest of Iran). Arab J Geosci 6(4):1229–1240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0414-4
Kumar T, Gautam AK, Kumar T (2014) Appraising the accuracy of GIS based multi-criteria decision making technique for delineation of groundwater potential zones. Water Resour Manag 28:4449–4466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0663-6
Kumar A, Krishna AP (2018) Assessment of groundwater potential zones in coal mining impacted hard-rock terrain of India by integrating geospatial and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) approach. Geocarto Int 33(2):105–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2016.1232314
Kumar R, Thaman S, Agarwal G, Poonam S (2011) Rain water harvesting and groundwater recharging in North Western Himalayan Region for sustainable agricultural productivity. Univ J Environ Res Technol 1(4):539–544
Machiwal D, Jha MK, Mal BC (2011) Assessment of groundwater potential in a semi-arid region of India using remote sensing, GIS and MCDM techniques. Water Resour Manag 25:1359–1386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9749-y
Machiwal D, Singh PK (2015) Comparing GIS-based multi-criteria decision-making and Boolean logic modelling approaches for delineating groundwater recharge zones, Arab Arabian. J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2002-5
Magesh NS, Chandrasekar N, Soundranayagam JP (2012) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in theni district, Tamil Nadu, using remote sensing, GIS and MIF techniques. Geosci Front 3(2):189–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2011.10.007
Maina FZ, Siirila-Woodburn ER, Newcomer ME, Xu Z, Steefel C (2020) Determining the impact of a severe dry to wet transition on watershed hydrodynamics in California, USA with an integrated hydrologic model. J Hydrol 580:124358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124358
Manap MA, Nampak H, Pradhan B, Lee S, Soleiman WNA, Ramli MF (2014) Application of probabilistic-based frequency ratio model in groundwater potential mapping using remote sensing data and GIS. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0795-z
Matheus Carnevali PB, Lavy A, Thomas AD, Crits-Christoph A, Diamond S, Méheust R et al (2021) Meanders as a scaling motif for understanding of floodplain soil microbiome and biogeochemical potential at the watershed scale. Microbiome 9(1):121. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-020-00957-z
Mogaji KA, Lim HS, Abdullah K (2014) Regional prediction of groundwater potential mapping in a multifaceted geology terrain using GIS-based Dempster-Shafer model. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1391-1
Mukherjee D (2016) A review on artificial groundwater recharge in India. Int J Civil Eng 3(1):60–65. https://doi.org/10.14445/23488352/IJCE-V3I1P108
Mundalik V, Fernandes C, Kadam AK, Umrikar BN (2018) Integrated geo-morphological, geospatial and AHP technique for groundwater prospects mapping in basaltic terrain, hydrospatial. Analysis 2(1):16–27. https://doi.org/10.21523/gcj3.18020102
Murthy KSR, Mamo AG (2009) Multi-criteria decision evaluation in groundwater zones identification in Moyale-Teltele subbasin, South Ethiopia. Int J Remote Sens 30:2729–2740. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160802468255
Musa KA, Akhir JM, Abdullah I (2000) Groundwater prediction potential zone in Langat Basin using the integration of remote sensing and GIS. http://www.gisdevelopment.net National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM) (Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India), West Bengal, National Disaster Risk Reduction Portal, Annual Report. 2014–2015
NASA Portal (2022): https://power.larc.nasa.gov/ (NASA/POWER SRB/FL ASHFlux/ MERRA2/G EOS 5.12.4 Grid 0.50x0.50).
Newcomer ME, Bouskill NJ, Wainwright H, Maavara T, Arora B, Siirila-Woodburn ER et al (2021) Hysteresis Patterns of Watershed Nitrogen Retention and Loss over the past 50 years in United States Hydrological Basins. Global Biogeochem Cycles. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GB006777
Newcomer ME, Gurdak JJ, Sklar LS, Nanus L (2014) Urban recharge beneath low impact development and effects of climate variability and change. Water Resour Res 50(2):1716–1734. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013WR014282
Parameswari K, Padmini TK (2018) Assessment of groundwater potential in Tirukalukundram block of southern Chennai Metropolitan Area. Environ Develop Sustain 20(4):1535–1552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-017-9952-6
Patra S, Mishra P, Mahapatra SC (2018) Delineation of groundwater potential zone for sustainable development: a case study from Ganga alluvial plain covering Hooghly district of India using remote sensing, geographic information system and analytic hierarchy process. J Clean Prod 172:2485–2502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.161
Petus C, Lewis M, White D (2012) Using MODIS Normalized Difference Vegetation Index to monitor seasonal and inter-annual dynamics of wetland vegetation in the Great Artesian Basin: a baseline for assessment of future changes in a unique ecosystem. In: International Society for Photogrammetry Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences xxxixx-B8:187-192. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprsarchives-XXXIX-B8-187-2012
Prasad RK, Mondal NC, Banerjee P, Nandakumar MV, Singh VS (2008) Deciphering potential groundwater zone in hard rock through the application of GIS. Environmental Geology 55(3):467–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0992-3
Punmia BC, Jain AK, Jain AK (2005) Soil mechanics and foundations Laxmi Publications (P) Ltd, New Delhi, sku:-OBS/2017/07/16/1069
Rahmati O, Samani NA, Mahdavi M, Pourghasemi HR, Zeinivand H (2015) Groundwater potential mapping at Kurdistan region of Iran using analytic hierarchy process & GIS. Arabian J Geosci 8(9):7059–7071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1668-4
