Abstract
Purpose
An accurate and reliable benchmark of registration accuracy and intervertebral motion compensation is important for spinal image guidance. In this study, we evaluated the utility of intraoperative CT (iCT) in place of bone-implanted screws as the ground-truth registration and illustrated its use to benchmark the performance of intraoperative stereovision (iSV).
Methods
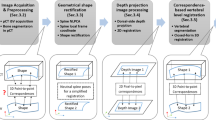
A template-based, multi-body registration scheme was developed to individually segment and pair corresponding vertebrae between preoperative CT and iCT of the spine. Intervertebral motion was determined from the resulting vertebral pair-wise registrations. The accuracy of the image-driven registration was evaluated using surface-to-surface distance error (SDE) based on segmented bony features and was independently verified using point-to-point target registration error (TRE) computed from bone-implanted mini-screws. Both SDE and TRE were used to assess the compensation accuracy using iSV.
Results
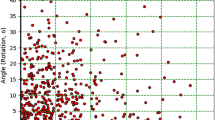
The iCT-based technique was evaluated on four explanted porcine spines (20 vertebral pairs) with artificially induced motion. We report a registration accuracy of 0.57 \(\pm \) 0.32 mm (range 0.34–1.14 mm) and 0.29 \(\pm \) 0.15 mm (range 0.14–0.78 mm) in SDE and TRE, respectively, for all vertebrae pooled, with an average intervertebral rotation of \(4.9^{\circ } \pm 1.2^{\circ }\) (range 1.5\(^{\circ }\)–7.9\(^{\circ }\)). The iSV-based compensation accuracy for one sample (four vertebrae) was 1.32 \(\pm \) 0.19 mm and 1.72 \(\pm \) 0.55 mm in SDE and TRE, respectively, exceeding the recommended accuracy of 2 mm.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates the effectiveness of iCT in place of invasive fiducials as a registration ground truth. These findings are important for future development of on-demand spinal image guidance using radiation-free images such as stereovision and ultrasound on human subjects.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cleary K, Peters TM (2010) Image-guided interventions: technology review and clinical applications. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 12:119–142
Deyo RA, Nachemson A, Mirza SK (2004) Spinal-fusion surgery—the case for restraint. Spine J 4:138S–142S
Holly LT (2006) Image-guided spinal surgery. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg 2(January):7–15
Tjardes T, Shafizadeh S, Rixen D, Paffrath T, Bouillon B, Steinhausen ES, Baethis H (2010) Image-guided spine surgery: state of the art and future directions. Eur Spine J 19(1):25–45
Tian N-F, Huang Q-S, Zhou P, Zhou Y, Wu R-K, Lou Y, Xu H-Z (2011) Pedicle screw insertion accuracy with different assisted methods: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Eur Spine J 20(6):846–859
Gelalis ID, Paschos NK, Pakos EE, Politis AN, Arnaoutoglou CM, Karageorgos AC, Ploumis A, Xenakis Ta (2012) Accuracy of pedicle screw placement: a systematic review of prospective in vivo studies comparing free hand, fluoroscopy guidance and navigation techniques. Eur Spine J 21(2):247–255
Jost GF, Yonemura KS, Von Jako RA (2014) Intraoperative imaging and image-guided therapy. In: Jolesz FA (ed) Intraoperative imaging and image-guided therapy. Springer, New York, pp 613–628
Tormenti MJ, Kostov DB, Gardner P a, Kanter AS, Spiro RM, Okonkwo DO (2010) Intraoperative computed tomography image-guided navigation for posterior thoracolumbar spinal instrumentation in spinal deformity surgery. Neurosurg Focus 28(3):E11
Härtl R, Lam KS, Wang J, Korge A, Kandziora F, Audigé L (2013) Worldwide survey on the use of navigation in spine surgery. World Neurosurg 79(1):162–172
Roessler K, Ungersboeck K, Dietrich W, Aichholzer M, Hittmeir K, Matula C, Czech T, Koos W (1997) Frameless stereotactic guided neurosurgery: clinical experience with an infrared based pointer device navigation system. Acta Neurochir 139(6):551–559
Brodwater B, Roberts D, Nakajima T, Friets E, Strohbehn J (1993) Extracranial application of the frameless stereotactic operating microscope: experience with lumbar spine. Neurosurgery 32(2):209–213
Nottmeier EW (2012) A review of image-guided spinal surgery. J Neurosurg Sci 56:35–47
Mirza SK, Wiggins GC, Kuntz C, York JE, Bellabarba C, Knonodi M a, Chapman JR, Shaffrey CI (2003) Accuracy of thoracic vertebral body screw placement using standard fluoroscopy, fluoroscopic image guidance, and computed tomographic image guidance: a cadaver study. Spine (Phila. Pa. 1976) 28(4):402–413
Ji S, Fan X, Paulsen K, Roberts D, Mirza SK, Lollis SS (2015) Patient registration using intraoperative stereovision in image-guided open spinal surgery. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. doi:10.1109/TBME.2015.2415731
Ji S, Fan X, Roberts DW, Hartov A, Schaewe TJ, Simon DA, Paulsen KD (2014) Brain shift compensation via intraoperative imaging and data assimilation. In: Neu C, Genin G (eds) CRC handbook of imaging in biological mechanics. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 229–240
Ji S, Wu Z, Hartov A, Roberts DW, Paulsen KD (2008) Mutual-information-based image to patient re-registration using intraoperative ultrasound in image-guided neurosurgery. Med Phys 35(10):4612
