Summary
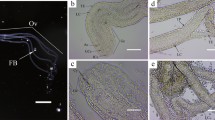
Three continuous cell lines, NIAS-PRC-819A, NIAS-PRC-819B, and NIAS-PRC-819C, were established from the pupal ovaries of the common white, Pieris rapae crucivora Boisduval (Insecta, Lepidoptera, Pieridae). The primary culture was initiated as explant cultures with ovariole fragments in MGM-464 medium supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum at 25° C. About 6 mo after the culture was set up, the first subculture was prepared. Thereafter, cells were subcultured with decreasing passage intervals, resulting in a cell population that multiplied continuously. The karyotypes of these cell lines were similar to each other, and the majority of the cells showed about 100 microchromosomes. The population-doubling times of these cell lines were 3 to 7 d. The cell lines were susceptible to a microsporidia, Nosema bombycis. Immunodiffusion experiments proved that these cell lines derived from the common white and not from other cell lines by contamination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carlson, J. G. Protoplasmic viscosity changes in different regions of the grass-hopper neuroblast during mitosis. Biol. Bull. 90:109–121; 1946.
Hau, M.; Watanabe, H. Transovarial transmission of two microsporidia in the silkworm, Bombyx mori, and disease occurrence in the progeny oopulation. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 51:41–45; 1988.
Makino, S. A review of the chromosome numbers in animals. Tokyo: Hokuryukan; 1956:300.
Mitsuhashi, J. Establishment of cell lines from pupal ovaries of the swallow tail, Papilio xuthus Linne (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 8:64–72; 1973.
Mitsuhashi, J. Establishment and some characteristics of a continuous cell line derived from fat bodies of the cabbage armyworm (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae). Dev. Growth Differ. 23:63–72; 1981.
Mitsuhashi, J. A continuous cell line derived from fat bodies of the common armyworm, Leucania separata (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 18:533–539; 1983.
Mitsuhashi, J. A continuously growing cell line from larval hemocytes of Malacosoma neustria testacea. Jpn. J. Entomol. 64:692–699; 1996.
Mitsuhashi, J. Development of highly nutritive culture media. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 37A:330–337; 2001.
Mitsuhashi, J. Invertebrate tissue culture methods, Tokyo: Springer-Verlag; 2002:446.
Mitsuhashi, J.; Inoue, H. Obtainment of a continuous cell line from the fat bodies of the mulberry tiger moth, Spilosoma imparilis (Lepidoptera, Arctiidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 23:488–490; 1988.
Ouchterlony, O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog. Allergy 5:1–77; 1958.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitsuhash, J., Hayasaka, S. & Imanishi, S. Continuous cell lines from the common white, Pieris rapae crucivora boisduval. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 39, 114–116 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-003-0003-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-003-0003-2