Razandi Y, Pourghasemi HR, Samani-Neisani N, Rahmati O (2015) Application of analytical hierarchy process, frequency ratio, and certainty factor models for groundwater potential mapping using GIS. Earth Sci Inf 8(4):867–883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-015-0220-8
Rogers DB, Newcomer ME, Raberg JH, Dwivedi D, Steefel C, Bouskill N et al (2021) Modeling the impact of riparian hollows on river corridor nitrogen exports. Front Water 3:590314. https://doi.org/10.3389/frwa.2021.590314
SLUSI Portal (2022): https://slusi.dacnet.nic.in/dmwai/WEST_BENGAL/WEST_BENGAL.html
Selvam S, Manimaran G, Sivasubramanian P, Balasubramanian N, Seshunarayana T (2014) GIS-based evaluation of water quality index of groundwater resources around Tuticorin coastal city, South India. Environ Earth Sci 71:2847–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2662-y
Senanayake IP, Dissanayake DMDOK, Mayadunna BB, Weerasekera WL (2016) An approach to delineate groundwater recharge potential sites in Ambalantota, Sri Lanka using GIS techniques. Geosci Front 7:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2015.03.002
Senthil-Kumar GR, Shankar K (2014) Assessment of groundwater potential zones using GIS. Front Geosci 2(1):1–10 http://scholar.google.com
Shekhar S, Pandey AC (2014) Delineation of groundwater potential zone in hard rock terrain of India using remote sensing, geographical information system (GIS) and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) techniques. Geocarto Int. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2014.894584
Suganthi S, Elango L, Subramanian SK (2014) Groundwater potential zonation by remote sensing and GIS techniques and its relation to the groundwater level in the coastal part of the Arani and Koratalai River Basin, Southern India. Earth Sci Res J 17:87–95
Taheri K, Gutiérrez F, Mohseni H, Raeisi E, Taheri M (2015) Sinkhole susceptibility mapping using the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and magnitude-frequency relationships: a case study in Hamadan province, Iran. Geomorphology 234:64–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.01.005
Taheri K, Taheri M, Parise M (2016) Impact of intensive groundwater exploitation on an unprotected covered karst aquifer: a case study in Kermanshah Province, western Iran. Environ Earth Sci 75:122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5995-5
Tam VT, De Smedt F, Batelaan O, Dassargues A (2004) Study on the relationship between lineaments and borehole specific capacity in a fractured and karstified limestone area in Vietnam. Hydrogeol J 12:662–673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-004-0329-1
Tehrany MS, Pradhan B, Jebur MN (2014) Flood susceptibility mapping using a novel ensemble weights-of-evidence and support vector machine models in GIS. J Hydrol 512:332–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.03.008
Thakur JK, Singh SK, Ekanthalu VS (2017) Integrating remote sensing, geographic information systems and global positioning system techniques with hydrological modeling. Appl Water Sci 7(4):1595–1608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0384-5
Thapa R, Gupta S, Guin S, Kaur H (2017) Assessment of groundwater potential zones using multi-influencing factor (MIF) and GIS: a case study from Birbhum district, West Bengal. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0571-z
Thapa R, Gupta S, Reddy DV (2016) Application of geospatial modelling technique in delineation of fluoride contamination zones within Dwarka Basin, Birbhum, India. Geosci Front. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2016.11.006
Thomas BF, Ali B, Famiglietti JS (2016) Precipitation intensity effects on groundwater recharge in the Southwestern United States. Water 8:2–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8030090
UN (United Nations 1967), Hydrogeological Map of Lebanon, Carte hydrogéologique du Liban au 1:100000ème, Beyrouth, Liban
Ulrich C, Hubbard S, Florsheim J, Rosenberry DO, Borglin S, Trotta M, Seymour D (2015) Riverbed Clogging associated with a California Riverbank Filtration System: An assessment of mechanisms and monitoring approaches. J Hydrol 529(3):1740–1753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.08.012
Wainwright HM, Uhlemann S, Franklin M, Falco N, Bouskill NJ, Newcomer ME, Dafflon B, Woodburn E, Minsley BJ, Williams HK, Hubbard SS (2021) Watershed zonation approach for tractably quantifying above-andbelowground watershed heterogeneity and functions. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-2021-228
Waltz JP (1969) Ground water. In: Chorley RJ (ed) Water, earth, and man: a synthesis of hydrology, geomorphology, and socio-economic geography. Methuen, London, pp 259–267. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0016756800058970
Zabihi M, Pourghasemi HR, Pourtaghi ZS, Behzadfar M (2016) GISbased multivariate adaptive regression spline and random forest models for groundwater potential mapping in Iran. Environ Earth Sci 75:665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5424-9
Acknowledgements
We are very thankful to ISI for the working environment and necessary help for the research work. We are also grateful to the different administrative departments for their valuable information and for providing data for the study. We are also grateful to the editors and reviewers for carefully reading the manuscript, and for their many insightful comments and suggestions. Kartic Bera is thankful to the University of Grants Commission, MHRD, Government of India, New Delhi, for the Post-Doctoral Fellowship award used to carry out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest. We declare that this article does not contain any studies with human subjects performed by us.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bera, K., Newcomer, M.E. & Banik, P. Groundwater recharge site suitability analysis through multi-influencing factors (MIF) in West Bengal dry-land areas, West Bengal, India. Acta Geochim 41, 1030–1048 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-022-00559-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-022-00559-6