Yan CXB, Goulet B, Chen SJ-S, Tampieri D, Collins DL (2012) Validation of automated ultrasound-CT registration of vertebrae. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 7(4):601–610
Yan CXB, Goulet B, Pelletier J, Chen SJ-S, Tampieri D, Collins DL (2011) Towards accurate, robust and practical ultrasound-CT registration of vertebrae for image-guided spine surgery. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 6(4):523–537
Rasoulian A, Osborn J, Sojoudi S, Nouranian S, Lessoway VA, Rohling RN, Abolmaesumi P (2014) A system for ultrasound-guided spinal injections? A feasibility study. In: IPCAI, pp 90–99
Nagpal S, Hacihaliloglu I, Ungi T, Rasoulian A, Osborn J, Lessoway Va, Rohling RN, Borschneck DP, Abolmaesumi P, Mousavi P (2014) A global CT to US registration of the lumbar spine. In: IPCAI, pp 108–117
West JB, Fitzpatrick JM, Sa Toms, Maurer CR, Maciunas RJ (2001) Fiducial point placement and the accuracy of point-based, rigid body registration. Neurosurgery 48(4):810–816 (discussion 816–817)
Winter S, Brendel B, Pechlivanis I, Schmieder K, Igel C (2008) Registration of CT and intraoperative 3-D ultrasound images of the spine using evolutionary and gradient-based methods. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 12(3):284–296
Lang A, Mousavi P, Gill S, Fichtinger G, Abolmaesumi P (2012) Multi-modal registration of speckle-tracked freehand 3D ultrasound to CT in the lumbar spine. Med Image Anal 16(3):675–686
Gill S, Abolmaesumi P, Fichtinger G, Boisvert J, Pichora D, Borshneck D, Mousavi P (2012) Biomechanically constrained groupwise ultrasound to CT registration of the lumbar spine. Med Image Anal 16(3):662–674
Klinder T, Ostermann J, Ehm M, Franz A, Kneser R, Lorenz C (2009) Automated model-based vertebra detection, identification, and segmentation in CT images. Med Image Anal 13(3):471–482
Ma J, Lu L, Zhan Y, Zhou X (2010) Hierarchical segmentation and identification of thoracic vertebra using learning-based edge detection and coarse-to-fine deformable model. In: MICCAI, pp 19–27
Kim Y, Kim D (2009) A fully automatic vertebra segmentation method using 3D deformable fences. Comput Med Imaging Graph 33:343–352
Rasoulian A, Member S, Rohling R, Member S (2013) Lumbar spine segmentation using a statistical multi-vertebrae anatomical shape \(+\) pose model. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 32(10):1890–1900
Ji S, Fan X, Roberts DW, Hartov A, Paulsen KD (2014) Cortical surface shift estimation using stereovision and optical flow motion tracking via projection image registration. Med Image Anal 18(7):1169–1183
Sinha TK, Dawant BM, Duay V, Cash DM, Weil RJ, Thompson RC, Weaver KD, Miga MI (2005) A method to track cortical surface deformations using a laser range scanner. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 24(6):767–781
Kjer HM, Wilm J (2010) Evaluation of surface registration algorithms for PET motion correction. Technical University of Denmark
Reaungamornrat S, Wang aS, Uneri a, Otake Y, Khanna aJ, Siewerdsen JH (2014) Deformable image registration with local rigidity constraints for cone-beam CT-guided spine surgery. Phys Med Biol 59(14):3761–3787
Fan X, Ji S, Hartov A, Roberts D, Paulsen K (2012) Registering stereovision surface with preoperative magnetic resonance images for brain shift compensation. In: Proceedings of SPIE, medical imaging 2012: visualization, image-guided procedures, and modeling, vol 8316
Paul P, Morandi X, Jannin P (2009) A surface registration method for quantification of intraoperative brain deformations in image-guided neurosurgery. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 13(6):976–983
Fujii R, Sakaura H, Mukai Y, Hosono N, Ishii T, Iwasaki M, Yoshikawa H, Sugamoto K (2007) Kinematics of the lumbar spine in trunk rotation: in vivo three-dimensional analysis using magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Spine J 16(11):1867–1874
Acknowledgments
This work was supported, in part, by the NIH R21 NS078607, The Dartmouth Clinical and Translational Science Institute under Award Number KL2TR001088 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) of the NIH (SJ), and the Dow-Crichlow Award (SSL). The content is solely the responsibility of the author(s) and does not necessarily represent the official views of Dartmouth SYNERGY or the NIH. The authors are grateful to Dr. Timothy Schaewe for technical assistance on SteathLink\(^\circledR \) and help from the Medtronic Navigation (Louisville, CO, USA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
K.D. Paulsen and D.W. Roberts receive research support from Medtronic Inc. and Carl Zeiss Inc. D.W. Roberts serves on the scientific advisory board for Medtronic Inc., Carl Zeiss Inc., and IMRIS Inc. Other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, S., Fan, X., Paulsen, K.D. et al. Intraoperative CT as a registration benchmark for intervertebral motion compensation in image-guided open spinal surgery. Int J CARS 10, 2009–2020 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-015-1255-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-015-1255-5