Summary
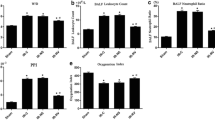
To investigate the effect of Dachengqi decoction on NF-κB p65 expression in lung of rats with partial intestinal obstruction and the underlying mechanism, 30 SD rats were randomly divided into three groups: sham-operation group, model group and Dachengqi decoction treatment group (Dachengqi group), with 10 animals in each group. The models were made by partially ligating their large intestines outside the body. The pathological changes were analyzed by HE staining. The expression of NF-κB p65 in rats lung were measured by using real-time polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry respectively. Moreover, the expression of caveolin-1 in rats lung was also measured to. Increased edema, interstitial thickening, hemorrhage, and infiltration of inflammatory cells were found in the model group. In contrast, this change was significantly reduced in Dachengqi group as compared with model group. In addition, the up-regulated caveolin-1 and NF-κB p65 were also suppressed by Dachengqi decoction in lung of rats with partial intestinal obstruction. We are led to concluded that the caveolin-1-NF-κB pathway plays an important role in the development of lung injury of rats with partial intestinal obstruction and Dachengqi decoction could down-regulate the expression of caveolin-1 and NF-κB p65 in lung of rats with partial intestinal obstruction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swank GM, Deitch EA. Role of the gut in multiple organ failure: bacterial translocation and permeability changes. World J Surg, 1996,20(4),411–417
Suliburk J, Helmer K, Moore F, et al. The gut in systemic inflammatory response syndrome and sepsis. Enzyme systems fighting multiple organ failure. Eur Surg Res, 2008,40(2):184–189
Moore FA. The role of the gastrointestinal tract in postinjury multiple organ failure. Am J Surg, 1999, 178(6):449–453
Yang SL, Li DB. Clinical study on therapy of clearing hallow viscera in treating critical patients with gastro-enteric function disorder. Chin J Integr Med (Chinese), 2006,12(2):122–125
Li D, Yang S, Chen R. Experimental study on the mechanism of protective effect of free fu on gut-derived endotoxin-mediated lung damage. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol [Med Sci], 2004,24(5):528–530
Coward WR, Okayama Y, Sagara H, et al. NF-kappa B and TNF-alpha: a positive autocrine loop in human lung mast cells? 2002,169(9):5287–5293
Li Q, Verma IM. NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol, 2002,2(10):725–734
Sen P, Wallet MA, Yi Z, et al. Apoptotic cells induce Mer tyrosine kinase-dependent blockade of NF-kappaB activation in dendritic cells. Blood, 2007,109(2):653–660
Kato T Jr, Delhase M, Hoffmann A, et al. CK2 is a C-terminal IkappaB kinase responsible for NF-kappaB activation during the UV response. Mol Cell, 2003,12(4): 829–839
Tergaonkar V, Bottero V, Ikawa M, et al. IkappaB kinase-independent IkappaBalpha degradation pathway: functional NF-kappaB activity and implications for cancer therapy. Mol Cell Biol, 2003,23(22):8070–8083
Baldwin AS Jr. The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol, 1996,14:649–683
Sweeney C, Li L, Shanmugam R, et al. Nuclear factor-κB is constitutively activated in prostate cancer in vitro and is overexpressed in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Clin Cancer Res, 2004, 10(16):5501–5507
Blackwell TS, Christman JW. The role of nuclear factor-kappa B in cytokine gene regulation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 1997,17(1):3–9
Christman JW, Lancaster LH, Blackwell TS. Nuclear factor kappa B: a pivotal role in the systemic inflammatory response syndrome and new target for therapy. Intensive Care Med, 1998,24(11):1131–1138
Siebenlist U, Franzoso G, Brown K. Structure, regulation and function of NF-kappa B. Annu Rev Cell Biol, 1994, 10:405–455
Everhart MB, Han W, Sherrill TP, et al. Duration and intensity of NF-kappaB activity determine the severity of endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. J Immunol, 2006, 176(8):4995–5005
Ohmori K, Takeda S, Miyoshi S, et al. Attenuation of lung injury in allograft rejection using NF-kappaB decoy transfection-novel strategy for use in lung transplantation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg, 2005,27(1):23–27
Sadikot RT, Han W, Everhart MB, et al. Selective I kappa B kinase expression in airway epithelium generates neutrophilic lung inflammation. J Immunol, 2003,170(2): 1091–1098
Skerrett SJ, Liggitt HD, Hajjar AM, et al. Respiratory epithelial cells regulate lung inflammation in response to inhaled endotoxin. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2004,287(1):L143–L152
Alcamo E, Mizgerd JP, Horwitz BH, et al. Targeted mutation of TNF receptor I rescues the RelA-deficient mouse and reveals a critical role for NF-kappa B in leukocyte recruitment. J Immunol, 2001,167(3):1592–1600
Ckless K, van der Vliet A, Janssen-Heininger Y. Oxidative-nitrosative stress and post-translational protein modifications: implications to lung structure-function relations. Arginase modulates NF-kappaB activity via a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2007,36(6):645–653
John TA, Vogel SM, Tiruppathi C, et al. Quantitative analysis of albumin uptake and transport in the rat microvessel endothelial monolayer. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2003,284(1):187–196
Razani B, Combs TP, Wang XB, et al. Caveolin-1-deficient mice are lean, resistant to diet-induced obesity, and show hypertriglyceridemia with adipocyte abnormalities. J Biol Chem, 2002,277(10): 8635–8647
Pelkmans L, Püntener D, Helenius A. Local actin poly-merization and dynamin recruitment in SV40-induced internalization of caveolae. Science, 2002,296(5567):535–539
Couet J, Sargiacomo M, Lisanti MP. Interaction of a receptor tyrosine kinase, EGF-R, with caveolins. Caveolin binding negatively regulates tyrosine and serine/threonine kinase activities. J Biol Chem, 1997,272(48):30429–30438
Williams TM, Hassan GS, Li J, et al. Caveolin-1 promotes tumor progression in an autochthonous mouse model of prostate cancer: genetic ablation of Cav-1 delays advanced prostate tumor development in tramp mice. J Biol Chem, 2005,280(26):25134–25145
Garrean S, Gao XP, Brovkovych V, et al. Caveolin-1 regulates NF-kappaB activation and lung inflammatory response to sepsis induced by lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol, 2006,177(7):4853–4860
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by a grant from the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 30873225).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Shen, L., Jin, Y. et al. Effect of Dachengqi decoction on NF-κB p65 expression in lung of rats with partial intestinal obstruction and the underlying mechanism. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 30, 217–221 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-010-0217-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-010-0217-y