Abstract
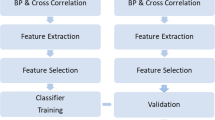
Parameter setting plays an important role for improving the performance of a brain computer interface (BCI). Currently, parameters (e.g. channels and frequency band) are often manually selected. It is time-consuming and not easy to obtain an optimal combination of parameters for a BCI. In this paper, motor imagery-based BCIs are considered, in which channels and frequency band are key parameters. First, a semi-supervised support vector machine algorithm is proposed for automatically selecting a set of channels with given frequency band. Next, this algorithm is extended for joint channel-frequency selection. In this approach, both training data with labels and test data without labels are used for training a classifier. Hence it can be used in small training data case. Finally, our algorithms are applied to a BCI competition data set. Our data analysis results show that these algorithms are effective for selection of frequency band and channels when the training data set is small.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Ani A, Al-Sukker A (2006) Effect of feature and channel selection on EEG classification. In: Proceedings of international conference on IEEE EMBS, pp 2171–2174
Bishop C (1995) Neural networks for pattern recognition. Plus, Oxford University Press, USA
Blanchard G, Blankertz B (2004) BCI competition 2003-data set IIa: spatial patterns of self-controlled brain rhythm modulations. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 51(6):1062–1066
Blankertz B, Tomioka R, Lemm S, Kawanabe M, Muller K (2008) Optimizing spatial filters for robust EEG single-trial analysis. IEEE Signal Process Magazine 25(1):41
Burges C (1998) A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Mining Knowledge Discovery 2(2):121–167
Chang C, Lin C (2001) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines [online]. Software available at http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/cjlin/libsvm
Dornhege G (2007) Toward brain-computer interfacing. MIT Press
Dornhege G, Blankertz B, Curio G, Muller K (2004) Boosting bit rates in noninvasive EEG single-trial classifications by feature combination and multiclass paradigms. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 51(6):993–1002
Dornhege G, Blankertz B, Krauledat M, Losch F, Curio G, Muller K (2006) Combined optimization of spatial and temporal filters for improving brain-computer interfacing. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 53(11):2274–2281
Freeman W (2007) Definitions of state variables and state space for brain–computer interface. Cogn Neurodyn 1(1):3–14
Garrett D, Peterson D, Anderson C, Thaut M (2003) Comparison of linear, nonlinear, and feature selection methods for EEG signal classification. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 11(2):141–144
Kaper M, Meinicke P, Grossekathoefer U, Lingner T, Ritter H (2004) BCI competition 2003-data set IIb: support vector machines for the P300 speller paradigm. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 51(6):1073–1076
Lal T, Schroder M, Hinterberger T, Weston J, Bogdan M, Birbaumer N, Scholkopf B (2004) Support vector channel selection in BCI. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 51(6):1003–1010
Lemm S, Blankertz B, Curio G, Muller K (2005) Spatio-spectral filters for improving the classification of single trial EEG. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52(9):1541–1548
Li Y, Guan C (2006) An extended EM algorithm for joint feature extraction and classification in brain-computer interfaces. Neural Comput 18(11):2730–2761
Li Y, Guan C (2008) Joint feature re-extraction and classification using an iterative semi-supervised support vector machine algorithm. Mach Learn 71(1):33–53
Meinicke P, Kaper M, Hoppe F, Heumann M, Ritter H (2003) Improving transfer rates in brain computer interfacing: a case study. In: Proceedings of advanced neural information processing system, pp 1131–1138
Muller K, Krauledat M, Dornhege G, Curio G, Blankertz B (2004) Machine learning techniques for brain-computer interfaces. Biomed Tech 49(1):11–22
Pfurtscheller G, Brunner C, Schlögl A, Lopes da Silva F (2006) Mu rhythm (de) synchronization and EEG single-trial classification of different motor imagery tasks. Neuroimage 31(1):153–159
Pregenzer M, Pfurtscheller G (1999) Frequency component selection for an EEG-based brain to computerinterface. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 7(4):413–419
Ramoser H, Muller-Gerking J, Pfurtscheller G (2000) Optimal spatial filtering of single trial EEG during imagined handmovement. IEEE Trans Rehabil Eng 8(4):441–446
Schroder M, Bogdan M, Hinterberger T, Birbaumer N (2003) Automated EEG feature selection for brain computer interfaces. In: Proceedings of 1st International IEEE EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, pp 626–629
Shenoy P, Krauledat M, Blankertz B, Rao R, Müller K (2006) Towards adaptive classification for BCI. J Neural Eng 3(R13–R23):1–1
Thulasidas M, Guan C, Wu J (2006) Robust classification of EEG signal for brain-computer interface. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 14(1):24–29
Vapnik V (1998) Statistical learning theory. New York, Wiley
Vidaurre C, Schlogl A, Cabeza R, Scherer R, Pfurtscheller G (2007) Study of on-line adaptive discriminant analysis for EEG-based brain computer interfaces. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 54(3):550–556
Wang Y, Gao S, Gao X (2005) Common spatial pattern method for channel selelction in motor imagery based brain-computer interface. In: Proceedings of international conference on IEEE EMBS, pp 5392–5395
Wang Y, Gao X, Zhang Z, Hong B, Gao S. BCI competition IIIdata set IVa: classifying single-trial EEG during motor imagery with a small training set. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehab Eng, to be published
Wolpaw J, McFarland D, Vaughan T (2000) Brain-computer interface research at the Wadsworth Center. IEEE Trans Rehabil Eng 8(2):222–226
Wolpaw J, Birbaumer N, McFarland D, Pfurtscheller G, Vaughan T (2002) Brain–computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin Neurophysiol 113(6):767–791
Wu W, Gao X, Hong B, Gao S (2008) Classifying single-trial EEG during motor imagery by iterative spatio-spectral patterns learning (ISSPL). IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 55(6):1733–1743
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Berlin BCI group for providing the data set IVa in BCI competition III.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 60825306 and 60802068; Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China under grant 9251064101000012 and supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, SCUT under grant 2009ZZ0055.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, J., Li, Y. & Yu, Z. A semi-supervised support vector machine approach for parameter setting in motor imagery-based brain computer interfaces. Cogn Neurodyn 4, 207–216 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-010-9114-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-010-9114-0