Abstract
Objective
Developing an efficient tool for accurate three-dimensional imaging from projections measured with C-arm systems.
Material and methods
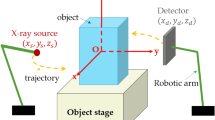
A circle-plus-arc trajectory, which is complete and thus amenable to accurate reconstruction, is used. This trajectory is particularly attractive as its implementation does not require moving the patient. For reconstruction, we use the “M-line method”, which allows processing the data in the efficient filtered backprojection mode. This method also offers the advantage of not requiring an ideal data acquisition geometry, i.e., the M-line algorithm can account for known deviations in the scanning geometry, which is important given that sizeable deviations are generally encountered in C-arm imaging.
Results
A robust implementation scheme of the “M-line method” that applies straightforwardly to real C-arm data is presented. In particular, a numerically stable technique to compute the view-dependent derivative with respect to the source trajectory parameter is applied, and an efficient way to compute the π-line backprojection intervals via a polygonal weighting mask is presented. Projection data of an anthropomorphic thorax phantom were acquired on a medical C-arm scanner and used to demonstrate the benefit of using a complete data acquisition geometry with an accurate reconstruction algorithm versus using a state-of-the-art implementation of the conventional Feldkamp algorithm with a circular short scan of cone-beam data. A significant image quality improvement based on visual assessment is shown in terms of cone-beam artifacts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pack J, Noo F (2005) Cone-beam reconstruction using 1d filtering along the projection of m-lines. Inverse Probl 21(3): 1105–1120
Katsevich A (2005) Image reconstruction for the circle-and-arc trajectory. Phys Med Biol 50(10): 2249–2265
Dennerlein F, Katsevich A, Lauritsch G, Hornegger J (2005) Exact and efficient cone-beam reconstruction algorithm for a short-scan circle combined with various lines. Proc SPIE 5747: 388–399
Grass M, Koppe R, Klotz E, Proksa R, Kuhn MH, Aerts H, Op De Beek J, Kemkers R (1999) Three-dimensional reconstruction of high contrast objects using c-arm image intensifier projection data. Comput Med Imaging Graph 23: 311–321
Riddell C, Trousset Y (2006) Rectification for cone-beam projection and backprojection. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 25(7): 950–962
Wiesent K, Barth K, Navab N, Durlak P, Brunner T, Schütz O, Seissler W (2000) Enhanced 3-d-reconstruction algorithm for c-arm systems suitable for interventional procedures. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 19(5): 391–403
Buzug TM (2008) Computed tomography—from photon statistics to modern cone-beam CT. Springer, Berlin
Zellerhoff M, Scholz B, Rührnschopf E-P, Brunner T (2005) Low contrast 3d-reconstruction from c-arm data. Proc SPIE 5745: 646–655
Hoppe S, Noo F, Dennerlein F, Lauritsch G, Hornegger J (2007) Geometric calibration of the circle-plus-arc trajectory. Phys Med Biol 52(23): 6943–6960
Katsevich A (2004) Image reconstruction for the circle-and-line trajectory. Phys Med Biol 49(22): 5059–5072
Pack J, Noo F, Kudo H (2004) Investigation of saddle trajectories for cardiac ct imaging in cone-beam geometry. Phys Med Biol 49(11): 2317–2336
Tuy HK (1983) An inversion formula for cone-beam reconstruction. SIAM J Appl Math 43(3): 546–552
Feldkamp LA, Davis LC, Kress JW (1984) Practical cone-beam algorithm. J Opt Soc Am A 1(6): 612–619
Hoppe S, Dennerlein F, Lauritsch G, Hornegger J, Noo F (2006) Cone-beam tomography from short-scan circle-plus-arc data measured on a c-arm system. In: Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, vol 6. San Diego, CA, USA, Oct.29–Nov. 4, pp 2873–2877
Hoppe S, Hornegger J, Lauritsch G, Dennerlein F, Noo F (2008) Truncation correction for oblique filtering lines. Med Phys 35: 5910–5920
Noo F, Pack J, Heuscher D (2003) Exact helical reconstruction using native cone-beam geometries. Phys Med Biol 48(23): 3787–3818
Noo F, Clackdoyle R, Mennessier C, White TA, Roney TJ (2000) Analytic method based on identification of ellipse parameters for scanner calibration in cone-beam tomography. Phys Med Biol 45(11): 3489–3508
Hartley R, Zisserman A (2003) Multiple view geometry in computer vision, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Noo F, Hoppe S, Dennerlein F, Lauritsch G, Hornegger J (2007) A new scheme for view-dependent data differentiation in fan-beam and cone-beam computed tomography. Phys Med Biol 52(17): 5393–5414
Parker DL (1982) Optimal short scan convolution reconstruction for fanbeam ct. Med Phys 9(2): 254–257
Silver MD (2000) A method for including redundant data in computed tomography. Med Phys 27(4): 773–774
Rodet T, Noo F, Defrise M (2004) The cone-beam algorithm of feldkamp, davis and kress preserves oblique line integrals. Med Phys 31(7): 1972–1975
Kak AC, Slaney M (1988) Principles of computerized tomographic imaging, 1st edn. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoppe, S., Hornegger, J., Dennerlein, F. et al. Accurate image reconstruction using real C-arm data from a Circle-plus-arc trajectory. Int J CARS 7, 73–86 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-011-0607-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-011-0607-z