Abstract
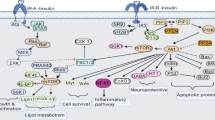
Cellular toxicity of hyperlipidemia has been long considered a major cause of various intractable disease such as diabetes. Discovering lipotoxicity antagonist with high efficiency and low side effects is of importance to develop therapeutics for relevant diseases. In the current study, we evaluate the anti-lipotoxic potential of punicalagin (PU) on pancreatic cells and investigate its underpinning mechanism involved. The administration of PU effectively improved cell viability, quenched intracellular reactive oxygen species, alleviated lipid peroxidation, and enhanced cellular antioxidative capacity in RINm5F cells stimulated by sodium palmitate. Besides that, PU treatment significantly inhibited the overload of mitochondrial calcium ions; alleviated the activation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress mediators including glucose-regulated protein 78, protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase, eukaryotic initiation factor 2α, activating transcription factor 6, caspase 12, and C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP); and attenuated the expression of cleaved caspase 3 and poly ADP-ribose polymerase in test cells. Further RNA interference experiment results and miR211-5p expression analysis revealed that PU may directly mitigate CHOP expression and upregulate the expression of miR211-5p to reduce ER stress-induced pancreatic cell death. The efficacy of PU in maintaining redox equilibrium and diminishing ER stress on pancreatic cells stressed by hyperlipidemia suggests that PU can be used as a promising dietary natural product to safeguard the pancreatic health against lipotoxicity.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Aleksandrova S, Alexova R, Dragomanova S, Kalfin R, Nicoletti F, Fagone P, Petralia MC, Mangano K, Tancheva L (2023) Preventive and therapeutic effects of Punica granatum L. polyphenols in neurological conditions. Int J Mol Sci 24:1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24031856
Al-Khawalde AAA, Abukhalil MH, Jghef MM, Alfwuaires MA, Alaryani FS, Aladaileh SH, Algefare AI, Karimulla S, Alasmari F, Aldal’in HK, Alanezi AA, Althunibat OY (2022) Punicalagin protects against the development of methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via activating Nrf2 signaling and decreasing oxidative stress, inflammation, and cell death. Int J Mol Sci 23:12334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012334
Benito-Vicente A, Jebari-Benslaiman S, Galicia-Garcia U, Larrea-Sebal A, Uribe KB, Martin C (2021) Molecular mechanisms of lipotoxicity-induced pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 359:357–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ircmb.2021.02.013
Bilekova S, Sachs S, Lickert H (2021) Pharmacological targeting of endoplasmic reticulum stress in pancreatic beta cells. Trends Pharmacol Sci 42:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2020.11.011
Cha JA, Song H, Kang B, Park MN, Park KS, Kim S, Shim B, Kim B (2018) miR-211 plays a critical role in Cnidium officinale Makino extract-induced, ROS/ER stress-mediated apoptosis in U937 and U266 cells. Int J Mol Sci 19:865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030865
Chaaba R, Bouaziz A, Ben Amor A, Mnif W, Hammami M, Mehri S (2023) Fatty acid profile and genetic variants of proteins involved in fatty acid metabolism could be considered as disease predictor. Diagnostics (basel) 13:979. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13050979
Chitnis NS, Pytel D, Bobrovnikova-Marjon E, Pant D, Zheng H, Maas NL, Frederick B, Kushner JA, Chodosh LA, Koumenis C, Fuchs SY, Diehl JA (2012) miR-211 is a prosurvival microRNA that regulates chop expression in a PERK-dependent manner. Mol Cell 48:353–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.08.025
Cione E, Torre CL, Cannataro R, Caroleo MC, Plastina P, Gallelli L (2020) Quercetin, epigallocatechin gallate, curcumin, and resveratrol: From dietary sources to human microRNA modulation. Molecules 25:63. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010063
Clementi ME, Pani G, Sampaolese B, Tringali G (2018) Punicalagin reduces H2O2-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in PC12 cells by modulating the levels of reactive oxygen species. Nutr Neurosci 21:447–454. https://doi.org/10.1080/1028415X.2017.1306935
Farghadan M, Zavaran-Hosseini A, Farhadi E, Vaziri AS, Tahmasebi MN, Jamshidi A, Mahmoudi M (2022) MicroRNA-211-5p overexpression effect on endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptotic genes in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol 21:418–428. https://doi.org/10.18502/ijaai.v21i4.10289
Fernandes-da-Silva A, Miranda CS, Santana-Oliveira DA, Oliveira-Cordeiro B, Rangel-Azevedo C, Silva-Veiga FM, Martins FF, Souza-Mello V (2021) Endoplasmic reticulum stress as the basis of obesity and metabolic diseases: focus on adipose tissue, liver, and pancreas. Eur J Nutr 60:2949–2960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-021-02542-y
Grieco FA, Schiavo AA, Brozzi F, Juan-Mateu J, Bugliani M, Marchetti P, Eizirik DL (2019) The microRNAs miR-211-5p and miR-204-5p modulate ER stress in human beta cells. J Mol Endocrinol 63:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1530/JME-19-0066
Hanstein AV, Tsikas D, Lenzen S, Jorns A, Plotz T (2023) Potentiation of lipotoxicity in human endoC-βH1 β-cells by glucose is dependent on the structure of free fatty acids. Mol Nutr Food Res 67:e2200582. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.202200582
Lytrivi M, Castell A, Poitout V, Cnop M (2020) Recent insights into mechanisms of β-cell lipo- and glucolipotoxicity in type 2 diabetes. J Mol Biol 432:1514–1534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2019.09.016
Maulucci G, Cohen O, Daniel B, Sansone A, Petropoulou PI, Filou S, Spyridonidis A, Pani G, De Spirito M, Chatgilialoglu C, Ferreri C, Kypreos KE, Sasson S (2016) Fatty acid-related modulations of membrane fluidity in cells: detection and implications. Free Radic Res 50:S40–S50. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715762.2016.1231403
