Abstract
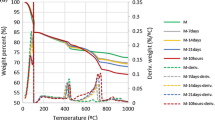
The paste was prepared by mixing MgO, microsilica and H2O in the presence of water reducer at different reaction ratios and temperatures, and characterized by XRD, DTA, TGA, IR, and solid-state 29Si NMR. The experimental results showed that, besides Mg(OH)2, magnesium silicate hydrate (M-S-H) was formed at a low temperature such as 25 and 50 °C. At a high temperature of 100 °C, Mg(OH)2 can be further transformed into M-S-H completely, for instance, within ca. 1 month in an excess of microsilica. The average composition and structure of M-S-H was mainly related to the reaction mixture and curing temperature and was discussed in detail.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Воже Новди(LV Changgao translator). Technology of Press and Vapor Materials[M]. Beijing: China Construct Industry Press, 1985 (in Chinese)
Bonen D, Cohen M D. Magnesium Sulfate Attack on Porland Cement Paste, Part I. Microstructure Analysis[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 1992, 22: 169–180
Bonen D, Cohen M D. Magnesium Sulfate Attack on Porland Cement Paste, Part II: Chemial and Mineralogical Analysis[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 1992, 22:707–718
Gollop W F, Tayloy H F W. Microstructural and Micro-analytical Studies of Sulfate Attack, Part I: Ordinary Portland Cement Paste[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 1992, 22:1 027–1 038
Brew D R M, Glasser F P. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Silicate Hydrate Gel[J]. Cem. Concr. Res., 2005, 35:85–98
Yuan Run-zhang. Cementious Materials[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology Press, 1990 (in Chinese)
Brnd Wunder. Antigorite: High-pressure Stability in the System MgO-SiO2-H2O (MSH) [J]. Lithos, 1997, 4: 213–227
Wei Jiangxiong, Chen Yimin, Li Yongxin. Research on the Cementious Materials in MgO-SiO2-H2O System at Room Temperature[C]. In:Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Cement and Concrete and Canmet/ACI International Symposium on Concrete Technology for Sustainable Development, Xi’an China, Sep.19–22, 2006: 705–711
Wei Jiangxiong. Research on Magnesium Silicate Hydrate Cementious Materials[D]. Beijing: China Building Materials Academy, 2004
Wei Jiangxiong, Chen Yimin, Li Yongxin. The Reaction Mechanism between MgO and Microsilica at Room Temperature[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Edit., 2006, 21:88–92
Farmer V C. The Infrared Spectra of Minerals[D]. UK: Mineralogical Society, 1974
Yang Nanru. Test Technology for Inorganic Materials[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology Press, 1991 (in Chinese)
Temuujin J, K Okada, K J D MacKenzie. Formation of Layered Magnesium Silicate during the Aging of Magnesium Hydroxide-silica Mixtures[J]. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1998, 81: 754–756
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National “973 Project”(2009CB623104), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(2009ZZ0044), and the Funds of Key Laboratory of Advance Civil Engineering Materials of the Ministry of Education
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, J., Yu, Q., Zhang, W. et al. Reaction products of MgO and microsilica cementitious materials at different temperatures. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 26, 745–748 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0304-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0304-3