Mohan S, Preetha RMR, Brown L, Ayyappan P, Raghu KG (2019) Endoplasmic reticulum stress: A master regulator of metabolic syndrome. Eur J Pharmacol 860:172553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172553
Mustapha S, Mohammed M, Azemi AK, Jatau AI, Shehu A, Mustapha L, Aliyu IM, Danraka RN, Amin A, Bala AA, Ahmad WANW, Rasool AHG, Mustafa MR, Mokhtar SS (2021) Current status of endoplasmic reticulum stress in type II diabetes. Molecules 26:4362. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144362
Namvarjah F, Shokri-Afra H, Moradi-Sardareh H, Khorzoughi RB, Pasalar P, Panahi G, Meshkani R (2022) Chlorogenic acid improves anti-lipogenic activity of metformin by positive regulating of AMPK signaling in HepG2 cells. Cell Biochem Biophys 80:537–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-022-01077-1
Olvera-Sandoval C, Fabela-Illescas HE, Fernández-Martínez E, Ortiz-Rodríguez MA, Cariño-Cortés R, Ariza-Ortega JA, Hernández-González JC, Olivo D, Valadez-Vega C, Belefant-Miller H, Betanzos-Cabrera G (2022) Potential mechanisms of the improvement of glucose homeostasis in type 2 diabetes by pomegranate juice. Antioxidants (basel) 11:553. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11030553
Pirzadeh M, Caporaso N, Rauf A, Shariati MA, Yessimbekov Z, Khan MU, Imran M, Mubarak MS (2021) Pomegranate as a source of bioactive constituents: a review on their characterization, properties and applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 61:982–999. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1749825
Quirós-Fernández R, López-Plaza B, Bermejo LM, Milla SP, Zangara A, Candela CG (2022) Oral supplement containing hydroxytyrosol and punicalagin improves dyslipidemia in an adult population without co-adjuvant treatment: A randomized, double-blind, controlled and crossover trial. Nutrients 14:1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091879
Radajewska A, Szyller J, Niewiadomska J, Noszczyk-Nowak A, Bil-Lula I (2023) Punica granatum L. polyphenolic extract as an antioxidant to prevent kidney injury in metabolic syndrome rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2023:6144967. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/6144967
Reyes-Fermín LM, Aparicio-Trejo OE, Avila-Rojas SH, Gómez-Sierra T, Martínez-Klimova E, Pedraza-Chaverri J (2020) Natural antioxidants’ effects on endoplasmic reticulum stress-related diseases. Food Chem Toxicol 138:111229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2020.111229
Sramek J, Nemcova-Furstova V, Kovar J (2021) Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis induction and its regulation by fatty acids in pancreatic β-cells. Int J Mol Sci 22:4285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084285
Subash-Babu P, Al-Numair N, Almuzaini T, Athinarayanan J, Alshatwi AA (2022) Punicalagin and ketogenic amino acids loaded organic lipid carriers enhance the bioavailability, mitochondrial β-oxidation, and ketogenesis in maturing adipocytes. Nanomaterials 12:368. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030368
Tabrez S, Jabir NR, Adhami VM, Khan MI, Moulay M, Kamal MA, Mukhtar H (2020) Nanoencapsulated dietary polyphenols for cancer prevention and treatment: Successes and challenges. Nanomedicine 15:1147–1162. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2019-0398
Varghese DS, Ali BR (2021) Pathological crosstalk between oxidized LDL and ER stress in human diseases: A comprehensive review. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:674103. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.674103
Wang N, Gao Q, Shi J, Chen Y, Ji W, Sheng X, Zhang R (2022) Acacetin antagonized lipotoxicity in pancreatic β-cells via ameliorating oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Biol Rep 49:8727–8740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07717-2
Xiang RL, Mei M, Su YC, Li L, Wang JY, Wu L (2015) Visfatin protects rat pancreatic β-cells against IFN-γ-induced apoptosis through AMPK and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Biomed Environ Sci 28(169–177):10. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2015.023
Yang H, Li X (2012) The role of fatty acid metabolism and lipotoxicity pancreatic β-cell injury: Identification of potential therapeutic targets. Acta Pharm Sin B 2:96–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2012.05.003
Zhang R, Shi J, Wang T, Qiu XN, Liu R, Li YT, Gao Q, Wang N (2020) Apigetrin ameliorates streptozotocin-induced pancreatic β-cell damages via attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 56:622–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-020-00478-x
Zhong J, Reece EA, Yang P (2015) Punicalagin exerts protective effect against high glucose-induced cellular stress and neural tube defects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 467:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.10.024
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81300673), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (grant number BK20130496), and Startup Foundation for Advanced Talents of Jiangsu University (grant number 13JDG004 & 13JDG006), and Cultivation Project for Young Core Teacher of Jiangsu University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Specifically, material preparation and data collection were performed by Yang K, Wang J, Liang J, and Yu S. Data analysis was conducted by Zhu A and Zhang R. Wang N and Zhang R co-supervised the work. Wang N wrote the draft of manuscript. Zhang R conceived the original experiment design and edited the paper writing. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study complies with all Ethical Standards. The current study does not include any human participants or animals so informed consents are not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, N., Yang, K., Wang, J. et al. Punicalagin relieves lipotoxic injuries on pancreatic β-cells via regulating the oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 59, 575–585 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-023-00806-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-023-00806-x